Anti-reflective glass significantly reduces glare and reflections compared to standard glass, enhancing visibility and clarity in windows, displays, and eyewear. This improvement benefits your visual experience by allowing more light transmission and minimizing distractions caused by surface reflections.
Table of Comparison
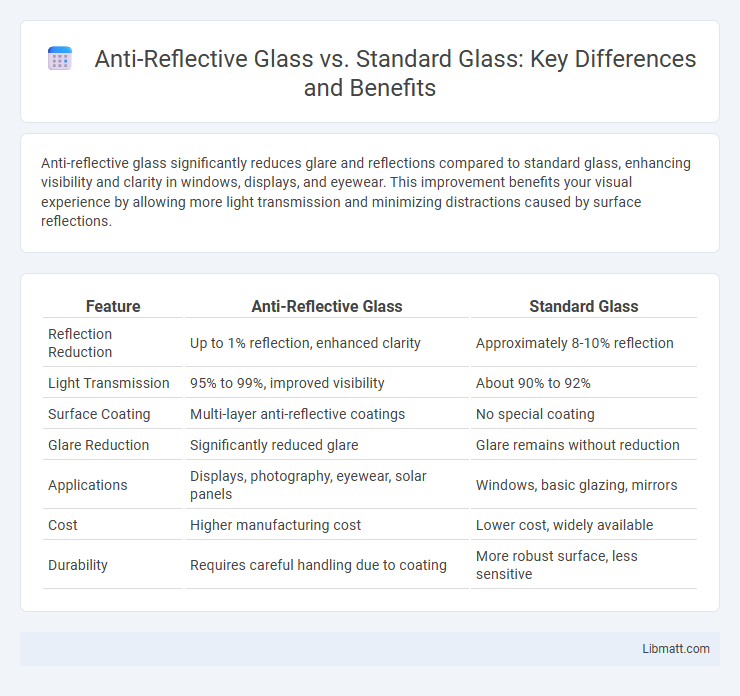
| Feature | Anti-Reflective Glass | Standard Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Reflection Reduction | Up to 1% reflection, enhanced clarity | Approximately 8-10% reflection |
| Light Transmission | 95% to 99%, improved visibility | About 90% to 92% |
| Surface Coating | Multi-layer anti-reflective coatings | No special coating |
| Glare Reduction | Significantly reduced glare | Glare remains without reduction |
| Applications | Displays, photography, eyewear, solar panels | Windows, basic glazing, mirrors |
| Cost | Higher manufacturing cost | Lower cost, widely available |
| Durability | Requires careful handling due to coating | More robust surface, less sensitive |
Introduction to Anti-Reflective Glass vs Standard Glass
Anti-reflective glass features a special coating that significantly reduces glare and reflections compared to standard glass, enhancing visibility and image clarity. This technology is commonly used in displays, camera lenses, and solar panels to improve light transmission and reduce eye strain. Understanding the difference between anti-reflective and standard glass helps you choose the right material for your needs, ensuring optimal performance in various lighting conditions.
What is Anti-Reflective Glass?
Anti-reflective glass features a special coating designed to reduce glare and minimize reflections, enhancing visual clarity and light transmission compared to standard glass. This coating improves your viewing experience by allowing more natural light to pass through, making it ideal for displays, eyewear, and solar panels. Unlike standard glass, anti-reflective glass significantly reduces eye strain and improves image quality in bright environments.
Features of Standard Glass
Standard glass typically features a smooth, transparent surface that allows natural light to pass through but often reflects a significant amount of glare. It lacks coatings that reduce reflections, which can cause visual discomfort and decreased clarity, especially in bright environments. Your choice of standard glass is suitable for applications where cost efficiency and basic light transmission are priorities over enhanced optical performance.
Comparing Light Transmission and Clarity
Anti-reflective glass significantly enhances light transmission by reducing surface reflections to less than 1%, compared to standard glass, which typically reflects around 8-10% of incoming light, resulting in clearer and more vivid images. Your viewing experience improves with anti-reflective glass, as it minimizes glare and maximizes clarity, making details more visible and colors more accurate in both indoor and outdoor conditions. This superior optical performance benefits applications ranging from eyeglasses to camera lenses and display screens, where precision and visibility are critical.
Reflection and Glare: Key Differences
Anti-reflective glass significantly reduces reflection and glare compared to standard glass by using specialized coatings that enhance light transmission. This results in clearer visibility and reduced eye strain, making it ideal for screens, windows, and eyewear. For your spaces or devices, choosing anti-reflective glass improves visual comfort and clarity by minimizing distracting reflections.
Applications of Anti-Reflective Glass
Anti-reflective glass is extensively used in applications requiring enhanced visibility and reduced glare, such as smartphone screens, camera lenses, and display panels. Its ability to minimize light reflection makes it ideal for solar panels, improving energy efficiency by allowing more light to pass through. Your electronic devices, eyewear, and architectural windows benefit from anti-reflective glass by delivering clearer images and heightened comfort in bright environments.
Cost Comparison: Anti-Reflective vs Standard Glass
Anti-reflective glass typically costs 20-50% more than standard glass due to advanced coating technologies that reduce glare and enhance clarity. The higher initial investment in anti-reflective glass is balanced by long-term benefits such as improved visibility and reduced eye strain, making it valuable for applications in displays, eyewear, and solar panels. Standard glass remains a budget-friendly option for general use where glare reduction is not critical.
Durability and Maintenance
Anti-reflective glass offers enhanced durability through specialized coatings that resist scratches, dust, and smudges better than standard glass, reducing the need for frequent cleaning and maintenance. Its surface treatment minimizes glare and reflections, maintaining clarity over time without deteriorating under UV exposure or harsh weather conditions. Choosing anti-reflective glass for your windows or displays ensures longer-lasting performance with less effort required for upkeep compared to conventional glass options.
Ideal Uses for Each Glass Type
Anti-reflective glass is ideal for display cases, camera lenses, and high-end windows where minimizing glare and enhancing visual clarity is crucial. Standard glass suits general construction, residential windows, and basic framing where cost-effectiveness and durability are prioritized over optical performance. Choosing between these glass types depends on whether visual transparency or budget-friendly protection is the primary requirement.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Needs
Anti-reflective glass significantly reduces glare and enhances visual clarity by minimizing surface reflections, making it ideal for display cases, eyewear, and solar panels. Standard glass is more cost-effective and suitable for general applications where glare reduction is not a priority. Selecting the right glass depends on balancing budget considerations with the need for improved visibility and light transmission.
Anti-reflective glass vs standard glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com