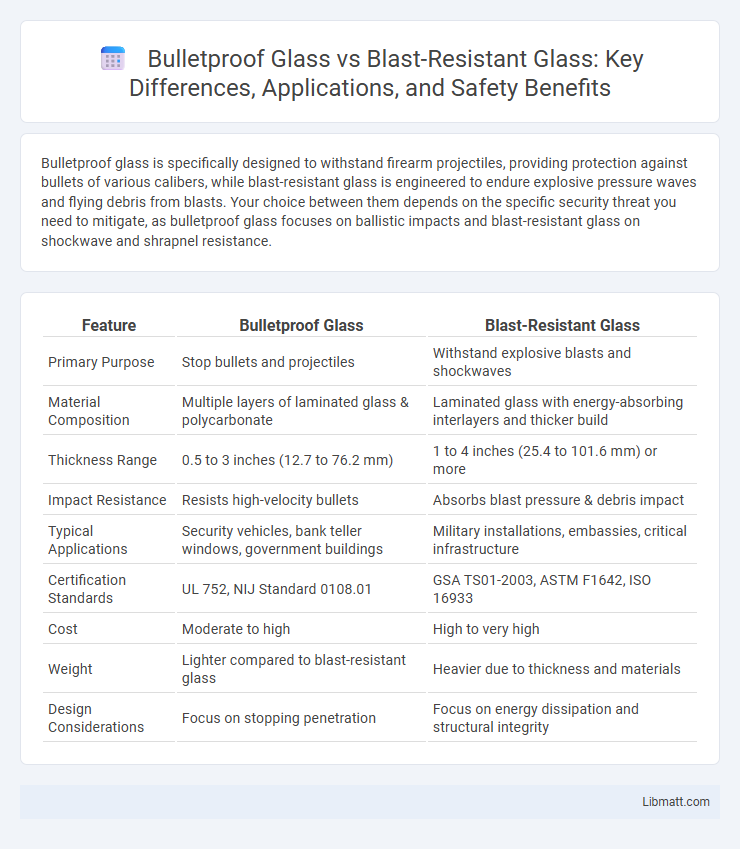
Bulletproof glass is specifically designed to withstand firearm projectiles, providing protection against bullets of various calibers, while blast-resistant glass is engineered to endure explosive pressure waves and flying debris from blasts. Your choice between them depends on the specific security threat you need to mitigate, as bulletproof glass focuses on ballistic impacts and blast-resistant glass on shockwave and shrapnel resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bulletproof Glass | Blast-Resistant Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Stop bullets and projectiles | Withstand explosive blasts and shockwaves |
| Material Composition | Multiple layers of laminated glass & polycarbonate | Laminated glass with energy-absorbing interlayers and thicker build |
| Thickness Range | 0.5 to 3 inches (12.7 to 76.2 mm) | 1 to 4 inches (25.4 to 101.6 mm) or more |
| Impact Resistance | Resists high-velocity bullets | Absorbs blast pressure & debris impact |
| Typical Applications | Security vehicles, bank teller windows, government buildings | Military installations, embassies, critical infrastructure |
| Certification Standards | UL 752, NIJ Standard 0108.01 | GSA TS01-2003, ASTM F1642, ISO 16933 |
| Cost | Moderate to high | High to very high |
| Weight | Lighter compared to blast-resistant glass | Heavier due to thickness and materials |
| Design Considerations | Focus on stopping penetration | Focus on energy dissipation and structural integrity |
Understanding Bulletproof Glass: Key Features
Bulletproof glass is designed to withstand gunfire by combining multiple layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate materials to absorb and disperse energy. This transparent armor offers protection against various calibers, making it ideal for high-risk environments such as banks, vehicles, or personal security. Your safety relies on the glass's ability to prevent penetration while maintaining clear visibility and structural integrity.
What Is Blast-Resistant Glass?
Blast-resistant glass is a specially engineered glazing system designed to withstand and absorb the impact and overpressure from explosions, reducing the risk of injury and damage caused by flying debris and shockwaves. Unlike standard bulletproof glass, which primarily resists narrow, high-velocity projectile impacts, blast-resistant glass incorporates multiple layers of laminated materials and advanced interlayers that disperse explosive energy while maintaining structural integrity. This specialized glass is commonly used in military, government, and high-risk commercial applications where protection against blasts and forced entry is critical.
Key Differences Between Bulletproof and Blast-Resistant Glass
Bulletproof glass is specifically engineered to stop or slow down bullets from penetrating, typically made from multiple layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate aimed at high-velocity impacts. Blast-resistant glass, on the other hand, is designed to withstand and absorb the force of explosions, reducing the risk of shattering and projectiles by using thicker laminates and specialized interlayers to disperse blast energy. The primary distinction lies in bulletproof glass prioritizing ballistic protection while blast-resistant glass focuses on pressure wave mitigation and debris containment.
Material Composition and Construction
Bulletproof glass is typically composed of multiple layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate, designed to absorb and disperse the impact energy of bullets through its layered construction. Blast-resistant glass incorporates thicker, more robust materials such as tempered glass combined with polycarbonate interlayers and resin to withstand high-pressure shock waves from explosions. The key distinction lies in blast-resistant glass's enhanced lamination and thicker substrate, enabling it to resist not only projectiles but also the intense forces generated by blasts.
Levels of Protection: Bullets vs. Explosions
Bulletproof glass offers multi-layered protection designed to stop handgun and rifle bullets, with varying levels rated by standards such as UL 752 based on the type and caliber of firearms it can withstand. Blast-resistant glass is engineered to absorb and dissipate explosive energy, preventing shrapnel and pressure waves from penetrating during blasts, meeting specifications like ASTM F2912 for explosive resistance. Your choice between the two should depend on whether protection is needed primarily against ballistic threats or powerful explosive forces often encountered in security-sensitive environments.
Applications of Bulletproof Glass
Bulletproof glass is widely applied in security vehicles, bank teller windows, and storefronts to protect against ballistic threats and enhance occupant safety. Your property benefits from bulletproof glass in government buildings, embassies, and armored vehicles where resistance to gunfire is essential. This specialized glass combines multiple layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate to effectively absorb and disperse the impact of bullets.
Applications of Blast-Resistant Glass
Blast-resistant glass is engineered to withstand high-impact explosions, making it essential for military installations, government buildings, and commercial facilities in high-risk areas. Its multi-layered construction absorbs and disperses explosive energy, protecting occupants and structural integrity during blasts. This specialized glass is also used in critical infrastructure such as airports, embassies, and financial institutions to enhance security against terrorism and accidental detonations.
Cost Comparison: Bulletproof vs. Blast-Resistant Glass
Bulletproof glass is generally more affordable than blast-resistant glass due to its lighter construction designed primarily to stop ballistic threats rather than explosive forces. Blast-resistant glass incorporates multiple laminated layers and thicker materials, significantly increasing manufacturing and installation costs. The price difference can range from 20% to 50% or more, depending on the level of protection and size requirements for each type.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Bulletproof glass installation requires precise fitting within reinforced frames to ensure maximum ballistic protection, often necessitating professional expertise and significant structural support. Blast-resistant glass demands specialized installation techniques to withstand explosive forces, including lamination layers designed to absorb shock and prevent shattering. Your maintenance routine should include regular inspections for cracks or delamination, as both types of glass lose effectiveness if compromised.
Choosing the Right Security Glass for Your Needs
Bulletproof glass offers high-level protection against firearms by layering multiple sheets of glass and polycarbonate, making it ideal for preventing bullet penetration. Blast-resistant glass is designed to withstand explosive forces by absorbing and dispersing shock waves, protecting against structural damage and shrapnel. Understanding the specific threats you face will help you choose the right security glass, ensuring your safety requirements are effectively met.
bulletproof glass vs blast-resistant glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com