Ultrafiltered milk undergoes a filtration process that removes water, lactose, and some minerals while retaining proteins and calcium, resulting in a creamier texture and higher protein content. Microfiltered milk uses a gentler filtration method to remove bacteria without significantly altering the milk's nutritional profile, preserving its natural flavor and freshness for your enjoyment.
Table of Comparison
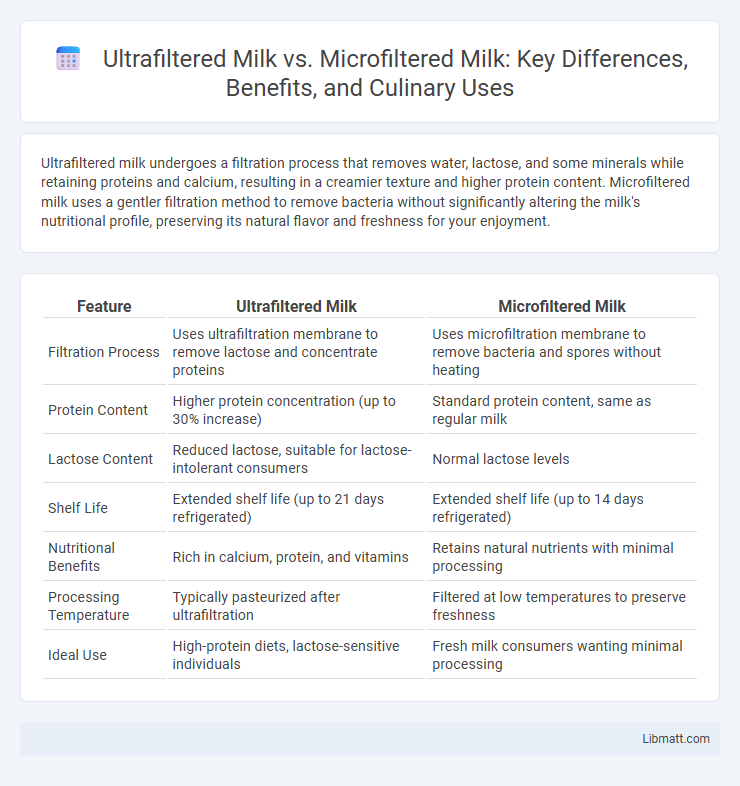
| Feature | Ultrafiltered Milk | Microfiltered Milk |
|---|---|---|
| Filtration Process | Uses ultrafiltration membrane to remove lactose and concentrate proteins | Uses microfiltration membrane to remove bacteria and spores without heating |
| Protein Content | Higher protein concentration (up to 30% increase) | Standard protein content, same as regular milk |
| Lactose Content | Reduced lactose, suitable for lactose-intolerant consumers | Normal lactose levels |
| Shelf Life | Extended shelf life (up to 21 days refrigerated) | Extended shelf life (up to 14 days refrigerated) |
| Nutritional Benefits | Rich in calcium, protein, and vitamins | Retains natural nutrients with minimal processing |
| Processing Temperature | Typically pasteurized after ultrafiltration | Filtered at low temperatures to preserve freshness |
| Ideal Use | High-protein diets, lactose-sensitive individuals | Fresh milk consumers wanting minimal processing |
Introduction to Ultrafiltered and Microfiltered Milk
Ultrafiltered milk undergoes a filtration process that removes water, lactose, and some minerals, resulting in higher protein and lower sugar content, which appeals to consumers seeking enhanced nutrition and creaminess. Microfiltered milk is processed using microfiltration technology to eliminate bacteria while retaining most of the milk's natural components, extending shelf life without lacto-saccharide modifications. Both ultrafiltered and microfiltered milks cater to different consumer preferences, with ultrafiltration focusing on nutritional concentration and microfiltration targeting purity and freshness.
What is Ultrafiltered Milk?
Ultrafiltered milk is milk that has been processed through a specialized filtration system to remove lactose, some water, and minerals while concentrating proteins and calcium. This results in milk with a creamier texture and higher protein content, often used to enhance nutrition without adding extra fat. Your choice of ultrafiltered milk can provide a richer taste and is suitable for those seeking high-protein dairy options.
What is Microfiltered Milk?
Microfiltered milk is milk that has undergone a filtration process using ceramic microfilters to remove bacteria and impurities while preserving essential nutrients and flavor. This method extends shelf life by reducing microbial load without heat treatment, maintaining a fresh taste compared to traditional pasteurization. Microfiltered milk typically retains higher levels of vitamins and proteins, making it a preferred choice for consumers seeking natural and nutritious dairy options.
The Filtration Processes Explained
Ultrafiltered milk undergoes a process where milk passes through a fine membrane that separates proteins and lactose from water, concentrating the nutrients and reducing sugar content. In contrast, microfiltered milk is filtered through ceramic microfilters to remove bacteria and spores while preserving vitamins and minerals, extending shelf life without heat pasteurization. Understanding these differences helps you choose milk based on nutritional needs and freshness preferences.
Nutritional Differences: Ultrafiltered vs Microfiltered Milk
Ultrafiltered milk contains higher protein and lower lactose levels due to its filtration process that removes some sugars and water, making it ideal for those seeking increased protein intake or lactose reduction. Microfiltered milk retains more natural nutrients like calcium and vitamins, as it undergoes gentle filtration to extend shelf life without significantly altering its nutritional profile. Your choice between ultrafiltered and microfiltered milk depends on whether you prioritize enhanced protein content or preserving the milk's original nutrient balance.
Taste and Texture Comparisons
Ultrafiltered milk boasts a creamier texture and richer taste due to the removal of water, lactose, and some minerals while retaining proteins and fats, resulting in a smoother mouthfeel. Microfiltered milk undergoes a gentle filtration process that removes bacteria without significantly altering the natural flavor or texture, maintaining a fresh and light profile. When choosing between the two, your preference depends on whether you prioritize a thicker, creamier consistency or a fresher, more natural milky taste.
Shelf Life and Storage
Ultrafiltered milk undergoes a filtration process that extends its shelf life to 30-40 days when unopened and stored at refrigeration temperatures of 34-38degF. Microfiltered milk, filtered through fine membranes to remove bacteria, typically lasts about 21 days under similar refrigeration conditions. Your choice between these milks affects how long you can store them fresh, with ultrafiltered offering longer refrigerated shelf stability.
Health Benefits and Considerations
Ultrafiltered milk undergoes a filtration process that removes lactose and some minerals, resulting in higher protein content and easier digestion for individuals with lactose intolerance. Microfiltered milk retains more of its natural minerals and vitamins while reducing harmful bacteria, offering enhanced safety without altering the nutritional profile significantly. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize higher protein intake and reduced lactose or prefer milk with a fuller nutrient spectrum and natural flavor.
Uses in Cooking and Baking
Ultrafiltered milk, with its higher protein content and creamier texture, enhances the richness and structure of baked goods like cakes and bread, making it ideal for recipes requiring moisture and density. Microfiltered milk, retaining more natural enzymes and a fresher taste, works well in cooking applications such as sauces and soups, where a smooth, subtle dairy flavor is crucial. You can choose ultrafiltered milk for baking to improve texture and microfiltered for cooking to preserve flavor integrity.
Which Milk Should You Choose?
Ultrafiltered milk undergoes a filtration process that removes lactose and concentrates protein and calcium, making it ideal for those seeking higher nutritional content and better digestibility. Microfiltered milk retains more of the milk's natural taste and nutrients by using finer filters to remove bacteria and extend shelf life without altering its composition significantly. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize enhanced nutrition and lower lactose or a fresher flavor with minimal processing.
Ultrafiltered Milk vs Microfiltered Milk Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com