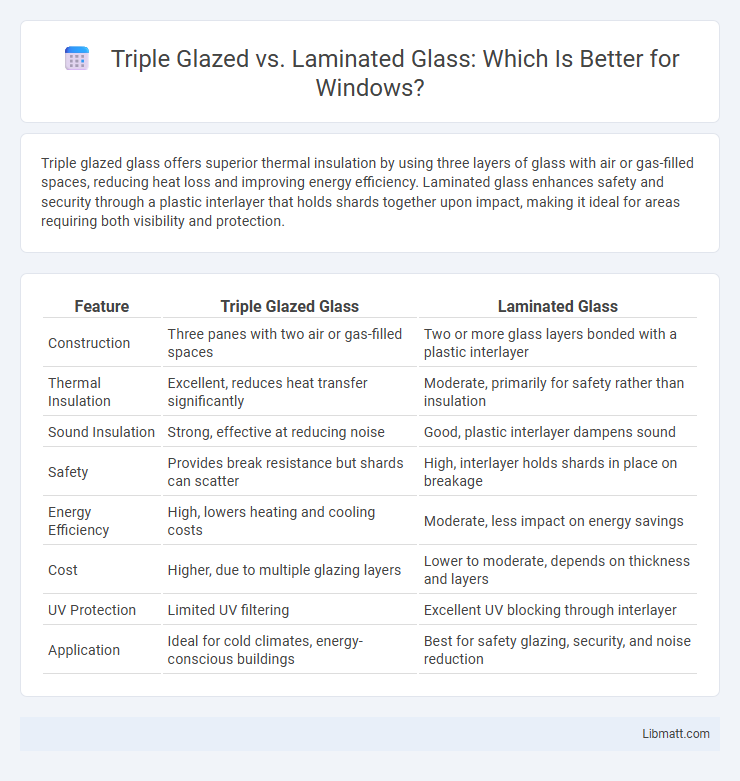
Triple glazed glass offers superior thermal insulation by using three layers of glass with air or gas-filled spaces, reducing heat loss and improving energy efficiency. Laminated glass enhances safety and security through a plastic interlayer that holds shards together upon impact, making it ideal for areas requiring both visibility and protection.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Triple Glazed Glass | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Construction | Three panes with two air or gas-filled spaces | Two or more glass layers bonded with a plastic interlayer |
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent, reduces heat transfer significantly | Moderate, primarily for safety rather than insulation |
| Sound Insulation | Strong, effective at reducing noise | Good, plastic interlayer dampens sound |
| Safety | Provides break resistance but shards can scatter | High, interlayer holds shards in place on breakage |
| Energy Efficiency | High, lowers heating and cooling costs | Moderate, less impact on energy savings |
| Cost | Higher, due to multiple glazing layers | Lower to moderate, depends on thickness and layers |
| UV Protection | Limited UV filtering | Excellent UV blocking through interlayer |
| Application | Ideal for cold climates, energy-conscious buildings | Best for safety glazing, security, and noise reduction |
Introduction to Triple Glazed and Laminated Glass
Triple glazed glass consists of three layers of glass separated by air or gas-filled spaces, offering superior thermal insulation and energy efficiency compared to single or double glazing. Laminated glass is made by bonding two or more layers of glass with an interlayer, enhancing safety, sound insulation, and impact resistance. Both types are commonly used in windows and facades to improve building performance but serve distinct purposes depending on thermal, acoustic, and security requirements.
How Triple Glazing Works
Triple glazing consists of three layers of glass separated by air or inert gas-filled spaces, enhancing thermal insulation and soundproofing compared to laminated glass which primarily provides safety and security through layers bonded with a plastic interlayer. The design of triple glazing reduces heat transfer by trapping insulating gas, improving energy efficiency and reducing condensation. This multi-pane system significantly improves indoor temperature regulation, making it ideal for colder climates.
Understanding Laminated Glass Composition
Laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded together with an interlayer, typically made of polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), which enhances safety and sound insulation. This composition ensures that when the glass breaks, shards adhere to the interlayer, reducing the risk of injury and improving security. Understanding this structure helps you choose the right glazing for impact resistance and noise reduction needs compared to triple glazed units.
Thermal Insulation: Triple Glazed vs Laminated Glass
Triple glazed glass offers superior thermal insulation compared to laminated glass due to its three panes separated by gas-filled spaces that significantly reduce heat transfer. Laminated glass primarily provides safety and sound insulation benefits but does not match the thermal performance of triple glazing. Energy efficiency ratings demonstrate that triple glazed units can reduce heat loss by up to 50% more than laminated glass windows, making them ideal for colder climates.
Soundproofing Capabilities Compared
Triple glazed glass offers superior soundproofing capabilities compared to laminated glass due to its three layers of glass separated by air or gas-filled spaces, which significantly reduce noise transmission. Laminated glass, while effective at dampening sound thanks to its interlayer that absorbs vibrations, generally cannot match the acoustic insulation provided by the additional layers and air gaps in triple glazing. For optimal soundproofing in noisy environments, triple glazed glass is the preferred choice due to its enhanced multi-layer structure reducing airborne noise more efficiently.
Safety and Security Differences
Triple glazed glass offers enhanced safety through its multiple layers that improve impact resistance and thermal insulation, reducing the risk of breakage under stress. Laminated glass consists of a plastic interlayer between two glass sheets, providing superior security by holding shards together upon impact, which prevents shattering and intrusion. While triple glazing maximizes energy efficiency and noise reduction, laminated glass specializes in safeguarding against forced entry and enhancing occupant protection.
Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
Triple glazed glass offers superior energy efficiency by providing enhanced insulation through three layers of glass, significantly reducing heat loss compared to laminated glass, which primarily focuses on safety rather than thermal performance. This improved insulation in triple glazing leads to lower heating and cooling costs, offering substantial energy savings over time despite a higher initial investment. Your choice of triple glazed windows can result in long-term cost savings by minimizing energy consumption and improving indoor temperature regulation.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Triple glazed glass offers superior durability due to its multiple layers of glass and insulating gas, providing enhanced resistance to thermal stress and impact compared to laminated glass. Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer, which enhances safety by holding shards together but may be more susceptible to delamination and surface damage over time. Maintenance for triple glazed windows typically involves ensuring seals remain intact to prevent gas leakage, whereas laminated glass requires careful inspection for interlayer integrity and potential edge damage to maintain its protective properties.
Aesthetic and Design Considerations
Triple glazed glass offers superior thermal performance with slimmer profile options, allowing for sleek, modern window designs that maximize natural light while maintaining energy efficiency. Laminated glass enhances safety and sound insulation without compromising clarity, available in various tints and textures that elevate your interior aesthetics through customizable design elements. Both materials provide distinct visual and functional benefits, enabling tailored architectural solutions to meet your specific style and performance needs.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Project
Triple glazed glass offers superior thermal insulation and noise reduction, making it ideal for energy-efficient buildings and soundproofing needs. Laminated glass enhances safety and security by holding shards together upon impact, suitable for high-traffic or hurricane-prone areas. Consider your project's priorities for energy efficiency, safety, and noise control to determine whether triple glazing or laminated glass best meets your requirements.
triple glazed vs laminated glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com