Kinetic glass adjusts its opacity by physically moving particles or layers within the glass, providing dynamic control over light and heat transmission. Smart glass uses electrical signals to change transparency instantly, offering energy efficiency and privacy controls ideal for modern architectural and automotive applications.
Table of Comparison
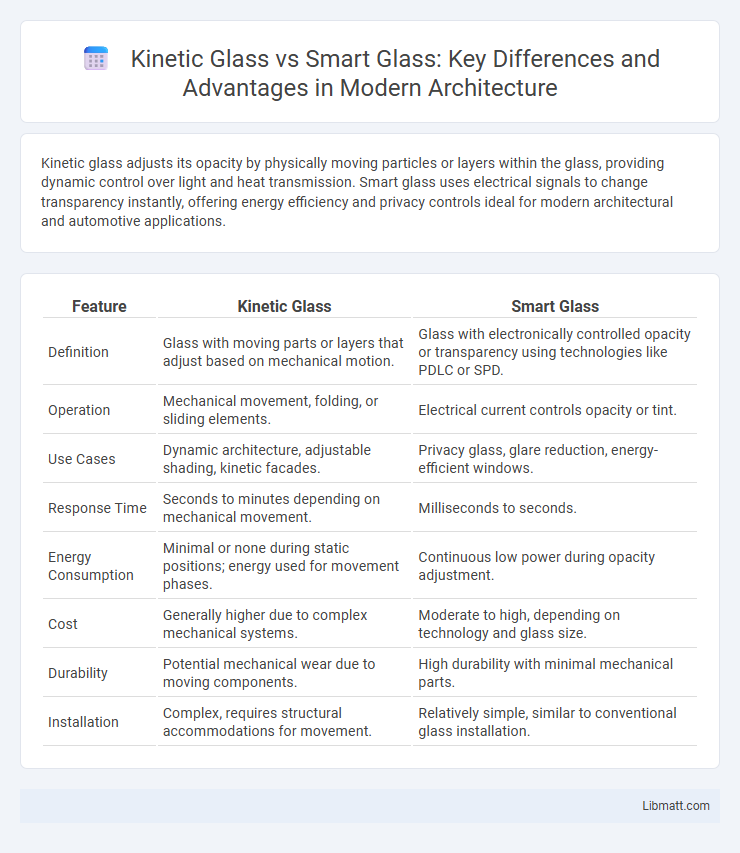
| Feature | Kinetic Glass | Smart Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Glass with moving parts or layers that adjust based on mechanical motion. | Glass with electronically controlled opacity or transparency using technologies like PDLC or SPD. |
| Operation | Mechanical movement, folding, or sliding elements. | Electrical current controls opacity or tint. |
| Use Cases | Dynamic architecture, adjustable shading, kinetic facades. | Privacy glass, glare reduction, energy-efficient windows. |
| Response Time | Seconds to minutes depending on mechanical movement. | Milliseconds to seconds. |
| Energy Consumption | Minimal or none during static positions; energy used for movement phases. | Continuous low power during opacity adjustment. |
| Cost | Generally higher due to complex mechanical systems. | Moderate to high, depending on technology and glass size. |
| Durability | Potential mechanical wear due to moving components. | High durability with minimal mechanical parts. |
| Installation | Complex, requires structural accommodations for movement. | Relatively simple, similar to conventional glass installation. |
Introduction to Kinetic Glass and Smart Glass
Kinetic glass incorporates dynamic components that respond to physical movement or changes in light, offering adaptable transparency and energy efficiency for architectural applications. Smart glass utilizes electrochromic, photochromic, or thermochromic technologies to control light transmission and privacy with electrical or environmental triggers. Both innovations enhance building performance by reducing glare, improving thermal control, and providing customizable aesthetics in modern construction.
How Kinetic Glass Works
Kinetic glass operates through motorized components that adjust the angle or orientation of glass panels to control light and heat transmission dynamically. By altering the positioning of louvers or segments, kinetic glass can optimize energy efficiency and comfort in real-time throughout the day. Your building's environmental control benefits from precise modulation of natural light, reducing reliance on artificial climate control systems.
How Smart Glass Functions
Smart glass functions by utilizing electrochromic, thermochromic, or photochromic technologies to control the transmission of light and heat through the glass. Electrochromic smart glass changes its opacity when an electrical voltage is applied, allowing users to adjust transparency for privacy or energy efficiency. This technology enhances building performance by reducing glare and controlling solar heat gain without compromising natural light.
Key Differences Between Kinetic Glass and Smart Glass
Kinetic glass features dynamic, movable components that alter its transparency or opacity through mechanical motion, enabling physical adjustment of light transmission. Smart glass, also known as switchable glass, employs electrochromic, photochromic, or thermochromic technologies to change transparency electronically or in response to environmental stimuli, offering seamless, energy-efficient light control. While kinetic glass relies on mechanical adjustments for tint changes, smart glass provides instant, programmable modulation without moving parts, enhancing durability and integration with automated building systems.
Applications of Kinetic Glass
Kinetic glass transforms architectural design by enabling dynamic control of light and heat through its movable panels, making it ideal for energy-efficient facades and responsive interior partitions. Its applications extend to commercial buildings, skylights, and outdoor shading systems, where adjusting transparency and insulation optimizes comfort and reduces HVAC costs. Your ability to customize energy use and natural lighting with kinetic glass enhances sustainability and occupant well-being in modern construction.
Common Uses of Smart Glass
Smart glass is widely used in office buildings and homes to enhance privacy and energy efficiency by controlling light transmission and reducing heat gain. It is also incorporated in automotive windows and skylights to improve comfort and safety. You can benefit from smart glass in retail displays and conference rooms where dynamic transparency adapts to various lighting and privacy needs.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Kinetic glass utilizes micro-movement technology to adjust its transparency, reducing solar heat gain and enhancing energy efficiency by minimizing cooling loads in buildings. Smart glass employs electrochromic or thermochromic technologies to modulate light transmission and heat flow, improving energy savings by dynamically controlling indoor temperatures and reducing reliance on HVAC systems. Overall, kinetic glass offers energy efficiency through adaptive mechanical adjustments, while smart glass provides more precise control over energy conservation by electronically altering window properties.
Design Flexibility and Aesthetics
Kinetic glass offers dynamic design flexibility with its ability to change shape and form, creating visually striking architectural elements that adapt to light and movement. Smart glass excels in aesthetic customization through controllable transparency and color, allowing your spaces to shift from clear to opaque smoothly while maintaining sleek, modern surfaces. Both technologies enhance interior design by combining functionality with innovative visual appeal tailored to your style preferences.
Cost Considerations and Installation
Kinetic glass typically involves higher upfront costs due to its complex mechanical components and specialized installation requirements, often leading to longer labor times compared to smart glass. Smart glass, utilizing electrochromic or thermochromic technologies, usually has moderate installation costs and can be integrated into existing window frames with less disruption. Both options require professional expertise, but kinetic glass installations may incur additional expenses from maintenance and mechanical calibration over time.
Future Trends in Glass Technology
Kinetic glass and smart glass represent cutting-edge advancements in glass technology, with kinetic glass featuring dynamic movement capabilities for energy efficiency and smart glass utilizing electrochromic properties to control light and heat transmission. Emerging trends indicate increased integration of artificial intelligence and IoT connectivity, enabling more responsive and customizable glass solutions for residential and commercial applications. Your future spaces will benefit from these innovations by enhancing comfort, reducing energy consumption, and improving architectural aesthetics through adaptive and interactive glass surfaces.
kinetic glass vs smart glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com