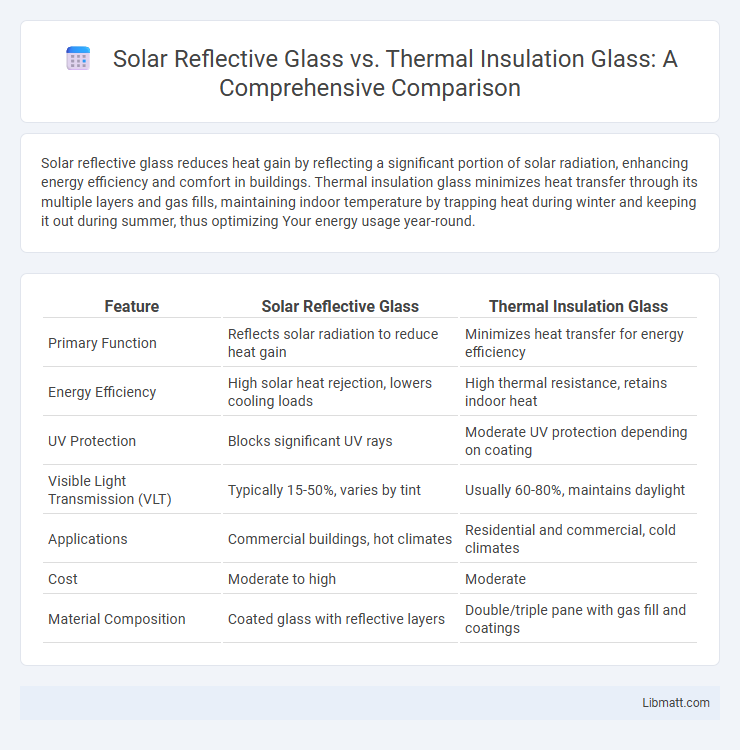
Solar reflective glass reduces heat gain by reflecting a significant portion of solar radiation, enhancing energy efficiency and comfort in buildings. Thermal insulation glass minimizes heat transfer through its multiple layers and gas fills, maintaining indoor temperature by trapping heat during winter and keeping it out during summer, thus optimizing Your energy usage year-round.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Solar Reflective Glass | Thermal Insulation Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Reflects solar radiation to reduce heat gain | Minimizes heat transfer for energy efficiency |
| Energy Efficiency | High solar heat rejection, lowers cooling loads | High thermal resistance, retains indoor heat |
| UV Protection | Blocks significant UV rays | Moderate UV protection depending on coating |
| Visible Light Transmission (VLT) | Typically 15-50%, varies by tint | Usually 60-80%, maintains daylight |
| Applications | Commercial buildings, hot climates | Residential and commercial, cold climates |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Moderate |
| Material Composition | Coated glass with reflective layers | Double/triple pane with gas fill and coatings |
Introduction to Solar Reflective Glass and Thermal Insulation Glass
Solar reflective glass minimizes heat gain by reflecting a significant portion of solar radiation, enhancing energy efficiency in buildings. Thermal insulation glass is designed to reduce heat transfer, maintaining indoor temperature stability by trapping air or inert gas between glass layers. Both types improve energy savings but serve distinct roles: solar reflective glass manages solar heat, while thermal insulation glass controls overall thermal conductivity.
How Solar Reflective Glass Works
Solar reflective glass functions by incorporating a specialized coating that reflects a significant portion of solar radiation, reducing heat transmission into buildings and enhancing energy efficiency. This coating selectively blocks infrared rays while allowing visible light to pass through, maintaining natural illumination without increasing indoor temperatures. Your choice of solar reflective glass can significantly lower cooling costs compared to traditional thermal insulation glass by minimizing heat gain from sunlight.
Mechanisms Behind Thermal Insulation Glass
Thermal insulation glass uses multiple layers and low-emissivity coatings to reduce heat transfer by minimizing conductive, convective, and radiative heat flow. The gas-filled spaces between panes, often filled with argon or krypton, enhance insulation by slowing air movement and improving thermal resistance. Your building benefits from stable indoor temperatures and energy savings by effectively limiting heat exchange with the external environment.
Key Differences: Solar Reflective vs Thermal Insulation Glass
Solar reflective glass primarily reduces heat gain by reflecting infrared and ultraviolet rays, enhancing energy efficiency in buildings exposed to direct sunlight. Thermal insulation glass minimizes heat transfer through the window by incorporating multiple panes and inert gas fills, improving indoor temperature regulation regardless of external weather conditions. The key difference lies in solar reflective glass targeting solar radiation, while thermal insulation glass focuses on reducing overall thermal conductivity.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Solar reflective glass reduces energy consumption by reflecting a significant portion of solar radiation, lowering cooling costs during hot seasons. Thermal insulation glass minimizes heat transfer between the interior and exterior, enhancing energy efficiency by maintaining consistent indoor temperatures year-round. Your choice depends on whether your priority is reducing heat gain from sunlight or improving overall temperature regulation for energy savings.
Benefits of Solar Reflective Glass
Solar reflective glass significantly reduces heat gain by reflecting a large portion of solar radiation, leading to lower cooling costs and enhanced energy efficiency in buildings. It also improves indoor comfort by minimizing glare and protecting furniture from harmful UV rays, maintaining your interior's aesthetics. Compared to thermal insulation glass, solar reflective glass excels in environments with intense sunlight, providing superior heat control and contributing to sustainable building design.
Advantages of Thermal Insulation Glass
Thermal insulation glass offers superior energy efficiency by significantly reducing heat transfer, which helps maintain consistent indoor temperatures and lowers heating and cooling costs. It enhances comfort by minimizing cold spots and condensation, creating a healthier indoor environment. Your building benefits from improved sound insulation and increased durability, making thermal insulation glass a smart investment for long-term energy savings and enhanced comfort.
Applications in Residential and Commercial Buildings
Solar reflective glass is ideal for commercial buildings where reducing solar heat gain and glare is crucial, effectively lowering cooling costs and enhancing occupant comfort. Thermal insulation glass is preferred in both residential and commercial settings to maintain indoor temperature stability, reducing energy consumption by minimizing heat transfer through windows. Your choice between these glass types depends on whether solar control or thermal efficiency is more critical for your building's climate and usage.
Cost Considerations and Return on Investment
Solar reflective glass generally entails a higher initial cost compared to thermal insulation glass due to specialized coatings that reflect solar radiation. However, its ability to reduce cooling loads significantly improves energy savings in warm climates, enhancing long-term return on investment. Thermal insulation glass offers cost-effective temperature regulation by minimizing heat transfer, leading to stable indoor temperatures and reduced heating expenses, particularly beneficial in colder regions.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Project
Solar reflective glass reduces heat gain by reflecting a significant portion of solar radiation, making it ideal for projects requiring energy efficiency and glare control. Thermal insulation glass, with its multi-layered structure and inert gas fills, offers superior resistance to heat transfer, enhancing indoor comfort and reducing heating and cooling costs. Choosing the right glass for your project depends on climate conditions, energy performance goals, and aesthetic preferences to maximize both functionality and cost savings.
solar reflective glass vs thermal insulation glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com