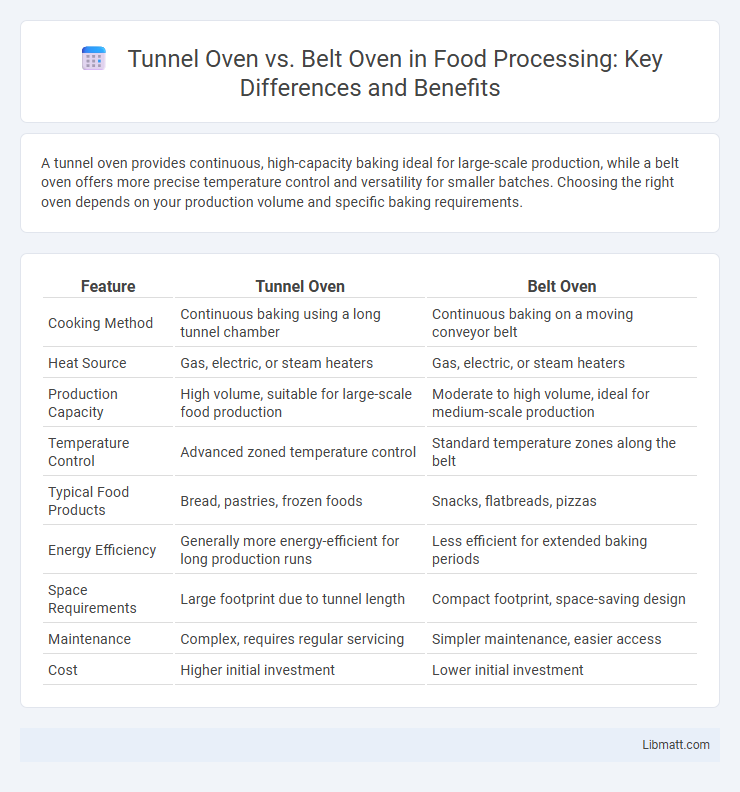
A tunnel oven provides continuous, high-capacity baking ideal for large-scale production, while a belt oven offers more precise temperature control and versatility for smaller batches. Choosing the right oven depends on your production volume and specific baking requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Tunnel Oven | Belt Oven |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Continuous baking using a long tunnel chamber | Continuous baking on a moving conveyor belt |
| Heat Source | Gas, electric, or steam heaters | Gas, electric, or steam heaters |
| Production Capacity | High volume, suitable for large-scale food production | Moderate to high volume, ideal for medium-scale production |
| Temperature Control | Advanced zoned temperature control | Standard temperature zones along the belt |
| Typical Food Products | Bread, pastries, frozen foods | Snacks, flatbreads, pizzas |
| Energy Efficiency | Generally more energy-efficient for long production runs | Less efficient for extended baking periods |
| Space Requirements | Large footprint due to tunnel length | Compact footprint, space-saving design |
| Maintenance | Complex, requires regular servicing | Simpler maintenance, easier access |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower initial investment |
Introduction to Tunnel Ovens and Belt Ovens
Tunnel ovens and belt ovens are industrial baking machines designed for continuous production with distinct operational features. Tunnel ovens use a long, enclosed chamber where products pass through on a conveyor belt, ensuring consistent heat exposure and uniform baking. Belt ovens also employ conveyor belts but typically feature shorter cooking zones and more adjustable temperature profiles, giving you greater control over baking times and product variability.
How Tunnel Ovens Work
Tunnel ovens operate by continuously moving products on a conveyor belt through a long, insulated chamber where controlled heat is applied evenly for baking or curing. The oven's temperature zones can be adjusted to optimize baking times and product consistency, making it ideal for high-volume production. Your choice between a tunnel oven and a belt oven depends on the required throughput and specific heating process for your food products.
How Belt Ovens Operate
Belt ovens operate by continuously moving products on a conveyor belt through a heated chamber, ensuring consistent temperature exposure for uniform baking or drying. The conveyor system allows precise control over baking time and temperature, adapting to various product sizes and types. Your processing efficiency improves with the ability to maintain steady heat distribution and handle high production volumes seamlessly.
Key Differences: Tunnel vs Belt Ovens
Tunnel ovens feature a continuous conveyor belt that moves products through a stationary heating chamber, providing consistent temperature zones ideal for high-volume baking processes. Belt ovens, on the other hand, often have shorter conveyor paths and offer more customizable heating zones, enabling better control for varied baking times and product types. The key difference lies in tunnel ovens' efficiency for large-scale, uniform baking compared to belt ovens' flexibility for smaller batches and diverse baking requirements.
Advantages of Tunnel Ovens
Tunnel ovens offer continuous production, ensuring consistent baking quality and high throughput ideal for large-scale industrial applications. Their design allows precise temperature control across multiple zones, enhancing product uniformity and energy efficiency. You benefit from reduced downtime and increased automation potential compared to belt ovens, optimizing operational efficiency.
Benefits of Belt Ovens
Belt ovens offer consistent heat distribution and efficient airflow, ensuring uniform cooking and baking results for a wide range of products. Their continuous operation improves productivity by allowing you to process large quantities with minimal manual intervention, reducing labor costs. Compact design and easier maintenance make belt ovens ideal for optimizing your production line space and minimizing downtime.
Applications and Industries for Each Oven Type
Tunnel ovens excel in high-volume baking applications such as bread, pizza, and pastry production within large-scale commercial bakeries and food manufacturing plants. Belt ovens are ideal for versatile cooking and baking processes in industries like snack foods, confectionery, and ready-meals, offering precise temperature control and adjustable conveyor speeds. Your choice depends on throughput requirements and product type, with tunnel ovens suited for continuous, high-capacity operations and belt ovens preferred for flexibility and varied cooking stages.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Tunnel ovens generally offer higher energy efficiency than belt ovens due to continuous baking processes that minimize heat loss and ensure consistent temperature control. Belt ovens tend to have more variable heating zones, often resulting in increased energy consumption to maintain uniform baking conditions. Energy-efficient tunnel ovens reduce greenhouse gas emissions and lower operational costs, making them preferable for large-scale industrial baking applications.
Cost Considerations and ROI
Tunnel ovens generally require higher initial capital investment compared to belt ovens due to their larger size and advanced automation features. Operating costs for tunnel ovens may be lower over time because of improved energy efficiency and continuous production capabilities, which can lead to faster return on investment (ROI) in high-volume operations. Belt ovens typically offer lower upfront costs and quicker installation, making them suitable for smaller-scale production with shorter ROI periods despite potentially higher per-unit energy consumption.
Choosing the Right Oven for Your Production Needs
Selecting between a tunnel oven and a belt oven depends primarily on production volume and product type; tunnel ovens excel in continuous high-capacity baking with consistent temperature control, ideal for large-scale operations. Belt ovens offer greater flexibility and customization for smaller batches or specialized products, providing precise baking zones and faster heat-up times. Evaluating factors such as production speed, energy efficiency, and maintenance requirements ensures the most efficient oven choice tailored to your manufacturing workflow.
Tunnel Oven vs Belt Oven Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com