Cocoa butter is the fat extracted from cocoa beans, providing smooth texture and rich flavor to chocolate, while cocoa solids contain the non-fat components responsible for the chocolate's intense taste and color. Understanding the difference between cocoa butter and cocoa solids helps you choose products based on desired flavor, texture, and health benefits.
Table of Comparison
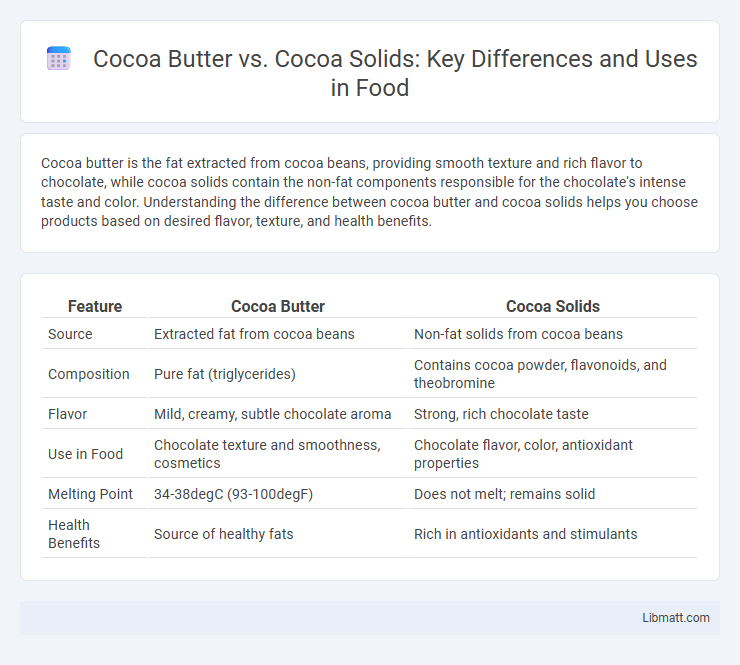
| Feature | Cocoa Butter | Cocoa Solids |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Extracted fat from cocoa beans | Non-fat solids from cocoa beans |
| Composition | Pure fat (triglycerides) | Contains cocoa powder, flavonoids, and theobromine |
| Flavor | Mild, creamy, subtle chocolate aroma | Strong, rich chocolate taste |
| Use in Food | Chocolate texture and smoothness, cosmetics | Chocolate flavor, color, antioxidant properties |
| Melting Point | 34-38degC (93-100degF) | Does not melt; remains solid |
| Health Benefits | Source of healthy fats | Rich in antioxidants and stimulants |
Introduction to Cocoa Butter and Cocoa Solids
Cocoa butter is the natural fat extracted from cocoa beans, commonly used in chocolate production and skincare products for its smooth texture and moisturizing properties. Cocoa solids consist of the non-fat components of cocoa beans, rich in antioxidants and responsible for the characteristic chocolate flavor and color. Both cocoa butter and cocoa solids are essential ingredients that define the quality and taste of chocolate products.
What is Cocoa Butter?
Cocoa butter is a pale yellow, edible vegetable fat extracted from cocoa beans during the chocolate-making process. It is prized for its smooth texture, moisturizing properties, and ability to stabilize chocolate's flavor and consistency. Your skincare products and confectionery items benefit greatly from cocoa butter's rich antioxidants and natural emollient qualities.
What are Cocoa Solids?
Cocoa solids are the non-fat components of the cocoa bean, containing chocolate flavor, color, and antioxidants. They include cocoa powder and cocoa mass, which influence the bitterness and intensity of chocolate products. High-quality chocolate typically contains a higher percentage of cocoa solids, contributing to its rich taste and health benefits.
Key Differences Between Cocoa Butter and Cocoa Solids
Cocoa butter is the natural fat extracted from cocoa beans, providing smooth texture and rich moisture in chocolate products, while cocoa solids contain the non-fat components responsible for chocolate's deep flavor and color. Cocoa solids include cocoa powder and metal-rich flavonoids, which contribute antioxidants and the characteristic bitterness in chocolate. The key difference lies in cocoa butter offering creamy mouthfeel and melting properties, whereas cocoa solids deliver robust taste and nutritional benefits.
Nutritional Profile Comparison
Cocoa butter is primarily composed of healthy fats, including stearic, oleic, and palmitic acids, providing a rich source of calories and fat-soluble antioxidants such as vitamin E. Cocoa solids contain significant amounts of dietary fiber, protein, and minerals like magnesium, iron, and zinc, along with flavonoids that contribute to antioxidant benefits. While cocoa butter offers energy-dense fats essential for skin and heart health, cocoa solids deliver a broader nutritional profile with micronutrients and bioactive compounds important for metabolic and cardiovascular support.
Health Benefits of Cocoa Butter vs Cocoa Solids
Cocoa butter is rich in healthy fats and antioxidants, promoting skin hydration and cardiovascular health, while cocoa solids contain higher levels of fiber, minerals, and flavonoids that support heart health and improve blood circulation. Your choice between cocoa butter and cocoa solids can impact the nutritional benefits you receive, with cocoa solids offering more pronounced antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Both components contribute to well-being, but cocoa solids provide greater health benefits related to cardiovascular and metabolic function.
Culinary Uses in Chocolate and Baking
Cocoa butter provides a smooth, creamy texture ideal for molding and glazing chocolates, while cocoa solids contribute the intense chocolate flavor and color vital for baked goods like brownies and cakes. Your recipes benefit from cocoa butter's fat content that enhances meltability and mouthfeel, whereas cocoa solids add richness and antioxidant properties. Balancing both components is essential in chocolate confectionery and baking for achieving optimal taste, texture, and appearance.
Cosmetic and Skincare Applications
Cocoa butter, rich in fatty acids and antioxidants, is widely used in cosmetics and skincare for its deep moisturizing and skin-nourishing properties, helping to improve hydration and elasticity. Cocoa solids contain flavonoids and polyphenols that offer antioxidant protection, promoting skin health by combating free radicals and reducing inflammation. Products combining cocoa butter and cocoa solids leverage both moisturizing benefits and antioxidant effects, making them popular in anti-aging creams and soothing skincare formulations.
Impact on Flavor and Texture
Cocoa butter contributes a smooth, creamy texture and mild, sweet flavor, enhancing the melt-in-mouth sensation of chocolate. Cocoa solids provide the rich, intense chocolate taste and a slightly gritty texture, affecting bitterness and complexity. The balance between cocoa butter and cocoa solids determines the final chocolate's flavor depth and mouthfeel.
Choosing the Right Ingredient for Your Needs
Cocoa butter and cocoa solids serve distinct purposes in chocolate production, influencing texture and flavor. Cocoa butter provides smoothness and a creamy mouthfeel, making it ideal for moisturizing skincare or mild-tasting chocolate, while cocoa solids contribute rich, intense chocolate flavor and antioxidant properties. Choosing the right ingredient depends on whether your priority is texture and skin benefits or strong chocolate taste and health advantages.
Cocoa Butter vs Cocoa Solids Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com