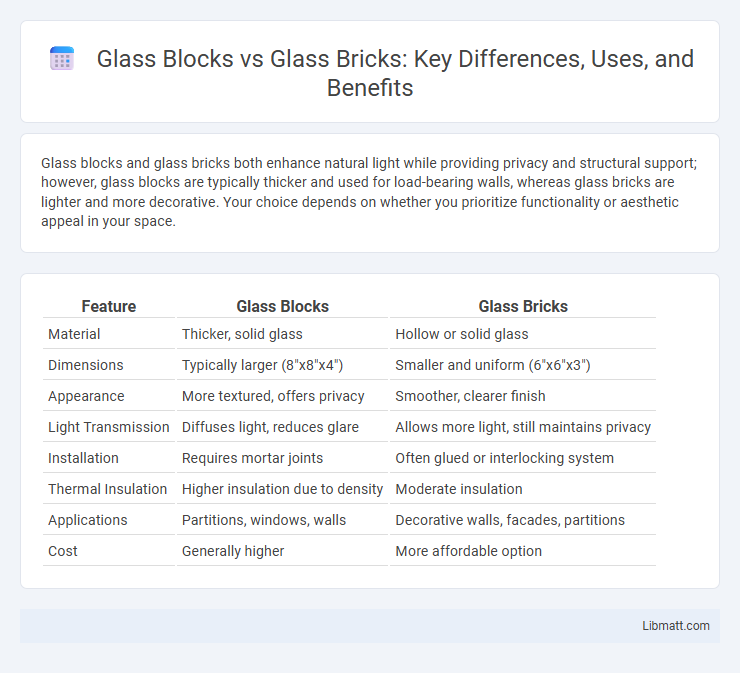
Glass blocks and glass bricks both enhance natural light while providing privacy and structural support; however, glass blocks are typically thicker and used for load-bearing walls, whereas glass bricks are lighter and more decorative. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize functionality or aesthetic appeal in your space.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Glass Blocks | Glass Bricks |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Thicker, solid glass | Hollow or solid glass |
| Dimensions | Typically larger (8"x8"x4") | Smaller and uniform (6"x6"x3") |
| Appearance | More textured, offers privacy | Smoother, clearer finish |
| Light Transmission | Diffuses light, reduces glare | Allows more light, still maintains privacy |
| Installation | Requires mortar joints | Often glued or interlocking system |
| Thermal Insulation | Higher insulation due to density | Moderate insulation |
| Applications | Partitions, windows, walls | Decorative walls, facades, partitions |
| Cost | Generally higher | More affordable option |
Introduction to Glass Blocks and Glass Bricks
Glass blocks and glass bricks are architectural elements designed to enhance interior and exterior spaces by allowing natural light while providing privacy and structural support. Glass blocks typically feature a thicker profile and are molded into various shapes with a textured surface to diffuse light, making them ideal for walls, windows, and partitions. Glass bricks, often used interchangeably with glass blocks, are more uniform in size and shape, commonly employed in decorative installations and load-bearing applications, blending aesthetic appeal with durability.
Defining Glass Blocks vs Glass Bricks
Glass blocks are thick, hollow, translucent units typically used in architectural walls to provide both light and privacy, characterized by their smooth, uniform appearance and structural strength. Glass bricks are similar in function but often feature more decorative textures and patterns, designed primarily for aesthetic appeal in interior design projects. The distinction lies in glass blocks' emphasis on structural support and privacy, while glass bricks prioritize visual interest and decorative versatility.
Key Differences in Design and Structure
Glass blocks typically feature a hollow, thicker design that offers enhanced insulation and soundproofing, while glass bricks are often solid or less hollow, emphasizing aesthetic appeal with more intricate patterns. The design of glass blocks includes sealed edges to prevent moisture penetration, making them ideal for exterior or wet environments, whereas glass bricks may lack this feature, limiting their use primarily to interior decorative projects. Your choice between glass blocks and glass bricks should consider these structural differences to meet specific functional and design requirements.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Process
Glass blocks are typically made from pressed glass that is fused and cured in a mold, resulting in a solid, uniform structure with air pockets for insulation. Glass bricks, while similar, often incorporate additional materials like acrylic or polymer layers to enhance durability and impact resistance during manufacturing. Understanding these differences in material composition and production methods helps you choose the right option for your architectural and design needs.
Visual Appearance and Aesthetic Options
Glass blocks exhibit a sleek, modern visual appearance with smooth surfaces and consistent translucency, creating a clean and minimalist aesthetic ideal for contemporary designs. Glass bricks often feature textured or patterned surfaces, offering a variety of decorative options that diffuse light and add artistic flair to interior and exterior walls. The choice between glass blocks and bricks depends on desired light diffusion, privacy levels, and stylistic preferences in architectural applications.
Installation Methods and Techniques
Glass blocks typically require mortar installation, where each block is set and leveled in a bed of mortar, ensuring structural stability and airtight seams. Glass bricks often feature interlocking systems or prefabricated frames that allow for quicker, dry-installation without extensive mortar usage. Proper alignment, sealing, and curing techniques are essential in both methods to achieve durability and optimal light transmission.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Glass blocks offer superior durability due to their thick, solid construction, making them highly resistant to impact and weather conditions compared to traditional glass bricks. The maintenance requirements for glass blocks are minimal, as their smooth surface resists dirt and stains, requiring only occasional cleaning with mild detergent. Glass bricks, often thinner and less robust, may be more prone to chipping or cracking and might need more frequent upkeep to maintain their appearance and structural integrity.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Properties
Glass blocks provide superior thermal insulation with a thicker profile and air-tight design, reducing heat transfer effectively compared to glass bricks. Acoustic insulation is also enhanced in glass blocks due to their denser structure, blocking more sound transmission. Glass bricks, while visually similar, typically offer lower performance in both thermal and acoustic insulation because of their thinner walls and less airtight construction.
Typical Applications in Architecture and Interior Design
Glass blocks, commonly used in architectural facades and exterior walls, provide enhanced natural light transmission while maintaining privacy and thermal insulation. Glass bricks, favored in interior design, serve as decorative elements in partitions, shower enclosures, and accent walls, offering aesthetic appeal and diffused light. Both materials contribute to energy efficiency and soundproofing in residential and commercial spaces.
Cost Comparison and Value for Money
Glass blocks generally cost less per unit than glass bricks, making them more budget-friendly for large projects. Glass bricks offer superior durability and aesthetic appeal, often justifying their higher price through long-term value and enhanced property resale potential. Choosing between the two depends on balancing upfront cost savings against the desired quality and architectural impact.
glass blocks vs glass bricks Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com