Bipolar ionization neutralizes airborne pathogens by releasing charged ions that attach to pollutants and deactivate viruses, while UV-C disinfection uses ultraviolet light to destroy the DNA or RNA of microorganisms, effectively sterilizing surfaces and air. Choosing the right technology depends on your specific needs for air purification, surface disinfection, and the environment in which it will be used.
Table of Comparison
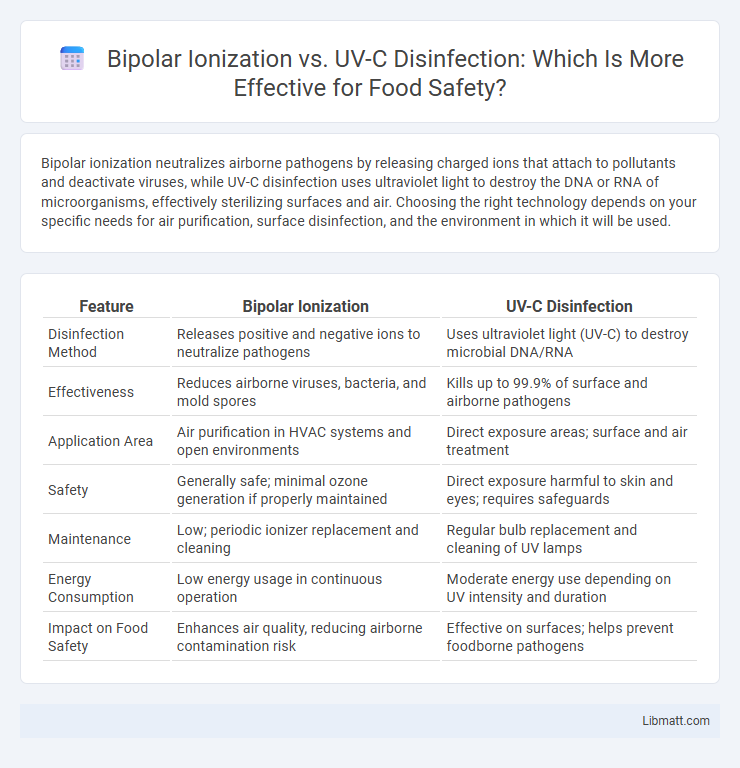
| Feature | Bipolar Ionization | UV-C Disinfection |
|---|---|---|
| Disinfection Method | Releases positive and negative ions to neutralize pathogens | Uses ultraviolet light (UV-C) to destroy microbial DNA/RNA |
| Effectiveness | Reduces airborne viruses, bacteria, and mold spores | Kills up to 99.9% of surface and airborne pathogens |
| Application Area | Air purification in HVAC systems and open environments | Direct exposure areas; surface and air treatment |
| Safety | Generally safe; minimal ozone generation if properly maintained | Direct exposure harmful to skin and eyes; requires safeguards |
| Maintenance | Low; periodic ionizer replacement and cleaning | Regular bulb replacement and cleaning of UV lamps |
| Energy Consumption | Low energy usage in continuous operation | Moderate energy use depending on UV intensity and duration |
| Impact on Food Safety | Enhances air quality, reducing airborne contamination risk | Effective on surfaces; helps prevent foodborne pathogens |
Introduction to Air Disinfection Technologies
Bipolar ionization and UV-C disinfection are advanced air disinfection technologies designed to enhance indoor air quality by reducing airborne pathogens. Bipolar ionization releases charged ions that attach to and neutralize viruses and bacteria, while UV-C disinfection uses ultraviolet light to destroy the DNA or RNA of microorganisms, rendering them inactive. Your choice between these methods depends on factors such as room size, maintenance requirements, and the specific types of contaminants you need to control.
What is Bipolar Ionization?
Bipolar ionization is an advanced air purification technology that releases both positive and negative ions to neutralize airborne contaminants such as viruses, bacteria, and allergens. Unlike UV-C disinfection, which uses ultraviolet light to kill microorganisms by damaging their DNA, bipolar ionization works by producing ions that attach to particles, causing them to cluster and settle out of the air or break down harmful substances. Your indoor air quality can improve significantly with bipolar ionization, especially in environments where continuous air treatment is essential.
Understanding UV-C Disinfection
UV-C disinfection utilizes ultraviolet light at wavelengths between 200-280 nm to effectively inactivate bacteria, viruses, and mold by damaging their DNA or RNA, preventing replication. This method is widely used in healthcare facilities and HVAC systems due to its proven ability to reduce airborne and surface pathogens without chemical residues. Understanding your environment's specific microbial risks helps determine if UV-C disinfection offers the most reliable solution for maintaining safe indoor air quality.
Mechanisms of Action: Bipolar Ionization vs UV-C
Bipolar ionization neutralizes airborne pathogens by releasing positive and negative ions that attach to contaminants, causing structural damage and clumping particles for easier filtration. UV-C disinfection employs ultraviolet light at wavelengths between 200-280 nm to disrupt the DNA and RNA of microorganisms, effectively inactivating viruses, bacteria, and mold. Your choice depends on environmental needs, with bipolar ionization targeting air quality improvement and UV-C providing direct surface and air sterilization.
Efficacy Against Airborne Pathogens
Bipolar ionization effectively reduces airborne pathogens by releasing charged ions that attach to and neutralize viruses and bacteria in the air. UV-C disinfection destroys microorganisms by damaging their DNA or RNA, providing rapid and proven inactivation of airborne pathogens. Your choice between these technologies should consider the specific environment and desired disinfection speed for optimal air quality control.
Safety Considerations and Potential Risks
Bipolar ionization and UV-C disinfection each present distinct safety considerations and potential risks; bipolar ionization can generate ozone and other byproducts that may irritate respiratory systems, requiring careful monitoring of air quality levels. UV-C disinfection involves exposure to ultraviolet light that can cause skin burns and eye injuries if safety protocols are not strictly followed. Implementing proper engineering controls and ensuring compliance with Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) guidelines significantly mitigate these risks.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Bipolar ionization systems typically require installation within HVAC ducts and periodic maintenance such as electrode replacement every 6 to 12 months to maintain ion output efficiency. UV-C disinfection units need direct line-of-sight placement in ventilation systems or surfaces and require routine cleaning of lamps and bulb replacement every 9,000 to 12,000 hours for optimal effectiveness. Both technologies demand professional installation to ensure proper placement and safety compliance, but bipolar ionization often involves less frequent physical maintenance compared to UV-C lamps.
Energy Efficiency and Operating Costs
Bipolar ionization systems typically consume less energy than UV-C disinfection devices, making them more energy-efficient for continuous air purification. UV-C systems often require higher electrical power to generate sufficient ultraviolet light intensity, leading to increased operating costs over time. Maintenance expenses for bipolar ionization are generally lower since it involves fewer component replacements compared to periodic bulb changes and cleaning needed for UV-C units.
Applications in Different Environments
Bipolar ionization is effective in commercial HVAC systems, healthcare facilities, and schools for continuous air purification by reducing airborne pathogens and allergens. UV-C disinfection excels in targeted surface sterilization and is widely used in hospitals, laboratories, and water treatment plants to destroy bacteria, viruses, and mold on contact. Your choice depends on whether you need ongoing air quality improvement or intensive surface sterilization in specific environments.
Comparing Real-World Performance and User Experience
Bipolar ionization and UV-C disinfection each demonstrate unique real-world efficacy in improving indoor air quality; bipolar ionization reduces airborne pathogens by generating charged ions that neutralize particles, while UV-C employs ultraviolet light to inactivate microorganisms on surfaces and in the air. User experience varies as bipolar ionization systems typically run continuously with low maintenance, whereas UV-C devices may require scheduled operation and safety precautions to avoid harmful exposure. Studies highlight that UV-C offers faster pathogen inactivation with visible results, whereas bipolar ionization provides ongoing air purification with less immediate feedback to users.
bipolar ionization vs UV-C disinfection Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com