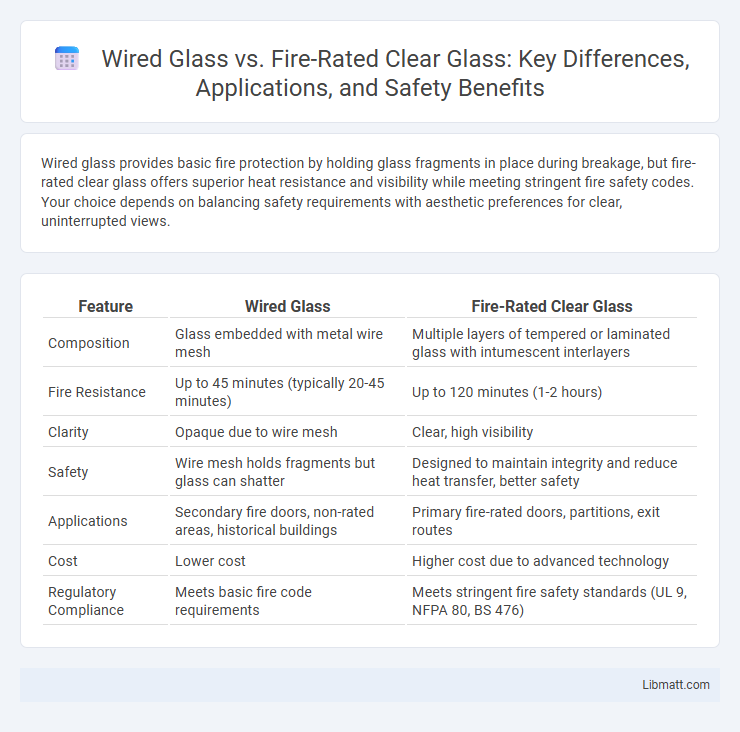
Wired glass provides basic fire protection by holding glass fragments in place during breakage, but fire-rated clear glass offers superior heat resistance and visibility while meeting stringent fire safety codes. Your choice depends on balancing safety requirements with aesthetic preferences for clear, uninterrupted views.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Wired Glass | Fire-Rated Clear Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Glass embedded with metal wire mesh | Multiple layers of tempered or laminated glass with intumescent interlayers |
| Fire Resistance | Up to 45 minutes (typically 20-45 minutes) | Up to 120 minutes (1-2 hours) |
| Clarity | Opaque due to wire mesh | Clear, high visibility |
| Safety | Wire mesh holds fragments but glass can shatter | Designed to maintain integrity and reduce heat transfer, better safety |
| Applications | Secondary fire doors, non-rated areas, historical buildings | Primary fire-rated doors, partitions, exit routes |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to advanced technology |
| Regulatory Compliance | Meets basic fire code requirements | Meets stringent fire safety standards (UL 9, NFPA 80, BS 476) |
Introduction to Wired Glass and Fire-Rated Clear Glass
Wired glass features an embedded metal mesh designed to hold glass shards in place during breakage, enhancing safety and fire resistance commonly used in industrial and institutional settings. Fire-rated clear glass, typically made with tempered or laminated layers, combines transparency with superior fire protection, maintaining visibility while meeting strict fire code requirements. Your choice between wired glass and fire-rated clear glass depends on balancing safety standards, visibility needs, and aesthetic preferences for fire-resistant glazing solutions.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Wired glass consists of a layer of glass embedded with a metal wire mesh, produced through heat strengthening or tempering to maintain the mesh's integrity during breakage. Fire-rated clear glass is typically engineered from multiple layers of glass and intumescent interlayers or ceramic materials, laminated and heat-treated to provide extended fire resistance and maintain visibility. Manufacturing fire-rated clear glass involves complex processes like heat soaking and lamination to ensure it withstands high temperatures without compromising structural clarity.
Fire Resistance and Safety Ratings
Wired glass offers fire resistance by preventing the passage of flames and smoke for up to 45 minutes, meeting fire-rated safety standards primarily through its embedded wire mesh, which helps maintain structural integrity under heat. Fire-rated clear glass, often composed of multiple layers of tempered or ceramic glass, provides superior fire resistance, typically rated for 60 to 120 minutes, and offers enhanced visibility without compromising safety. Your choice between wired glass and fire-rated clear glass should consider the required fire resistance time and safety ratings to ensure compliance with building codes and optimal protection.
Impact Resistance and Breaking Behavior
Wired glass offers moderate impact resistance due to its embedded wire mesh, which helps hold fragments together upon breaking but tends to shatter in larger, sharp pieces. Fire-rated clear glass, often made from tempered or laminated layers, provides superior impact resistance by maintaining integrity under force and breaking into less hazardous, smaller granules. The breaking behavior of wired glass poses higher safety risks, while fire-rated clear glass is engineered for safer fracture patterns and enhanced protection during fire exposure.
Visual Clarity and Aesthetics
Fire-rated clear glass offers superior visual clarity and a modern aesthetic compared to wired glass, which features embedded metal mesh that can obstruct views and create a textured appearance. The transparent nature of fire-rated clear glass enhances natural light transmission, maintaining open and polished interiors without compromising safety. Your choice of fire-rated clear glass supports both fire protection and a sleek, unobtrusive look in architectural designs.
Applications in Building Design
Wired glass is commonly used in corridors, stairwells, and fire doors to provide fire resistance while maintaining visibility, making it ideal for safety-critical partitions in commercial buildings. Fire-rated clear glass, including ceramic or tempered options, offers higher fire performance and thermal insulation, suited for areas requiring stringent fire control like elevator shafts, external windows, and lobby enclosures. Selecting between wired glass and fire-rated clear glass depends on your building design's specific fire safety requirements and aesthetic goals.
Building Codes and Compliance
Wired glass meets many traditional building codes for fire resistance due to its embedded wire mesh, which provides structural integrity during fires, but it often falls short in areas requiring full egress compliance or impact safety standards. Fire-rated clear glass, such as ceramic or multilayer laminated glass, complies with stricter modern building codes by offering both fire resistance and safety glazing certifications, ensuring better compliance with both fire and life-safety regulations. When selecting materials, your choice should align with specific local building codes and compliance requirements to ensure optimal fire protection and occupant safety.
Cost Comparison and Budget Considerations
Wired glass generally offers a lower upfront cost compared to fire-rated clear glass, making it an economical choice for projects with tight budgets. Fire-rated clear glass, while more expensive, provides enhanced aesthetics and superior fire protection, often justifying the investment in safety-sensitive areas. You should weigh initial expenses against long-term benefits when deciding which glass type suits your budget and project requirements.
Installation Methods and Maintenance
Wired glass typically requires precise fitting within steel frames using fire-resistant glazing compound or sealants to ensure fire integrity, while fire-rated clear glass is installed using metal framing systems with specialized gaskets and fire-rated glazing tapes for enhanced sealing. Maintenance of wired glass involves regular inspections for surface cracks and wire mesh corrosion that can compromise fire resistance, whereas fire-rated clear glass necessitates cleaning with non-abrasive materials and periodic checks for framing and sealant integrity to maintain its fire-protective properties. Both glass types demand compliance with building codes and certified fire ratings during installation and upkeep to ensure optimal fire safety performance.
Choosing the Right Fire-Rated Glass for Your Project
Choosing the right fire-rated glass involves understanding the differences between wired glass and fire-rated clear glass regarding safety and visibility. Wired glass provides basic fire resistance and impact protection, often used in industrial settings, but limits visual clarity due to embedded wire mesh. Fire-rated clear glass offers superior fire protection with enhanced transparency, making it ideal for commercial spaces requiring both safety compliance and aesthetic appeal.
Wired glass vs fire-rated clear glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com