Liquid whole egg offers convenience and freshness for recipes needing immediate use, while powdered egg provides a longer shelf life and easy storage options without refrigeration. Your choice depends on the need for perishability, preparation time, and application in cooking or baking.
Table of Comparison
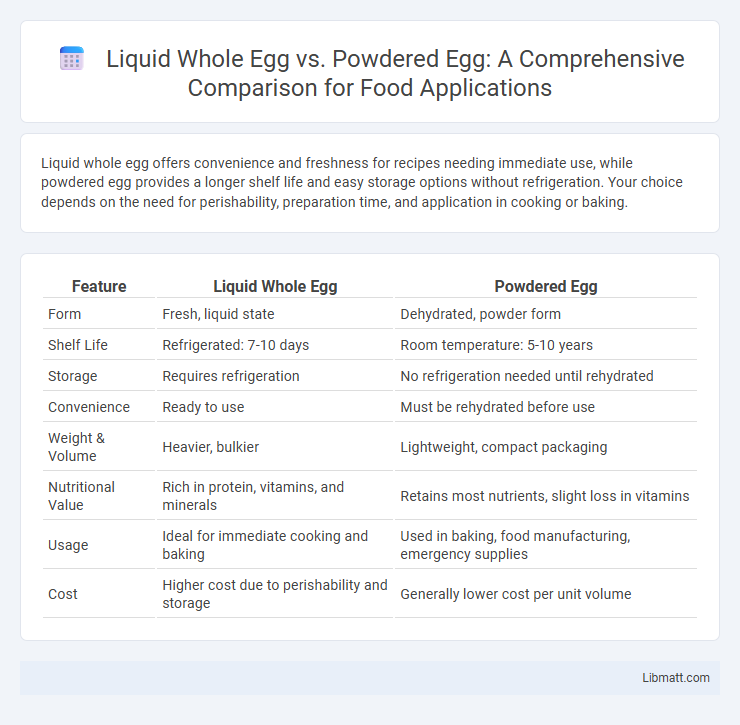
| Feature | Liquid Whole Egg | Powdered Egg |
|---|---|---|
| Form | Fresh, liquid state | Dehydrated, powder form |
| Shelf Life | Refrigerated: 7-10 days | Room temperature: 5-10 years |
| Storage | Requires refrigeration | No refrigeration needed until rehydrated |
| Convenience | Ready to use | Must be rehydrated before use |
| Weight & Volume | Heavier, bulkier | Lightweight, compact packaging |
| Nutritional Value | Rich in protein, vitamins, and minerals | Retains most nutrients, slight loss in vitamins |
| Usage | Ideal for immediate cooking and baking | Used in baking, food manufacturing, emergency supplies |
| Cost | Higher cost due to perishability and storage | Generally lower cost per unit volume |
Introduction to Liquid Whole Egg and Powdered Egg
Liquid whole egg offers convenience and ease of use in food preparation with its pre-cracked, ready-to-use form, maintaining the natural taste and nutritional value of fresh eggs. Powdered egg is dehydrated whole egg processed into a shelf-stable powder that extends storage life and reduces refrigeration needs while preserving protein content and essential nutrients. Both forms provide versatile options for commercial bakeries, food service, and industrial applications where consistent egg quality and safety are critical.
Nutritional Comparison: Liquid vs. Powdered Eggs
Liquid whole eggs retain a higher moisture content, providing slightly better bioavailability of certain vitamins such as B12 and choline compared to powdered eggs. Powdered eggs, created through dehydration, maintain most macronutrients like protein and fat but may experience minor losses in heat-sensitive nutrients such as vitamin A and some antioxidants. Both forms offer similar protein content, with powdered eggs favored for longer shelf life and convenience in food manufacturing.
Processing Methods of Liquid and Powdered Eggs
Liquid whole eggs are produced by cracking, breaking, and pasteurizing fresh eggs to maintain freshness and reduce bacterial contamination, while powdered eggs undergo a dehydration process where liquid eggs are spray-dried at controlled temperatures to remove moisture and extend shelf life. The key difference in processing methods lies in liquid eggs being stored refrigerated with limited shelf life, whereas powdered eggs benefit from extended storage at room temperature due to moisture removal and preservation techniques. Your choice between liquid and powdered eggs may depend on the convenience of storage, transportation needs, and application in food manufacturing or home cooking.
Shelf Life and Storage Differences
Liquid whole eggs typically have a shelf life of 7 to 10 days when refrigerated at 40degF, requiring continuous cold storage to maintain freshness and safety. Powdered eggs boast a significantly longer shelf life, often lasting up to 5 to 10 years when stored in a cool, dry environment, making them ideal for long-term storage without refrigeration. Your choice between liquid and powdered eggs depends on your need for immediate use versus extended storage and convenience.
Culinary Applications and Versatility
Liquid whole egg offers superior culinary flexibility with its ready-to-use form, ideal for baking, scrambling, and creating emulsions without rehydration. Powdered egg provides extended shelf life and easy storage, making it perfect for emergency food supplies and industrial baking, though it requires reconstitution and may slightly alter texture. Your choice depends on whether immediate convenience or long-term storage and versatility in various recipes is the priority.
Taste and Texture Analysis
Liquid whole eggs provide a fresher taste and a creamier texture that closely resembles farm-fresh eggs, making them ideal for dishes where egg flavor and consistency are paramount. Powdered eggs often possess a slightly chalky or cooked flavor with a grainier texture due to the dehydration and reconstitution process, which can alter the mouthfeel. Culinary professionals tend to prefer liquid whole eggs for applications requiring smoothness and authenticity, whereas powdered eggs offer convenience with minor compromises in sensory quality.
Food Safety and Pasteurization
Liquid whole egg undergoes pasteurization to eliminate harmful bacteria such as Salmonella, ensuring enhanced food safety for immediate use in commercial and foodservice applications. Powdered egg products are also pasteurized during the drying process, offering extended shelf life and reduced refrigeration requirements without compromising microbial safety. Both forms meet stringent food safety standards, but liquid eggs require constant cold storage to maintain pasteurization benefits, whereas powdered eggs provide greater versatility in storage and transportation.
Cost Analysis: Which Is More Economical?
Liquid whole egg typically incurs higher costs due to refrigeration and shorter shelf life requirements, increasing storage and transportation expenses. Powdered egg offers greater cost efficiency through extended shelf stability, reduced freight charges, and minimized waste, making it a more economical choice for large-scale food production. Despite a higher upfront processing cost, powdered egg's long-term savings in logistics and storage contribute to overall reduced expenditure.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Liquid whole eggs require refrigeration and have a shorter shelf life, leading to higher energy consumption and food waste compared to powdered eggs. Powdered eggs, dehydrated and shelf-stable, reduce transportation emissions due to lighter weight and minimize refrigeration needs, enhancing sustainability. Utilizing powdered eggs supports resource efficiency and lowers environmental impact throughout the supply chain.
Choosing the Right Egg Format for Your Needs
Liquid whole egg offers convenience and fresher taste, ideal for immediate use in cooking or baking, while powdered egg provides extended shelf life and easy storage, perfect for long-term use or emergency supplies. Your choice depends on factors like recipe requirements, storage capacity, and frequency of use. Selecting the right egg format ensures optimal texture, flavor, and nutritional value in your dishes.
liquid whole egg vs powdered egg Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com