Synthetic preservatives often provide longer shelf life and stronger antimicrobial protection, ensuring your products remain fresh and safe for extended periods. Natural preservatives, derived from plant or mineral sources, offer a safer, eco-friendly alternative with fewer health risks but may require more careful formulation to maintain effectiveness.
Table of Comparison
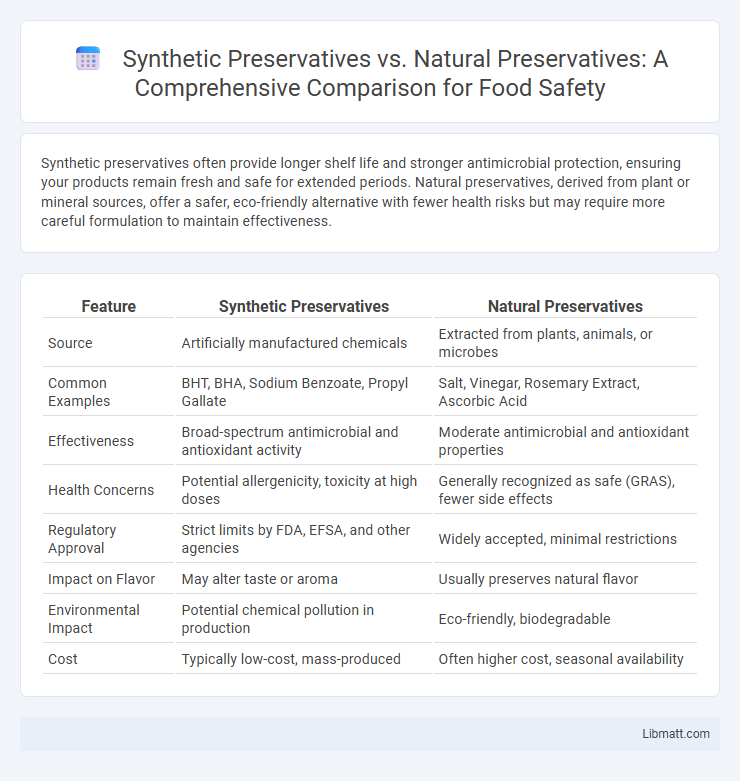
| Feature | Synthetic Preservatives | Natural Preservatives |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Artificially manufactured chemicals | Extracted from plants, animals, or microbes |
| Common Examples | BHT, BHA, Sodium Benzoate, Propyl Gallate | Salt, Vinegar, Rosemary Extract, Ascorbic Acid |
| Effectiveness | Broad-spectrum antimicrobial and antioxidant activity | Moderate antimicrobial and antioxidant properties |
| Health Concerns | Potential allergenicity, toxicity at high doses | Generally recognized as safe (GRAS), fewer side effects |
| Regulatory Approval | Strict limits by FDA, EFSA, and other agencies | Widely accepted, minimal restrictions |
| Impact on Flavor | May alter taste or aroma | Usually preserves natural flavor |
| Environmental Impact | Potential chemical pollution in production | Eco-friendly, biodegradable |
| Cost | Typically low-cost, mass-produced | Often higher cost, seasonal availability |
Introduction to Food Preservatives
Food preservatives play a crucial role in extending shelf life and preventing spoilage by inhibiting microbial growth and oxidation. Synthetic preservatives, such as sodium benzoate and potassium sorbate, offer consistent effectiveness and longer preservation periods, while natural preservatives like rosemary extract and vitamin E provide antioxidant benefits with cleaner label appeal. Your choice between synthetic and natural preservatives depends on factors like food type, safety standards, and consumer preferences for ingredient transparency.
What Are Synthetic Preservatives?
Synthetic preservatives are chemical compounds manufactured to inhibit microbial growth and prolong the shelf life of products such as food, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals. Common examples include parabens, sodium benzoate, and butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT), which provide effective, controlled preservation but may raise concerns regarding allergenicity and potential toxicity. These preservatives are favored in industrial applications for their stability, consistency, and cost-effectiveness compared to natural alternatives.
What Are Natural Preservatives?
Natural preservatives are substances derived from plants, animals, or minerals that extend the shelf life of food, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals by preventing microbial growth and oxidation. Common examples include rosemary extract, vitamin E, and essential oils such as tea tree and clove, which possess antioxidant and antimicrobial properties. These preservatives offer a safer, eco-friendly alternative to synthetic chemicals like parabens and sodium benzoate, aligning with consumer demand for clean-label and organic products.
Key Differences Between Synthetic and Natural Preservatives
Synthetic preservatives are chemically manufactured compounds designed to extend shelf life by preventing microbial growth, while natural preservatives derive from plant extracts, essential oils, or other natural sources offering antioxidant and antimicrobial properties. Synthetic preservatives generally provide longer-lasting and more predictable protection but may raise concerns regarding potential allergens or chemical residues. Your choice between synthetic and natural preservatives depends on product formulation, desired shelf life, and consumer preferences for clean-label or organic ingredients.
Effectiveness in Extending Shelf Life
Synthetic preservatives such as sodium benzoate and potassium sorbate are highly effective in extending shelf life due to their strong antimicrobial properties against a broad spectrum of bacteria, molds, and yeasts. Natural preservatives like rosemary extract, citric acid, and vitamin E provide antioxidant benefits and moderate antimicrobial effects, often requiring higher concentrations or combination with other methods to achieve similar shelf life extension. The choice between synthetic and natural preservatives depends on product formulation, regulatory guidelines, and consumer preference for clean-label ingredients.
Safety and Health Concerns
Synthetic preservatives such as parabens and BHA are often scrutinized for potential links to hormone disruption and cancer risk, raising safety concerns in consumer health. Natural preservatives like rosemary extract and vitamin E are generally considered safer due to their antioxidant properties but may offer limited shelf-life protection compared to synthetic alternatives. Evaluating the risk-benefit profile of preservatives involves balancing effective microbial inhibition with minimizing toxicity and allergic reactions in sensitive populations.
Regulatory Standards and Approvals
Regulatory standards for synthetic preservatives are typically stringent, with agencies like the FDA and EMA requiring extensive safety testing and clear labeling before approval. Natural preservatives often face less rigorous regulatory scrutiny but must still comply with regulations concerning purity, toxicity, and allergenicity in various regions. Your choice between synthetic and natural preservatives should consider these differing approval processes to ensure product safety and regulatory compliance.
Environmental Impact of Preservative Types
Synthetic preservatives often contribute to environmental pollution due to their chemical persistence and potential to bioaccumulate in ecosystems, posing risks to aquatic life and soil health. Natural preservatives, derived from plant extracts, essential oils, or organic acids, typically degrade more rapidly and have a lower ecological footprint, supporting biodiversity and reducing chemical contamination. Choosing natural preservatives can align with sustainable practices by minimizing toxic runoff and promoting eco-friendly waste management.
Consumer Preferences and Market Trends
Consumer preferences increasingly favor natural preservatives due to concerns over synthetic additives and potential health risks, driving a significant shift in market trends. Brands incorporating plant-based antioxidants and naturally derived antimicrobial agents see higher demand and improved product perception. Your choice of preservatives can impact customer loyalty as the natural preservative market grows rapidly, reflecting heightened awareness and preference for clean-label ingredients.
Future Outlook for Food Preservation Methods
Advancements in food preservation increasingly emphasize natural preservatives due to consumer demand for clean-label products and sustainability concerns, with compounds like rosemary extract, nisin, and chitosan gaining prominence. Synthetic preservatives, such as sodium benzoate and potassium sorbate, remain widely used for their cost-effectiveness and efficacy but face regulatory scrutiny and potential reformulation pressures. Emerging technologies like nanotechnology and biopreservation are poised to revolutionize the future of food preservation by enhancing the functionality and safety of both natural and synthetic additives.
Synthetic Preservatives vs Natural Preservatives Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com