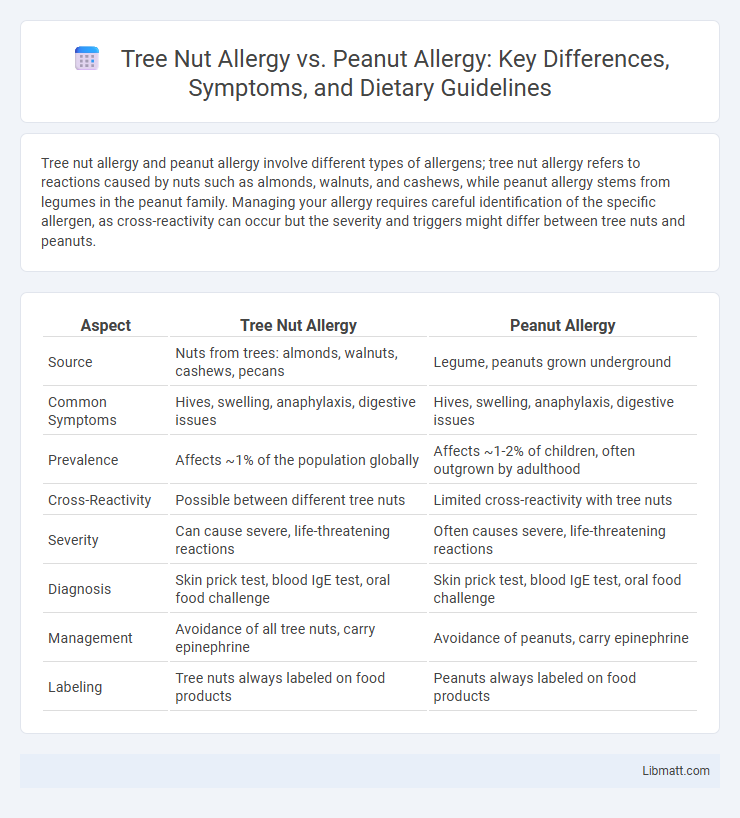
Tree nut allergy and peanut allergy involve different types of allergens; tree nut allergy refers to reactions caused by nuts such as almonds, walnuts, and cashews, while peanut allergy stems from legumes in the peanut family. Managing your allergy requires careful identification of the specific allergen, as cross-reactivity can occur but the severity and triggers might differ between tree nuts and peanuts.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Tree Nut Allergy | Peanut Allergy |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Nuts from trees: almonds, walnuts, cashews, pecans | Legume, peanuts grown underground |
| Common Symptoms | Hives, swelling, anaphylaxis, digestive issues | Hives, swelling, anaphylaxis, digestive issues |
| Prevalence | Affects ~1% of the population globally | Affects ~1-2% of children, often outgrown by adulthood |
| Cross-Reactivity | Possible between different tree nuts | Limited cross-reactivity with tree nuts |
| Severity | Can cause severe, life-threatening reactions | Often causes severe, life-threatening reactions |
| Diagnosis | Skin prick test, blood IgE test, oral food challenge | Skin prick test, blood IgE test, oral food challenge |
| Management | Avoidance of all tree nuts, carry epinephrine | Avoidance of peanuts, carry epinephrine |
| Labeling | Tree nuts always labeled on food products | Peanuts always labeled on food products |
Introduction to Tree Nut and Peanut Allergies
Tree nut allergy and peanut allergy are distinct food allergies caused by different proteins found in tree nuts and peanuts, respectively. Tree nut allergies involve allergens from nuts such as almonds, walnuts, and cashews, whereas peanut allergies stem from legume proteins specific to peanuts. Understanding these differences helps you manage exposure risks and avoid allergic reactions effectively.
Understanding the Difference: Tree Nut vs Peanut Allergy
Tree nut allergy and peanut allergy differ primarily in their origin; tree nuts come from various tree species such as almonds, walnuts, and cashews, while peanuts are legumes related to beans and lentils. Both allergies can trigger similar immune responses including anaphylaxis, but individuals allergic to one are not always allergic to the other due to distinct protein structures. Accurate diagnosis through allergen-specific IgE testing is crucial for managing exposure and preventing severe allergic reactions.
Common Symptoms of Tree Nut and Peanut Allergies
Tree nut and peanut allergies commonly cause symptoms such as hives, swelling, itching, and difficulty breathing due to an immune response to specific proteins. Both allergies can trigger anaphylaxis, a severe and potentially life-threatening reaction requiring immediate medical attention. Awareness of these symptoms is crucial for timely diagnosis and effective management in affected individuals.
Causes and Risk Factors
Tree nut allergy and peanut allergy are caused by immune system overreactions to specific proteins found in nuts and legumes, respectively. Genetic predisposition, family history of allergies, and early exposure to allergenic foods increase the risk for both types of allergies. Understanding your personal and family history helps identify potential risk factors and manage exposure to these allergenic triggers effectively.
Cross-Reactivity Between Tree Nuts and Peanuts
Cross-reactivity between tree nuts and peanuts occurs because they share similar protein structures, which can trigger allergic reactions in sensitive individuals. Despite both being legumes and nuts respectively, the immune system may mistake proteins in one for the other, increasing the risk of multiple nut allergies. Testing for specific IgE antibodies helps identify cross-reactivity, guiding avoidance strategies and allergy management.
Foods to Avoid: Tree Nuts vs Peanuts
People with tree nut allergies should avoid foods containing almonds, cashews, walnuts, pistachios, and pecans, as these nuts can trigger severe allergic reactions. Those with peanut allergies must strictly avoid peanuts and peanut-containing products such as peanut butter, peanut oil, and many processed snacks. Cross-contamination is a significant risk, so carefully reading food labels and avoiding bulk bins or shared equipment is essential for both allergy types.
Diagnosis: How Allergies Are Identified
Diagnosis of tree nut allergy and peanut allergy commonly involves a combination of patient history, skin prick tests, and specific IgE blood tests to identify allergen sensitization. Oral food challenges conducted under medical supervision provide definitive confirmation of these allergies by observing reactions to controlled exposures. Your allergist may also consider component-resolved diagnostics to pinpoint the exact allergenic proteins, improving the accuracy and reliability of the diagnosis.
Emergency Management and Treatment Options
Emergency management of tree nut and peanut allergies requires immediate administration of epinephrine through an auto-injector at the onset of anaphylaxis symptoms. Both allergies demand strict avoidance strategies and carrying prescribed antihistamines for mild reactions, but severe reactions prioritize rapid epinephrine use followed by emergency medical care. Your preparedness includes recognizing early symptoms, having an action plan, and ensuring quick access to emergency treatment to prevent life-threatening complications.
Living With Nut Allergies: Tips for Daily Life
Managing nut allergies requires constant vigilance, especially when distinguishing between tree nut allergy and peanut allergy, as both demand strict avoidance to prevent severe reactions. Label reading becomes essential, targeting ingredients like almonds, cashews, or peanuts, and maintaining communication about allergies in social, school, and dining environments minimizes exposure risks. Employing allergen-free meal planning, carrying emergency epinephrine, and educating close contacts significantly enhance safety and quality of life for individuals navigating nut allergies daily.
Future Research and Advances in Allergy Care
Future research in allergy care is rapidly advancing with a focus on improved diagnostic tools and personalized immunotherapy for both tree nut allergy and peanut allergy. Emerging treatments such as oral immunotherapy (OIT) and biologics aim to increase tolerance and reduce the severity of allergic reactions. Your healthcare providers can leverage these innovations to better manage symptoms and enhance quality of life for individuals with nut allergies.
Tree Nut Allergy vs Peanut Allergy Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com