Safety glass and tempered glass both provide enhanced protection compared to regular glass, but safety glass typically consists of laminated layers that hold shards together upon impact, reducing injury risk. Tempered glass undergoes a heat treatment process that increases its strength and causes it to shatter into small, less harmful pieces, making it ideal for high-stress applications like car windows or shower doors.
Table of Comparison
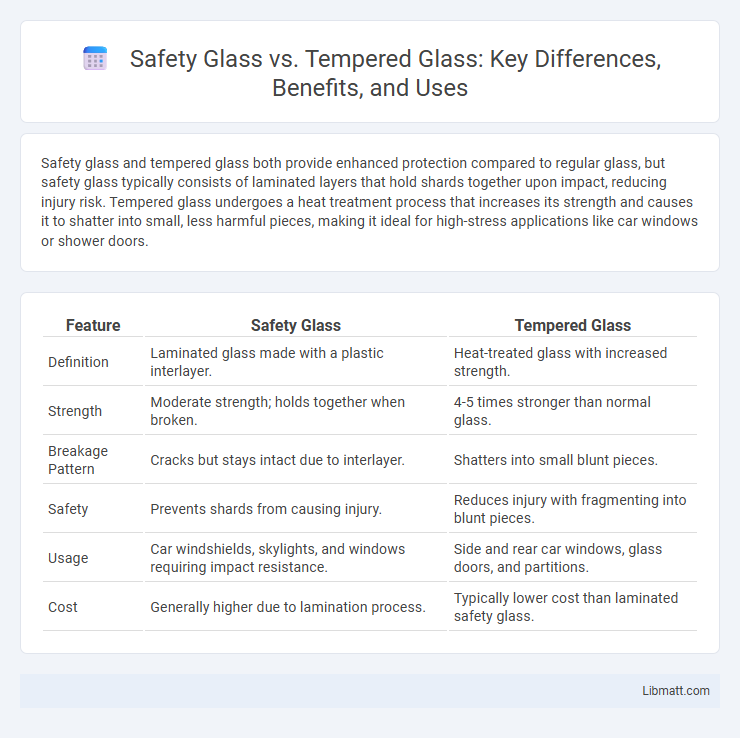
| Feature | Safety Glass | Tempered Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Laminated glass made with a plastic interlayer. | Heat-treated glass with increased strength. |
| Strength | Moderate strength; holds together when broken. | 4-5 times stronger than normal glass. |
| Breakage Pattern | Cracks but stays intact due to interlayer. | Shatters into small blunt pieces. |
| Safety | Prevents shards from causing injury. | Reduces injury with fragmenting into blunt pieces. |
| Usage | Car windshields, skylights, and windows requiring impact resistance. | Side and rear car windows, glass doors, and partitions. |
| Cost | Generally higher due to lamination process. | Typically lower cost than laminated safety glass. |
Introduction to Safety Glass and Tempered Glass
Safety glass and tempered glass are essential materials designed to enhance protection and reduce injury risks in various applications. Safety glass typically includes laminated glass, consisting of two or more glass layers bonded with a plastic interlayer that holds shards together when broken. Tempered glass undergoes a thermal or chemical treatment to increase strength, breaking into small, blunt pieces rather than sharp shards, making it ideal for environments requiring durability and impact resistance.
What is Safety Glass?
Safety glass is a type of glass designed to reduce the risk of injury upon impact by either breaking into small, blunt pieces or holding together with an interlayer. Commonly used in automotive windshields, building windows, and glass doors, safety glass includes laminated glass, which combines two or more layers of glass with a plastic interlayer, and tempered glass, which is heat-treated for added strength. Its primary purpose is to enhance protection and minimize hazards from sharp shards in accidents or breakage scenarios.
What is Tempered Glass?
Tempered glass is a type of safety glass that undergoes a controlled thermal or chemical treatment process to increase its strength compared to standard glass. This heat treatment creates compressive stresses on the surface and tensile stresses inside, making it up to five times stronger and more resistant to impact and thermal stress. Upon breaking, tempered glass shatters into small, blunt granules rather than sharp shards, significantly reducing the risk of injury.
Key Differences Between Safety Glass and Tempered Glass
Safety glass generally refers to glass designed to reduce injury upon breakage and includes laminated and tempered types, while tempered glass is a specific form of safety glass treated with heat or chemicals to increase strength and shatter into small, blunt pieces. Laminated safety glass consists of two or more layers bonded with an interlayer that holds shards together, providing enhanced protection compared to tempered glass. Your choice between these types depends on the application requirements for strength, impact resistance, and post-breakage safety features.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Tempered glass boasts superior strength compared to regular safety glass, as it undergoes heat treatment that increases its resistance to impact and thermal stress. Safety glass, typically laminated, offers enhanced durability through a plastic interlayer that prevents shattering upon impact, providing additional protection against injury. When choosing between them, your decision should consider whether impact resistance or breakage containment aligns better with your safety needs.
Applications of Safety Glass vs. Tempered Glass
Safety glass, including laminated glass, is widely used in automotive windshields and building windows for its shatter-resistant properties that hold together upon impact, enhancing occupant protection. Tempered glass, known for its high strength and thermal resistance, is commonly applied in side and rear vehicle windows, shower doors, and glass doors where breakage results in small, less harmful fragments. These distinct applications reflect each glass type's unique safety benefits and performance requirements in various architectural and automotive contexts.
Safety Features and Breakage Patterns
Safety glass, such as laminated glass, consists of multiple layers with an interlayer that holds shards in place upon impact, preventing dangerous splinters and enhancing occupant protection. Tempered glass undergoes rapid heating and cooling to increase strength, breaking into small, blunt granules rather than sharp shards to reduce injury risk. These distinct breakage patterns make laminated safety glass ideal for windshields, while tempered glass is commonly used in side windows and doors where controlled shattering is preferred.
Cost Comparison: Safety Glass vs. Tempered Glass
Tempered glass typically costs more than standard safety glass due to its heat treatment process, which enhances strength and durability. Safety glass, such as laminated glass, offers excellent impact resistance at a lower price point but may not match tempered glass's ability to shatter into small, less dangerous pieces. Your choice between safety glass and tempered glass should consider both budget constraints and specific safety requirements for the application.
Industry Standards and Regulations
Safety glass complies with strict industry standards such as ASTM C1036 and EN 12150, which specify criteria for impact resistance, thickness, and thermal stability. Tempered glass must meet regulations including ANSI Z97.1 and CPSC 16 CFR 1201, ensuring it breaks into small, blunt pieces to minimize injury risk. Both safety and tempered glass are rigorously tested to adhere to building codes and regulatory frameworks that govern automotive, architectural, and consumer product applications.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Needs
Safety glass, including tempered glass, is designed to reduce injury risks by breaking into small, less harmful pieces, making it ideal for environments with high safety requirements. Tempered glass undergoes a heat-treatment process that enhances strength and heat resistance, making it suitable for applications requiring durability and impact resistance, such as car windows and shower doors. When choosing the right glass for your needs, consider the level of safety, strength, and specific usage conditions to ensure optimal protection and performance.
safety glass vs tempered glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com