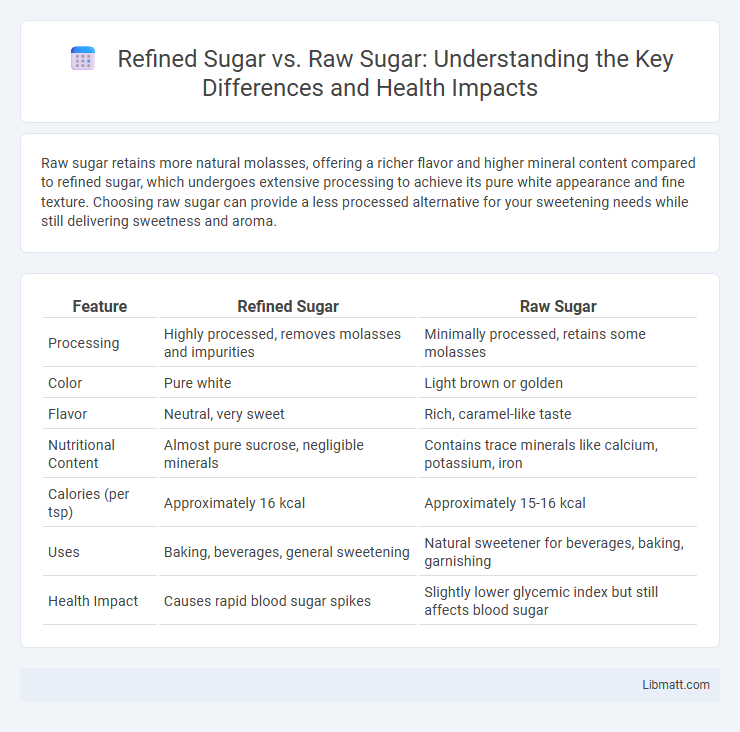
Raw sugar retains more natural molasses, offering a richer flavor and higher mineral content compared to refined sugar, which undergoes extensive processing to achieve its pure white appearance and fine texture. Choosing raw sugar can provide a less processed alternative for your sweetening needs while still delivering sweetness and aroma.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Refined Sugar | Raw Sugar |
|---|---|---|
| Processing | Highly processed, removes molasses and impurities | Minimally processed, retains some molasses |
| Color | Pure white | Light brown or golden |
| Flavor | Neutral, very sweet | Rich, caramel-like taste |
| Nutritional Content | Almost pure sucrose, negligible minerals | Contains trace minerals like calcium, potassium, iron |
| Calories (per tsp) | Approximately 16 kcal | Approximately 15-16 kcal |
| Uses | Baking, beverages, general sweetening | Natural sweetener for beverages, baking, garnishing |
| Health Impact | Causes rapid blood sugar spikes | Slightly lower glycemic index but still affects blood sugar |
Introduction to Refined Sugar and Raw Sugar
Refined sugar is a highly processed sweetener derived from sugar cane or sugar beets, stripped of molasses and impurities to produce pure sucrose crystals commonly used in baking and beverages. Raw sugar, on the other hand, undergoes minimal processing, retaining some molasses content, which gives it a coarser texture and a light brown color with a richer flavor. The differences in processing impact the nutrient content, flavor profile, and culinary uses of refined sugar and raw sugar.
What is Refined Sugar?
Refined sugar is a highly processed form of sucrose derived from sugarcane or sugar beets, where impurities, molasses, and minerals are removed through chemical and mechanical processes. This results in pure white granules commonly used in baking, beverages, and processed foods for its neutral flavor and extended shelf life. Your choice between refined and raw sugar impacts both the nutritional content and flavor profile of your recipes.
What is Raw Sugar?
Raw sugar is minimally processed from sugar cane or sugar beets, retaining natural molasses that give it a brown color and richer flavor. It contains trace minerals like calcium, potassium, and iron, which are mostly removed during refining. You can use raw sugar as a less processed alternative to white sugar for a slightly more complex taste and texture in recipes.
Processing Differences: Refined vs Raw Sugar
Raw sugar undergoes minimal processing, retaining some natural molasses that gives it a brown color and a slightly richer flavor. Refined sugar is heavily processed through multiple stages of washing, filtering, and crystallization, removing impurities and molasses to produce pure, white granulated sugar. These processing differences impact the texture, flavor profile, and nutritional content between raw and refined sugars.
Nutritional Comparison: Refined vs Raw Sugar
Raw sugar retains trace minerals like calcium, potassium, and iron due to minimal processing, whereas refined sugar is stripped of these nutrients during purification. Both types primarily consist of sucrose, but raw sugar's slight mineral content provides a marginal nutritional advantage. Caloric values remain similar, with each containing approximately 16 calories per teaspoon.
Health Impacts of Refined Sugar
Refined sugar undergoes extensive processing that removes natural nutrients, leading to a high glycemic index which contributes to rapid blood sugar spikes and increased risk of insulin resistance, obesity, and type 2 diabetes. Studies link excessive consumption of refined sugar to inflammation, liver fat accumulation, and cardiovascular diseases due to its fructose content. Unlike raw sugar, refined sugar lacks minerals and antioxidants, exacerbating metabolic health issues and promoting poor dietary outcomes.
Health Impacts of Raw Sugar
Raw sugar contains molasses, which provides trace minerals like calcium, potassium, and iron that contribute modestly to nutritional value compared to refined sugar. Unlike refined sugar, raw sugar undergoes less processing, retaining antioxidants that may help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation. Consuming raw sugar in moderation can minimize blood sugar spikes and support metabolic health better than highly processed refined sugar.
Taste and Culinary Uses
Refined sugar has a cleaner, more neutral sweetness ideal for baking and beverages where a pure sugar flavor is desired, while raw sugar retains subtle molasses notes that add depth and complexity to recipes like sauces and marinades. Your choice between refined and raw sugar can influence the texture and color of baked goods, with raw sugar providing a coarser texture and richer hue. Using raw sugar enhances the flavor profile in recipes that benefit from a caramelized or earthy taste.
Environmental and Ethical Considerations
Raw sugar production tends to have a lower environmental impact than refined sugar as it requires less processing, reducing energy consumption and chemical use. Ethical considerations highlight that raw sugar often supports small-scale farmers and fair trade practices, promoting better labor conditions compared to large-scale industrial refining typically linked with exploitation and intensive resource use. Sustainable sourcing of raw sugar can minimize deforestation and water pollution, making it a more responsible choice for environmentally and socially conscious consumers.
Which Sugar Should You Choose?
Raw sugar retains more natural molasses and minerals like calcium, potassium, and iron, offering a slightly richer flavor and some nutritional benefits compared to refined sugar. Refined sugar undergoes extensive processing to remove impurities, resulting in a pure, white product with a neutral taste but fewer nutrients. You should choose raw sugar if you prefer a less processed option with trace minerals, while refined sugar is better suited for recipes requiring a clean, sweet profile without altering flavor.
Refined Sugar vs Raw Sugar Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com