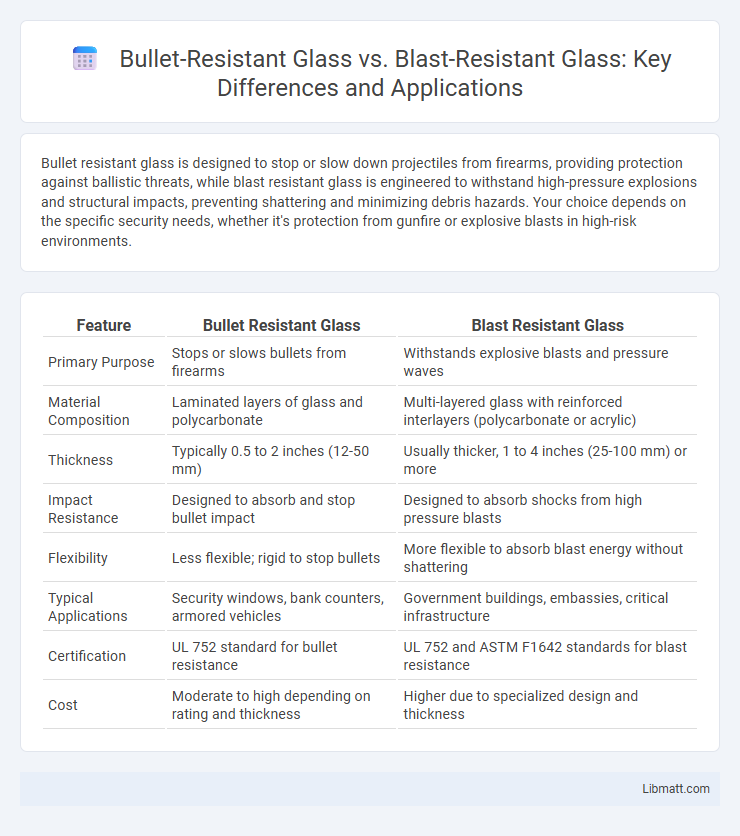
Bullet resistant glass is designed to stop or slow down projectiles from firearms, providing protection against ballistic threats, while blast resistant glass is engineered to withstand high-pressure explosions and structural impacts, preventing shattering and minimizing debris hazards. Your choice depends on the specific security needs, whether it's protection from gunfire or explosive blasts in high-risk environments.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bullet Resistant Glass | Blast Resistant Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Stops or slows bullets from firearms | Withstands explosive blasts and pressure waves |
| Material Composition | Laminated layers of glass and polycarbonate | Multi-layered glass with reinforced interlayers (polycarbonate or acrylic) |
| Thickness | Typically 0.5 to 2 inches (12-50 mm) | Usually thicker, 1 to 4 inches (25-100 mm) or more |
| Impact Resistance | Designed to absorb and stop bullet impact | Designed to absorb shocks from high pressure blasts |
| Flexibility | Less flexible; rigid to stop bullets | More flexible to absorb blast energy without shattering |
| Typical Applications | Security windows, bank counters, armored vehicles | Government buildings, embassies, critical infrastructure |
| Certification | UL 752 standard for bullet resistance | UL 752 and ASTM F1642 standards for blast resistance |
| Cost | Moderate to high depending on rating and thickness | Higher due to specialized design and thickness |
Introduction to Bullet Resistant and Blast Resistant Glass
Bullet resistant glass is engineered to withstand high-velocity projectiles, providing protection against firearms and preventing penetration from bullets. Blast resistant glass is designed to absorb and dissipate energy from explosions, minimizing the risk of shattering due to pressure waves and flying debris. Both types of glass utilize layered materials such as polycarbonate and laminated glass, but their core functions differ based on impact resistance versus blast absorption.
Key Differences Between Bullet Resistant and Blast Resistant Glass
Bullet resistant glass is specifically engineered to withstand firearm projectiles, utilizing multiple laminated layers to absorb and disperse bullet energy, whereas blast resistant glass is designed to endure high-pressure shock waves from explosions, often incorporating a thicker, more flexible interlayer to prevent shattering and debris projection. The primary distinction lies in their performance criteria: bullet resistant glass prioritizes stopping bullets of various calibers, while blast resistant glass focuses on resisting overpressure and containing hazardous fragments during blasts. Material composition and testing standards, such as UL 752 for bullet resistance and ASTM F1642 for blast resistance, reflect these divergent protective capabilities.
Materials and Construction Techniques
Bullet resistant glass typically consists of multiple layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate materials designed to absorb and disperse the energy of a high-velocity projectile, while blast resistant glass incorporates laminated glass combined with thicker interlayers of polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) to withstand extreme pressure waves caused by explosions. Bullet resistant glass emphasizes density and hardness to stop bullets, using heat-treated or chemically strengthened glass layers, whereas blast resistant glass prioritizes flexibility and structural integrity to prevent shattering and contain debris under dynamic loading conditions. Construction techniques for bullet resistant glass focus on optimizing thickness and layering for ballistic performance, while blast resistant glass construction involves engineered assembly to ensure window frames and glass interlayers work together to absorb and redistribute blast forces.
Levels of Protection: Bullet vs. Blast Resistance
Bullet resistant glass is engineered to withstand high-velocity projectiles by absorbing and dispersing energy to prevent penetration, typically rated using standards such as UL 752 or NIJ levels based on specific bullet calibers and velocities. Blast resistant glass, on the other hand, is designed to endure shock waves and pressure from explosions, meeting blast performance criteria outlined in standards like ASTM F1642 or GSA standards, focusing on pressure resistance and post-blast integrity. While bullet resistant glass prioritizes stopping ballistic threats, blast resistant glass emphasizes structural resilience against explosive forces, often incorporating laminates and interlayers optimized to resist fragmentation and maintain barrier function after blasts.
Testing Standards and Certification
Bullet resistant glass undergoes rigorous testing following standards such as UL 752 and NIJ 0108.01 to certify its ability to withstand specific firearm projectiles, ensuring reliable protection against ballistic threats. Blast resistant glass is tested under ASTM F1642 and STC (Sound Transmission Class) ratings, certifying its performance against high-pressure explosions and shockwave impacts, safeguarding your environment in hazardous situations.
Applications in Security and Safety
Bullet resistant glass is primarily utilized in security applications such as bank teller windows, armored vehicles, and government buildings to protect against firearm attacks by stopping or slowing bullet penetration. Blast resistant glass is engineered for safety in environments exposed to explosive threats, including military facilities, embassies, and critical infrastructure, designed to withstand pressure waves and flying debris from blasts. Both types enhance protection but serve distinct roles where ballistic resistance focuses on preventing penetration and blast resistance mitigates impact from explosions.
Performance in Real-World Scenarios
Bullet resistant glass is engineered to withstand high-velocity projectiles, providing reliable protection against firearms in urban and combat environments. Blast resistant glass is designed to absorb and dissipate energy from explosive blasts, preventing shattering and protecting occupants from shockwaves and flying debris. In real-world scenarios, bullet resistant glass excels in active shooter situations, while blast resistant glass is crucial for buildings exposed to terrorist attacks or industrial explosions.
Cost Considerations and Budget Impact
Bullet resistant glass generally incurs higher initial costs due to specialized materials and rigorous testing standards, often ranging from $50 to $100 per square foot depending on threat levels. Blast resistant glass, while also expensive, can vary more widely in price based on factors like laminate thickness and frame reinforcement, sometimes exceeding $150 per square foot for high-performance applications. Evaluating your specific security needs against budget constraints helps determine the most cost-effective solution for protecting your property.
Maintenance and Longevity
Bullet resistant glass requires regular inspections to detect chips or cracks that can compromise its integrity, with maintenance focused on sealing and frame condition to prevent moisture infiltration. Blast resistant glass, designed to withstand high-pressure waves, demands thorough upkeep of both the glass layers and interlayer materials to maintain flexibility and resilience over time. Both types benefit from professional assessments to ensure durability and extended service life, but blast resistant glass often involves more complex maintenance procedures due to its multilayer construction.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
Bullet resistant glass is designed to stop or slow down projectiles from firearms, offering protection against gunfire, while blast resistant glass is engineered to withstand explosive forces and prevent shattering during blasts. Understanding the specific threats, such as ballistic attacks or blast pressure waves, helps you choose the right solution tailored to your security requirements. Properly assessing your environment ensures the selected glass provides optimal safety without compromising durability or visibility.
Bullet resistant glass vs blast resistant glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com