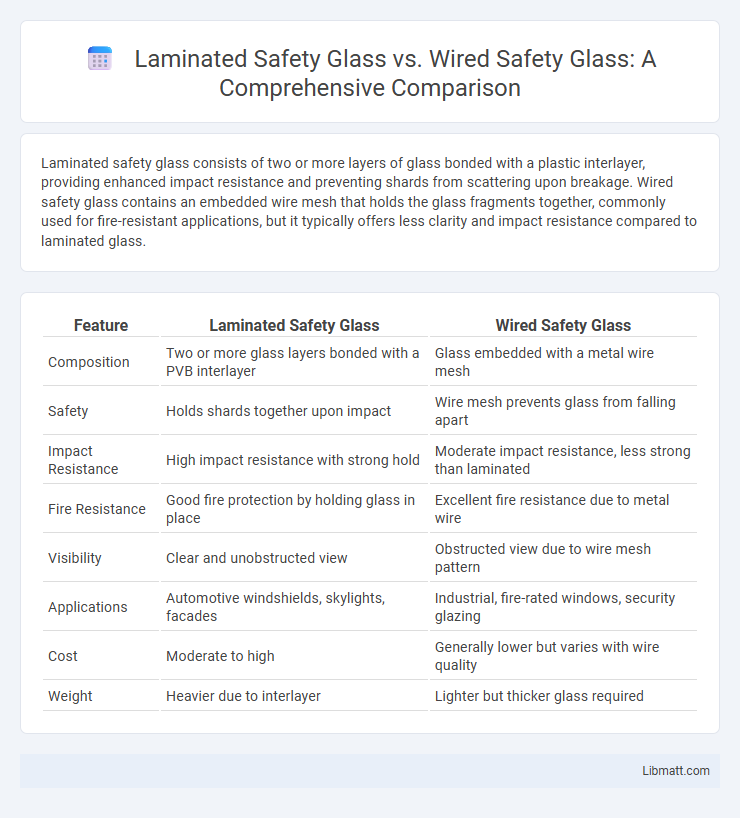
Laminated safety glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded with a plastic interlayer, providing enhanced impact resistance and preventing shards from scattering upon breakage. Wired safety glass contains an embedded wire mesh that holds the glass fragments together, commonly used for fire-resistant applications, but it typically offers less clarity and impact resistance compared to laminated glass.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Laminated Safety Glass | Wired Safety Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Two or more glass layers bonded with a PVB interlayer | Glass embedded with a metal wire mesh |
| Safety | Holds shards together upon impact | Wire mesh prevents glass from falling apart |
| Impact Resistance | High impact resistance with strong hold | Moderate impact resistance, less strong than laminated |
| Fire Resistance | Good fire protection by holding glass in place | Excellent fire resistance due to metal wire |
| Visibility | Clear and unobstructed view | Obstructed view due to wire mesh pattern |
| Applications | Automotive windshields, skylights, facades | Industrial, fire-rated windows, security glazing |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Generally lower but varies with wire quality |
| Weight | Heavier due to interlayer | Lighter but thicker glass required |
Introduction to Safety Glass Types
Laminated safety glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer, offering enhanced impact resistance and preventing shattering upon breakage. Wired safety glass incorporates a metal mesh embedded within the glass to hold fragments in place during breakage, commonly used for fire-resistant applications. Understanding these distinctions helps you choose the right safety glass type based on durability and safety requirements.
What is Laminated Safety Glass?
Laminated safety glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded together with an interlayer, usually made of polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), which holds the glass layers in place upon impact. This construction enhances shatter resistance, reducing the risk of injury by preventing the glass from breaking into sharp, dangerous shards. Laminated safety glass is commonly used in automotive windshields, architectural applications, and security glazing due to its superior strength and safety performance compared to wired safety glass.
What is Wired Safety Glass?
Wired safety glass consists of a layer of wire mesh embedded within the glass, designed to hold the shards together if the glass breaks, enhancing fire resistance and reducing injury risk. Unlike laminated safety glass, which uses interlayers to absorb impact, wired glass primarily offers structural integrity during fires by preventing the spread of flames and smoke. You should consider wired safety glass in environments where fire safety and maintaining a barrier during heat exposure are critical.
Key Differences Between Laminated and Wired Safety Glass
Laminated safety glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer, providing superior impact resistance and preventing shattering by holding fragments together, while wired safety glass embeds a metal mesh within the glass to maintain structural integrity during breakage. You benefit from laminated safety glass in applications requiring enhanced security and sound insulation, whereas wired safety glass is often favored for fire-resistant windows due to its ability to contain heat and flames. The key differences lie in their construction, safety performance, and typical use cases, with laminated glass excelling in durability and wired glass offering better fire containment.
Impact Resistance Comparison
Laminated safety glass demonstrates superior impact resistance due to its interlayer, which holds the glass together upon breakage, reducing the risk of injury and maintaining structural integrity. Wired safety glass, while offering enhanced fire resistance and preventing large shards from falling, generally exhibits lower impact strength because the embedded wire mesh can create weak points. In critical safety applications, laminated glass is preferred for its ability to absorb and withstand high-impact forces more effectively than wired safety glass.
Fire and Heat Resistance: Wired vs Laminated
Laminated safety glass offers superior fire and heat resistance due to its construction with multiple layers of glass bonded by a tough interlayer, which helps maintain structural integrity under high temperatures and prevents shattering. Wired safety glass contains embedded wire mesh that provides some fire resistance by holding the glass fragments in place, but it tends to crack and weaken faster than laminated glass when exposed to intense heat. For applications requiring enhanced fire performance, laminated safety glass is preferred because it combines impact resistance with better thermal stability.
Security and Intrusion Protection
Laminated safety glass offers superior security and intrusion protection by holding shattered pieces together with a durable interlayer, preventing easy break-ins. Wired safety glass contains embedded wire mesh, providing some resistance to impact but can be compromised more easily than laminated glass. Your choice should prioritize laminated safety glass for enhanced security in high-risk areas.
Acoustic and UV Protection Qualities
Laminated safety glass offers superior acoustic insulation due to its interlayer, which effectively dampens sound vibrations, making it ideal for noisy environments. It also provides enhanced UV protection by blocking up to 99% of harmful ultraviolet rays, preventing interior fading and skin damage. Wired safety glass, while offering basic safety features, lacks the acoustic and UV filtering properties, making laminated glass the preferred choice for sound reduction and UV shielding.
Applications and Common Uses
Laminated safety glass is widely used in automotive windshields, building facades, and skylights thanks to its ability to hold shards together upon impact, ensuring enhanced safety in vehicles and architectural applications. Wired safety glass, commonly found in industrial windows, fire-rated doors, and older architectural installations, provides additional fire resistance with embedded wire mesh but can impair visibility compared to laminated glass. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize impact resistance and optical clarity or fire protection and security in specific environments.
Which Safety Glass is Right for Your Project?
Laminated safety glass offers superior impact resistance and sound insulation, making it ideal for projects requiring enhanced security and noise reduction. Wired safety glass contains embedded metal wire mesh for fire resistance but may compromise clarity and strength compared to laminated options. Choose laminated safety glass for architectural applications prioritized for safety and aesthetics, while wired safety glass suits fire-rated requirements in industrial or institutional buildings.
laminated safety glass vs wired safety glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com