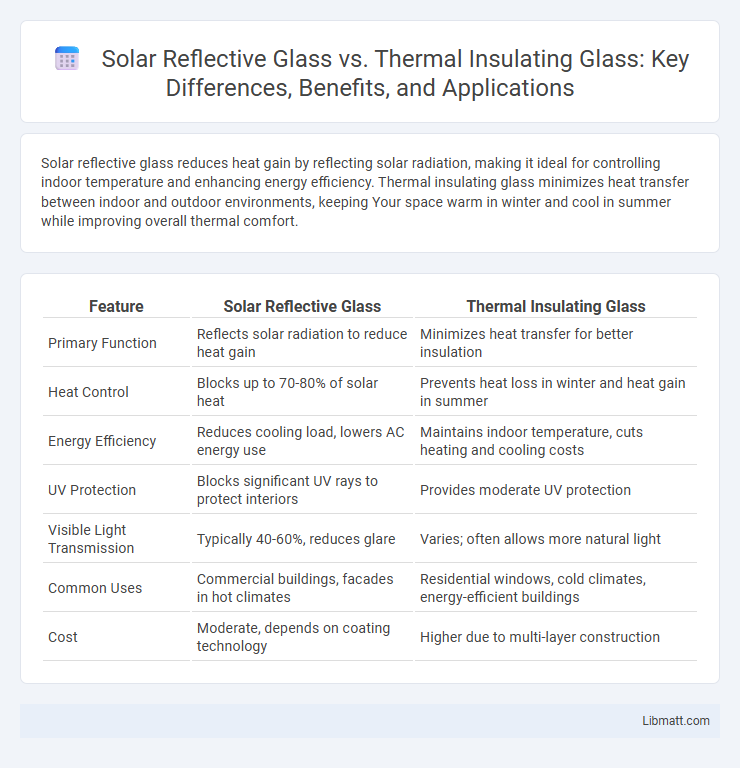
Solar reflective glass reduces heat gain by reflecting solar radiation, making it ideal for controlling indoor temperature and enhancing energy efficiency. Thermal insulating glass minimizes heat transfer between indoor and outdoor environments, keeping Your space warm in winter and cool in summer while improving overall thermal comfort.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Solar Reflective Glass | Thermal Insulating Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Reflects solar radiation to reduce heat gain | Minimizes heat transfer for better insulation |
| Heat Control | Blocks up to 70-80% of solar heat | Prevents heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer |
| Energy Efficiency | Reduces cooling load, lowers AC energy use | Maintains indoor temperature, cuts heating and cooling costs |
| UV Protection | Blocks significant UV rays to protect interiors | Provides moderate UV protection |
| Visible Light Transmission | Typically 40-60%, reduces glare | Varies; often allows more natural light |
| Common Uses | Commercial buildings, facades in hot climates | Residential windows, cold climates, energy-efficient buildings |
| Cost | Moderate, depends on coating technology | Higher due to multi-layer construction |
Introduction to Solar Reflective and Thermal Insulating Glass
Solar reflective glass is engineered with a special coating that reflects solar radiation, reducing heat gain and glare while maintaining natural light transmission. Thermal insulating glass consists of multiple layers, often with inert gas fills and low-emissivity coatings, designed to minimize heat transfer and improve energy efficiency in buildings. Both types enhance indoor comfort and energy savings but target different aspects of thermal management in architectural applications.
How Solar Reflective Glass Works
Solar reflective glass works by incorporating a special metallic coating that reflects a significant portion of solar radiation, reducing heat transmission into the interior space. This coating selectively reflects infrared and ultraviolet rays while allowing visible light to pass through, enhancing indoor comfort and energy efficiency. The glass effectively minimizes cooling loads in buildings by blocking solar heat gain without compromising natural daylight.
Functionality of Thermal Insulating Glass
Thermal insulating glass minimizes heat transfer between the interior and exterior, maintaining consistent indoor temperatures and enhancing energy efficiency. It typically consists of multiple glass panes separated by a gas-filled space, reducing heat loss during winter and heat gain in summer. Your building benefits from lower energy costs and improved thermal comfort with the advanced insulation performance of thermal insulating glass.
Key Differences Between Solar Reflective and Thermal Insulating Glass
Solar reflective glass reduces solar heat gain by reflecting a significant portion of sunlight, improving energy efficiency in hot climates while maintaining natural daylight. Thermal insulating glass minimizes heat transfer through conduction and convection, providing superior insulation to keep interiors warm in cold climates and cool in warm conditions. Both types enhance energy savings but target different thermal challenges through distinct material coatings and technologies.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Solar reflective glass reduces heat gain by reflecting sunlight, lowering cooling costs and enhancing energy efficiency in warm climates. Thermal insulating glass minimizes heat transfer through its multi-layered design, providing superior insulation and reducing heating expenses in colder environments. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize blocking solar heat or retaining indoor warmth for optimal energy savings.
Impact on Indoor Comfort and Temperature Control
Solar reflective glass significantly reduces indoor heat gain by blocking a high percentage of solar radiation, directly enhancing indoor comfort and lowering cooling costs in hot climates. Thermal insulating glass minimizes heat transfer between indoor and outdoor environments through its insulating properties, maintaining stable indoor temperatures regardless of seasonal changes. Both types improve temperature control, but solar reflective glass excels at preventing overheating, while thermal insulating glass is more effective for retaining heat in colder conditions.
Suitability for Different Climate Zones
Solar reflective glass is ideal for hot and sunny climates as it effectively reduces solar heat gain, lowering cooling costs and enhancing indoor comfort. Thermal insulating glass excels in cold and temperate regions by minimizing heat loss, improving energy efficiency, and maintaining warm indoor temperatures. Selecting the appropriate glass type depends on climate zone requirements, balancing solar heat control and thermal insulation for optimal performance.
Aesthetic Considerations and Design Flexibility
Solar reflective glass offers a sleek, modern appearance with a range of tinting options that enhance your building's aesthetic while reducing glare and heat gain. Thermal insulating glass prioritizes performance with multi-layered designs and gas fills, providing excellent energy efficiency that can be subtly integrated into various architectural styles. Both types deliver design flexibility, but solar reflective glass often allows for more visible customization to complement exterior facades without compromising thermal comfort.
Cost Comparison and Long-Term Savings
Solar reflective glass generally has a lower upfront cost compared to thermal insulating glass but offers moderate energy savings by reducing solar heat gain. Thermal insulating glass, although more expensive initially, provides superior thermal resistance and long-term savings by minimizing heat transfer and lowering heating and cooling bills. Your investment in thermal insulating glass can result in greater energy efficiency and cost reductions over the lifespan of your windows.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Building
Solar reflective glass minimizes heat gain by reflecting infrared rays, making it ideal for buildings in hot climates or areas with intense sunlight. Thermal insulating glass, often double-glazed with a low-emissivity coating, excels at reducing heat loss and improving energy efficiency in colder environments. Your choice depends on climate conditions and energy goals, ensuring optimal comfort and cost savings year-round.
Solar reflective glass vs thermal insulating glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com