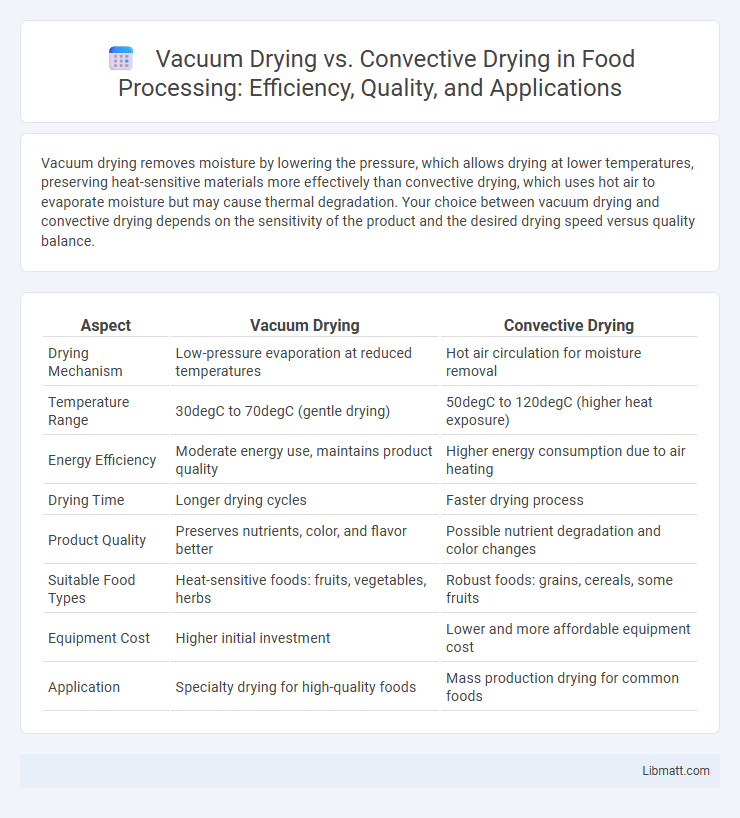
Vacuum drying removes moisture by lowering the pressure, which allows drying at lower temperatures, preserving heat-sensitive materials more effectively than convective drying, which uses hot air to evaporate moisture but may cause thermal degradation. Your choice between vacuum drying and convective drying depends on the sensitivity of the product and the desired drying speed versus quality balance.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Vacuum Drying | Convective Drying |
|---|---|---|
| Drying Mechanism | Low-pressure evaporation at reduced temperatures | Hot air circulation for moisture removal |
| Temperature Range | 30degC to 70degC (gentle drying) | 50degC to 120degC (higher heat exposure) |
| Energy Efficiency | Moderate energy use, maintains product quality | Higher energy consumption due to air heating |
| Drying Time | Longer drying cycles | Faster drying process |
| Product Quality | Preserves nutrients, color, and flavor better | Possible nutrient degradation and color changes |
| Suitable Food Types | Heat-sensitive foods: fruits, vegetables, herbs | Robust foods: grains, cereals, some fruits |
| Equipment Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower and more affordable equipment cost |
| Application | Specialty drying for high-quality foods | Mass production drying for common foods |
Introduction to Vacuum and Convective Drying
Vacuum drying removes moisture by lowering pressure below atmospheric levels, enabling water to evaporate at lower temperatures, which preserves heat-sensitive materials and reduces oxidation risks. Convective drying relies on hot air circulation to evaporate moisture, often consuming more energy and potentially degrading temperature-sensitive products due to higher drying temperatures. Your choice between these methods depends on product sensitivity, drying speed, and energy efficiency requirements.
Principles of Vacuum Drying
Vacuum drying operates by lowering the atmospheric pressure around the material, which reduces the boiling point of water and enables moisture evaporation at significantly lower temperatures compared to convective drying. This method preserves heat-sensitive substances and maintains product quality by minimizing thermal degradation. Your drying process benefits from increased energy efficiency and faster drying times while ensuring better retention of color, flavor, and nutritional value.
Fundamentals of Convective Drying
Convective drying relies on the transfer of heat and mass through hot air circulating around the material, causing moisture to evaporate from the surface and diffuse outward. Air velocity, temperature, and humidity are critical parameters influencing the drying rate and efficiency in this process. Your choice between vacuum drying and convective drying depends on the sensitivity of the product to heat and the desired drying speed.
Comparative Energy Efficiency
Vacuum drying consumes less energy compared to convective drying due to lower drying temperatures and reduced evaporation times, preserving sensitive materials more efficiently. Convective drying requires higher temperatures and continuous air circulation, leading to increased energy usage and possible thermal degradation. Evaluating your process needs, vacuum drying often offers superior energy efficiency for temperature-sensitive products, reducing operational costs significantly.
Impact on Product Quality
Vacuum drying preserves sensitive nutrients and bioactive compounds better than convective drying by operating at lower temperatures and reduced oxygen levels, which minimizes oxidative damage and thermal degradation. Convective drying often results in greater nutrient loss, color changes, and texture damage due to the higher drying temperatures and prolonged exposure to air. Therefore, vacuum drying is preferred for high-value products like pharmaceuticals, heat-sensitive foods, and botanicals where maintaining product quality is critical.
Drying Time and Process Speed
Vacuum drying significantly reduces drying time by lowering the boiling point of moisture, enabling faster evaporation at lower temperatures compared to convective drying. This accelerated process speed preserves product quality by minimizing heat exposure, making vacuum drying ideal for heat-sensitive materials. Your drying operations can benefit from enhanced efficiency and shorter cycle times when choosing vacuum drying over conventional convective methods.
Applications in Various Industries
Vacuum drying is widely utilized in pharmaceutical and food industries for heat-sensitive products, preserving active compounds and nutrients through low-temperature drying. Convective drying remains prevalent in agriculture and textile sectors due to its efficiency in removing moisture from bulk materials using hot air. Both methods serve diverse industrial applications, with vacuum drying preferred for delicate materials and convective drying favored for cost-effective mass processing.
Cost Analysis and Investment
Vacuum drying typically involves higher initial investment costs due to specialized equipment and energy requirements, but it offers energy efficiency by operating at lower temperatures and reduced drying times. Convective drying systems have lower upfront costs and simpler technology but incur higher operational expenses from prolonged heating and greater energy consumption. Evaluating total cost of ownership highlights vacuum drying's potential for cost savings in industrial applications with sensitive materials despite the steeper capital expenditure.
Environmental Considerations
Vacuum drying consumes less energy compared to convective drying due to lower operating temperatures and reduced drying times, leading to a smaller carbon footprint. Convective drying requires continuous airflow and higher temperatures, resulting in greater energy consumption and increased greenhouse gas emissions. The eco-efficiency of vacuum drying makes it a preferred choice for sustainable industrial practices.
Choosing the Right Drying Method
Vacuum drying preserves heat-sensitive materials by operating at lower temperatures and reduced pressure, minimizing thermal degradation and oxidation. Convective drying is more suitable for heat-stable products requiring faster drying rates and is often more cost-effective for large-scale applications. Assessing product sensitivity, drying time, energy consumption, and quality retention is crucial in selecting the optimal drying technique.
vacuum drying vs convective drying Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com