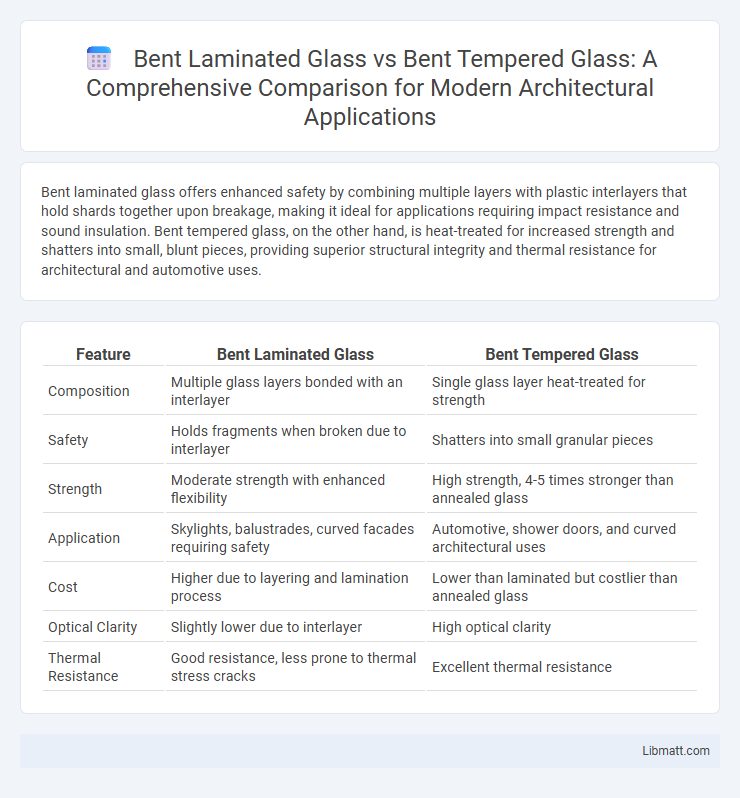
Bent laminated glass offers enhanced safety by combining multiple layers with plastic interlayers that hold shards together upon breakage, making it ideal for applications requiring impact resistance and sound insulation. Bent tempered glass, on the other hand, is heat-treated for increased strength and shatters into small, blunt pieces, providing superior structural integrity and thermal resistance for architectural and automotive uses.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bent Laminated Glass | Bent Tempered Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Multiple glass layers bonded with an interlayer | Single glass layer heat-treated for strength |
| Safety | Holds fragments when broken due to interlayer | Shatters into small granular pieces |
| Strength | Moderate strength with enhanced flexibility | High strength, 4-5 times stronger than annealed glass |
| Application | Skylights, balustrades, curved facades requiring safety | Automotive, shower doors, and curved architectural uses |
| Cost | Higher due to layering and lamination process | Lower than laminated but costlier than annealed glass |
| Optical Clarity | Slightly lower due to interlayer | High optical clarity |
| Thermal Resistance | Good resistance, less prone to thermal stress cracks | Excellent thermal resistance |
Introduction to Bent Laminated and Bent Tempered Glass
Bent laminated glass consists of multiple glass layers bonded with interlayers to enhance safety and durability, offering superior resistance to impact and shattering. Bent tempered glass undergoes heat treatment to increase strength and fracture into small, blunt pieces upon breakage, providing high thermal and mechanical resistance. Your choice between these two depends on specific safety requirements and architectural design preferences.
Defining Bent Laminated Glass
Bent laminated glass consists of multiple glass layers bonded with an interlayer, offering enhanced safety and structural integrity during bending processes. This glass type maintains its curved shape while providing superior impact resistance and reduced likelihood of shattering compared to bent tempered glass. Your choice of bent laminated glass ensures improved durability and security for architectural applications requiring both flexibility and safety.
Defining Bent Tempered Glass
Bent tempered glass is a type of safety glass that undergoes a heat treatment process to increase strength and durability, followed by bending into specific curved shapes while maintaining its tempered properties. Unlike bent laminated glass, which consists of multiple layers bonded together for added safety and sound insulation, bent tempered glass offers superior impact resistance and shatterproof performance in architectural and automotive applications. The tempering process ensures that when broken, the glass shatters into small, blunt pieces, minimizing injury risk.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Bent laminated glass is produced by shaping multiple layers of glass with interlayer films under heat and pressure, ensuring flexibility and enhanced safety through bonding. Bent tempered glass undergoes a thermal tempering process involving rapid cooling after bending, resulting in increased strength and resistance but without interlayer lamination. The key manufacturing difference lies in the lamination and bonding steps for laminated glass versus the controlled heating and quenching for tempered glass, impacting durability and safety characteristics.
Key Structural Differences
Bent laminated glass consists of multiple glass layers bonded with an interlayer, providing enhanced safety and durability by holding shards together upon breakage. Bent tempered glass undergoes heat treatment to increase strength and shatters into small, blunt pieces, prioritizing impact resistance but lacking the layered interlayer structure of laminated glass. The key structural difference lies in laminated glass's multi-layer composition for safety and flexibility, whereas tempered glass relies on surface compression for strength and controlled breakage.
Performance and Safety Considerations
Bent laminated glass offers superior safety with its interlayer holding shards together upon impact, reducing injury risk and maintaining structural integrity in your building. Bent tempered glass provides enhanced strength and resistance to thermal stress, but shatters into small, less dangerous pieces when broken, ensuring occupant safety. Your choice depends on performance needs, as laminated glass excels in impact resistance and noise reduction, while tempered glass is optimal for high-strength applications and rapid fragmentation safety.
Aesthetic and Design Flexibility
Bent laminated glass offers superior design flexibility by combining multiple glass layers with a plastic interlayer, allowing for intricate curved shapes and enhanced safety without compromising clarity or color options. Bent tempered glass provides excellent strength and impact resistance with a sleek, smooth surface but is more limited in curvature depth due to the tempering process. Your choice depends on whether aesthetic complexity or structural toughness is the priority for your architectural or interior design project.
Typical Applications in Architecture and Design
Bent laminated glass is frequently used in architectural projects requiring enhanced safety and sound insulation, such as skylights, balustrades, and curved facades, benefiting from its ability to hold shards together upon impact. Bent tempered glass is often preferred for dynamic structural elements like curved windows, canopies, and curtain walls due to its superior strength and thermal resistance, ensuring safety under high-stress conditions. Both types support innovative design aesthetics but serve distinct functional roles based on stress tolerance and safety requirements in building environments.
Cost Implications and Maintenance
Bent laminated glass generally has higher initial costs due to its complex manufacturing process involving glue layering, but it offers superior safety and durability, reducing long-term maintenance expenses. Bent tempered glass tends to be less expensive upfront but requires more frequent inspections and prompt replacement when damaged, increasing ongoing maintenance costs. Your choice should weigh upfront investment against potential savings in maintenance and safety over time.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Project
Bent laminated glass offers enhanced safety with its multiple interlayers that hold shards together upon breakage, making it ideal for projects requiring impact resistance and sound insulation. Bent tempered glass provides superior strength and thermal resistance due to its heat treatment, suitable for applications demanding durability and high-performance safety. Assess your project's specific needs for safety, strength, and noise reduction to choose the right glass type that balances functionality and aesthetics effectively.
Bent laminated glass vs bent tempered glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com