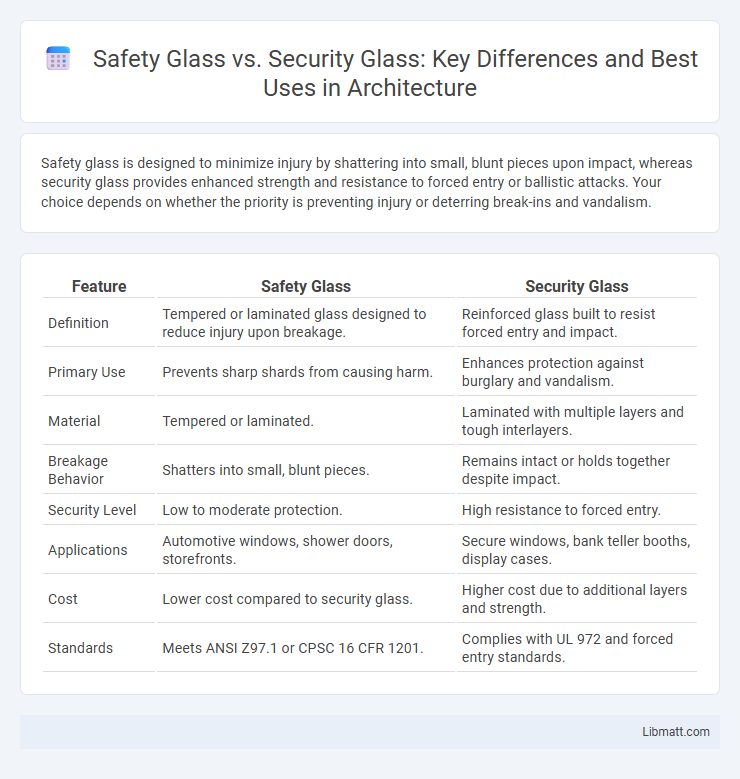
Safety glass is designed to minimize injury by shattering into small, blunt pieces upon impact, whereas security glass provides enhanced strength and resistance to forced entry or ballistic attacks. Your choice depends on whether the priority is preventing injury or deterring break-ins and vandalism.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Safety Glass | Security Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Tempered or laminated glass designed to reduce injury upon breakage. | Reinforced glass built to resist forced entry and impact. |
| Primary Use | Prevents sharp shards from causing harm. | Enhances protection against burglary and vandalism. |
| Material | Tempered or laminated. | Laminated with multiple layers and tough interlayers. |
| Breakage Behavior | Shatters into small, blunt pieces. | Remains intact or holds together despite impact. |
| Security Level | Low to moderate protection. | High resistance to forced entry. |
| Applications | Automotive windows, shower doors, storefronts. | Secure windows, bank teller booths, display cases. |
| Cost | Lower cost compared to security glass. | Higher cost due to additional layers and strength. |
| Standards | Meets ANSI Z97.1 or CPSC 16 CFR 1201. | Complies with UL 972 and forced entry standards. |
Introduction to Safety Glass and Security Glass
Safety glass is designed to minimize injury by breaking into small, blunt pieces upon impact, commonly used in vehicle windows and building facades. Security glass offers enhanced protection by combining multiple layers and tough materials to resist forced entry and provide higher durability. Understanding the differences helps you choose the appropriate glass type for safety and security requirements.
Definitions: What is Safety Glass?
Safety glass is a type of glass specially designed to minimize injury upon breakage, typically made by chemically or thermally treating the glass to increase its strength and cause it to shatter into small, blunt pieces rather than sharp shards. Common forms of safety glass include tempered glass and laminated glass, both engineered to enhance impact resistance and reduce the risk of severe cuts or penetration. This glass is widely used in automotive windshields, building windows, and doors where human safety is a critical concern.
Definitions: What is Security Glass?
Security glass is a specialized type of safety glass engineered to resist forced entry and withstand high impact forces. It typically consists of multiple laminated layers of glass and polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayers that maintain structural integrity even when shattered. This enhanced durability makes security glass ideal for applications requiring protection against break-ins, explosions, or ballistic threats.
Key Differences Between Safety Glass and Security Glass
Safety glass is designed to minimize injury by breaking into small, blunt pieces upon impact, typically used in car windows and building facades. Security glass offers enhanced protection through thicker layers and laminated materials that resist forced entry and blunt force, making it ideal for banks, storefronts, and secure facilities. Understanding the key differences helps you select the appropriate glass type based on the level of protection required for your space.
Common Types of Safety Glass
Common types of safety glass include tempered glass, which is heat-treated to increase strength and shatters into small, blunt pieces on impact, and laminated glass, composed of two or more layers of glass bonded with an interlayer that holds shards together upon breakage. Heat-strengthened glass, offering intermediate strength between annealed and tempered glass, resists thermal stress but does not shatter as safely as tempered glass. These varieties enhance protection in automotive, architectural, and industrial applications by reducing injury risks and improving structural integrity.
Common Types of Security Glass
Common types of security glass include laminated glass, which features multiple layers bonded with a durable interlayer that prevents shattering and enhances resistance to impact. Tempered glass undergoes heat treatment to increase its strength, breaking into small, blunt pieces rather than sharp shards for improved safety. Your choice between these options depends on the level of protection required, with laminated glass offering superior intrusion resistance and tempered glass providing enhanced toughness against breakage.
Applications: Where Safety Glass is Used
Safety glass is commonly used in automotive windshields, residential windows, and shower enclosures due to its ability to reduce injury by breaking into small, less harmful pieces upon impact. Your home and vehicle benefit from safety glass in areas prone to accidental impact or high visibility hazards. It is ideal for applications requiring protection against shattering while maintaining optical clarity.
Applications: Where Security Glass is Used
Security glass is commonly used in high-risk areas requiring enhanced protection, such as banks, government buildings, jewelry stores, and vehicle windshields. Its laminated or tempered construction provides resistance against forced entry, ballistic threats, and severe impacts, making it ideal for commercial storefronts, prisons, and secure facilities. Security glass applications extend to residential settings with advanced safety concerns, including doors, windows, and skylights designed to deter break-ins and withstand environmental hazards.
Pros and Cons: Safety Glass vs Security Glass
Safety glass, typically made from tempered or laminated glass, offers excellent resistance to impact and shatters into small, less dangerous pieces, reducing injury risk during accidents. Security glass combines laminated layers with toughened glass, providing enhanced protection against forced entry and ballistic threats but often comes at a higher cost and increased weight. Your choice depends on whether impact safety or intrusion resistance is the priority, as safety glass prioritizes human protection while security glass emphasizes property security.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Needs
Safety glass and security glass differ primarily in their design and application; safety glass, such as tempered or laminated glass, is engineered to minimize injury by breaking into small, less harmful pieces, while security glass provides enhanced resistance to impact and forced entry, often incorporating multiple layers or specialized interlayers. Choosing the right glass depends on your specific requirements, including the level of protection needed, installation environment, and local building codes. Understanding these factors ensures you select the best glass type to safeguard your property effectively.
safety glass vs security glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com