Ghee differs from clarified butter by undergoing a longer cooking process, which removes moisture and milk solids, resulting in a nuttier flavor and higher smoke point ideal for high-heat cooking. Your choice depends on whether you prefer a richer taste and increased shelf life from ghee or the simpler, faster preparation of clarified butter.
Table of Comparison
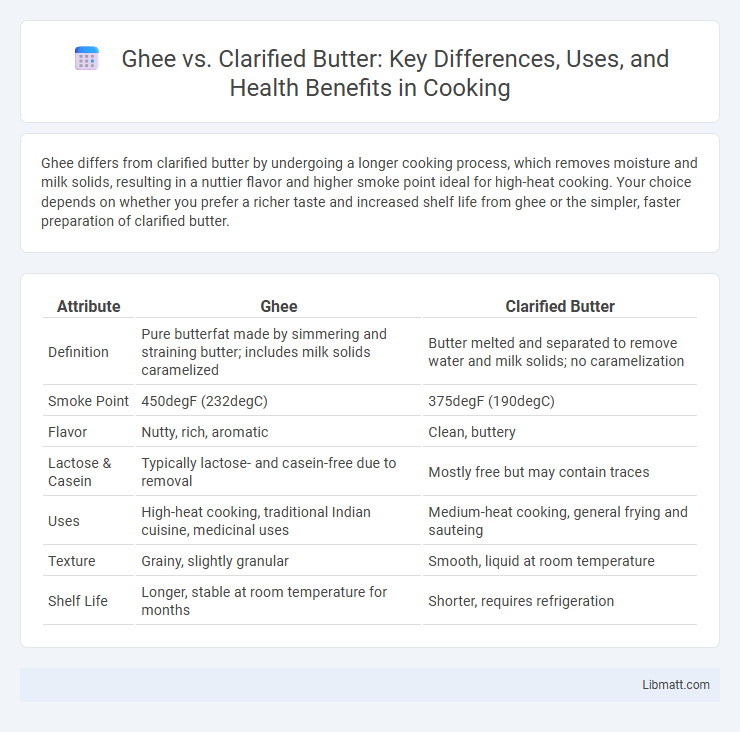
| Attribute | Ghee | Clarified Butter |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pure butterfat made by simmering and straining butter; includes milk solids caramelized | Butter melted and separated to remove water and milk solids; no caramelization |
| Smoke Point | 450degF (232degC) | 375degF (190degC) |
| Flavor | Nutty, rich, aromatic | Clean, buttery |
| Lactose & Casein | Typically lactose- and casein-free due to removal | Mostly free but may contain traces |
| Uses | High-heat cooking, traditional Indian cuisine, medicinal uses | Medium-heat cooking, general frying and sauteing |
| Texture | Grainy, slightly granular | Smooth, liquid at room temperature |
| Shelf Life | Longer, stable at room temperature for months | Shorter, requires refrigeration |
Introduction: Ghee vs Clarified Butter
Ghee and clarified butter are both types of purified butter fats, but ghee undergoes a longer cooking process that caramelizes milk solids, giving it a richer flavor and higher smoke point. Clarified butter is made by melting butter and removing the milk solids and water, resulting in a clear, golden fat commonly used in cooking. Understanding the differences between ghee and clarified butter can help you choose the best option for your culinary needs and dietary preferences.
What is Ghee?
Ghee is a type of clarified butter that originates from Indian cuisine and is made by simmering butter to remove water content and milk solids, resulting in a rich, nutty flavor and extended shelf life. Unlike regular clarified butter, ghee is cooked longer to caramelize the milk solids before straining, enhancing its aroma and taste. Its high smoke point, around 485degF (252degC), makes ghee ideal for cooking methods like frying and sauteing.
What is Clarified Butter?
Clarified butter is butter that has been melted to separate the milk solids and water from the pure butterfat, resulting in a clear, golden liquid with a higher smoke point than regular butter. It is commonly used in cooking for frying and sauteing due to its ability to withstand higher temperatures without burning. Unlike ghee, clarified butter is not simmered to develop a nutty flavor, thus retaining a milder taste.
The Traditional Methods of Preparation
Ghee is crafted using a slow simmering process that involves boiling butter until the milk solids caramelize and separate, imparting a nutty flavor and long shelf life without refrigeration. Clarified butter is made by melting butter gently and straining out the milk solids without caramelization, resulting in a clear, golden liquid with a milder taste. Your choice between the two can influence flavor complexity and cooking properties depending on the traditional method used.
Differences in Flavor and Aroma
Ghee offers a rich, nutty flavor and a pronounced caramel aroma due to the milk solids being browned during the cooking process, whereas clarified butter has a cleaner, milder taste with minimal aroma since the milk solids are simply removed without browning. The Maillard reaction in ghee development enhances its complex flavor profile, making it more suitable for dishes requiring depth and warmth. Clarified butter serves as a neutral fat ideal for high-heat cooking without altering the dish's original flavor.
Nutritional Comparison
Ghee contains slightly higher levels of short-chain fatty acids like butyrate, which support gut health, compared to clarified butter that primarily offers pure milk fat with minimal milk solids. Both ghee and clarified butter are rich in fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K, but ghee's longer cooking process enhances its antioxidant content, contributing to improved oxidative stability. While ghee has a richer nutrient profile including conjugated linoleic acid (CLA), both remain calorie-dense with roughly 112-120 calories per tablespoon, making portion control important in diets.
Health Benefits of Ghee and Clarified Butter
Ghee contains higher concentrations of antioxidants, vitamins A, D, E, and K, and has a richer profile of medium-chain fatty acids that support digestion and boost immunity compared to clarified butter. Clarified butter offers a pure butterfat source with fewer milk solids, reducing lactose and casein content, which benefits those with dairy sensitivities. Both ghee and clarified butter promote heart health and anti-inflammatory effects, but ghee's additional bioactive compounds provide enhanced health benefits.
Culinary Uses and Cooking Applications
Ghee offers a richer, nuttier flavor compared to clarified butter, making it ideal for Indian, Middle Eastern, and Southeast Asian dishes where deep, aromatic flavors are essential. Clarified butter maintains a cleaner, more neutral taste and is preferred for sauteing, frying, and baking due to its high smoke point and smooth texture. Your choice between ghee and clarified butter influences the flavor profile and cooking technique, enhancing specific culinary applications based on desired taste and heat tolerance.
Storage and Shelf Life
Ghee offers a longer shelf life than clarified butter due to its lower moisture content, allowing it to stay fresh for up to a year when stored in an airtight container at room temperature. Clarified butter, containing more milk solids, should be refrigerated and typically lasts up to a month before spoiling. Your choice between the two can impact storage convenience and product longevity in your kitchen.
Which One Should You Choose?
Ghee offers a richer, nutty flavor and contains antioxidants and slightly higher levels of vitamins A, E, and K compared to clarified butter, making it a healthier choice for cooking at high temperatures. Clarified butter, which is simply butter with milk solids removed, has a more neutral taste and is ideal for recipes requiring pure butterfat without altering the flavor. For those seeking enhanced health benefits and deeper flavor, ghee is the better option, while clarified butter suits culinary uses demanding subtle buttery essence.
Ghee vs Clarified Butter Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com