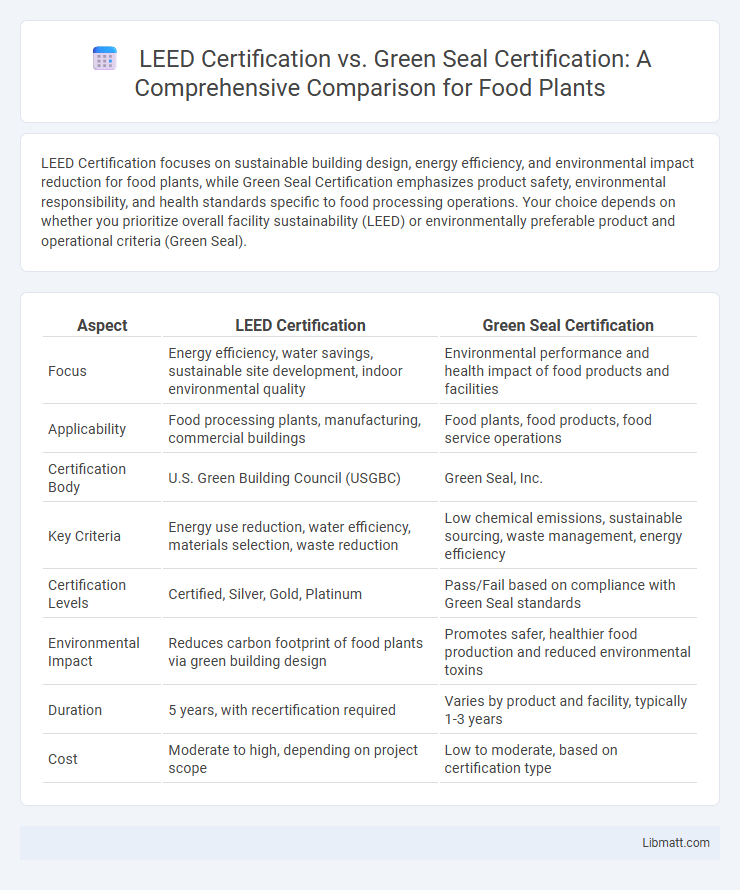
LEED Certification focuses on sustainable building design, energy efficiency, and environmental impact reduction for food plants, while Green Seal Certification emphasizes product safety, environmental responsibility, and health standards specific to food processing operations. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize overall facility sustainability (LEED) or environmentally preferable product and operational criteria (Green Seal).
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | LEED Certification | Green Seal Certification |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Energy efficiency, water savings, sustainable site development, indoor environmental quality | Environmental performance and health impact of food products and facilities |
| Applicability | Food processing plants, manufacturing, commercial buildings | Food plants, food products, food service operations |
| Certification Body | U.S. Green Building Council (USGBC) | Green Seal, Inc. |
| Key Criteria | Energy use reduction, water efficiency, materials selection, waste reduction | Low chemical emissions, sustainable sourcing, waste management, energy efficiency |
| Certification Levels | Certified, Silver, Gold, Platinum | Pass/Fail based on compliance with Green Seal standards |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces carbon footprint of food plants via green building design | Promotes safer, healthier food production and reduced environmental toxins |
| Duration | 5 years, with recertification required | Varies by product and facility, typically 1-3 years |
| Cost | Moderate to high, depending on project scope | Low to moderate, based on certification type |
Introduction to Sustainability Certifications for Food Plants
Sustainability certifications for food plants, such as LEED Certification and Green Seal Certification, play crucial roles in promoting environmental responsibility and operational efficiency. LEED Certification emphasizes energy efficiency, water savings, and sustainable site development, catering to the architectural and construction aspects of food processing facilities. Green Seal Certification focuses specifically on the use of safer chemicals, waste reduction, and healthier indoor environments, offering targeted guidance for food plants looking to minimize their ecological footprint.
Overview of LEED Certification
LEED Certification for food plants evaluates sustainability through energy efficiency, water savings, waste reduction, and indoor environmental quality based on a point system managed by the U.S. Green Building Council. This certification promotes environmentally responsible construction and operation practices, ensuring your facility reduces its ecological footprint while improving worker health and productivity. LEED points are earned by meeting rigorous standards across categories like sustainable sites, materials, and innovation in design specific to food processing environments.
Overview of Green Seal Certification
Green Seal Certification for food plants emphasizes rigorous environmental standards in areas such as energy efficiency, water conservation, waste reduction, and use of safer chemicals, ensuring sustainable operational practices. This certification requires third-party verification to confirm compliance with established criteria designed for environmental health and performance improvements specific to the food production industry. Your facility's commitment to Green Seal can enhance sustainability credentials while reducing environmental impact through measurable, science-based standards.
Key Differences Between LEED and Green Seal
LEED Certification primarily evaluates the environmental performance and sustainability of building design, construction, and operation, focusing on energy efficiency, water use, and indoor environmental quality in food plants. Green Seal Certification specifically targets product and operational sustainability, emphasizing chemical safety, waste reduction, and eco-friendly practices relevant to food processing and sanitation. The key difference lies in LEED's broader building sustainability framework compared to Green Seal's focus on green product standards and operational impact within food plants.
Certification Criteria: LEED vs Green Seal
LEED certification for food plants emphasizes sustainable site development, water savings, energy efficiency, materials selection, and indoor environmental quality, with a strong focus on overall building performance and resource efficiency. Green Seal certification targets environmentally responsible cleaning, food packaging, and operational practices, emphasizing reduced chemical use, waste minimization, and safer food production processes. While LEED provides a comprehensive framework for green building design and construction, Green Seal specializes in certifying the sustainability of operational products and practices within food facilities.
Application Processes for Food Plants
LEED Certification for food plants involves a comprehensive assessment of sustainable site development, water savings, energy efficiency, and indoor environmental quality, requiring detailed documentation and performance data submitted through the Green Business Certification Inc. (GBCI) platform. Green Seal Certification for food plants emphasizes product-specific criteria, chemical safety, energy conservation, and waste reduction with a focus on food safety compliance, evaluated through on-site audits and verification of operational practices. The application process for LEED is more design and construction-oriented with prerequisite credits, while Green Seal focuses heavily on ongoing operational standards and chemical use policies tailored to food plant environments.
Cost Comparison of LEED and Green Seal Certifications
LEED certification for food plants typically involves higher upfront costs due to comprehensive building and energy efficiency requirements, often ranging from $20,000 to $100,000 depending on project size and complexity. Green Seal certification focuses on product sustainability and operational practices with lower certification fees, generally under $10,000, emphasizing reduced environmental impact through materials and processes rather than building infrastructure. Cost differences highlight LEED's investment in long-term green building performance versus Green Seal's approach to eco-friendly food production and operational sustainability.
Impact on Food Plant Operations and Reputation
LEED Certification enhances food plant operations by promoting energy efficiency, waste reduction, and improved indoor air quality, which leads to lower operational costs and healthier work environments. Green Seal Certification specifically targets sustainable cleaning and maintenance practices, ensuring non-toxic, chemical-safe processes that protect both food safety and worker health. Both certifications bolster reputation by demonstrating a commitment to environmental stewardship and consumer safety, attracting eco-conscious clients and enhancing market competitiveness.
Case Studies: Food Plants with LEED and Green Seal Certifications
Food plants with LEED Certification demonstrate enhanced energy efficiency and sustainable site management, as seen in the PepsiCo Modesto facility, which reduced water use by 30% and improved waste diversion rates. Green Seal Certified food plants, such as the Amy's Kitchen production site, showcase rigorous adherence to sustainable product formulation and environmentally responsible cleaning protocols. Your choice between LEED and Green Seal certifications can align with whether your focus is on building sustainability or product-specific environmental standards.
Choosing the Right Certification for Your Food Plant
LEED Certification emphasizes sustainable building design, energy efficiency, and water conservation, making it ideal for food plants aiming to reduce environmental impact through structural improvements. Green Seal Certification focuses specifically on sustainability in product manufacturing and operational practices, including waste reduction and use of safer chemicals, aligning with food plants prioritizing eco-friendly production and packaging. Food plants should evaluate their primary sustainability goals--whether facility-based improvements or product and operational standards--to select the certification that best supports their environmental and business objectives.
LEED Certification vs Green Seal Certification (for food plants) Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com