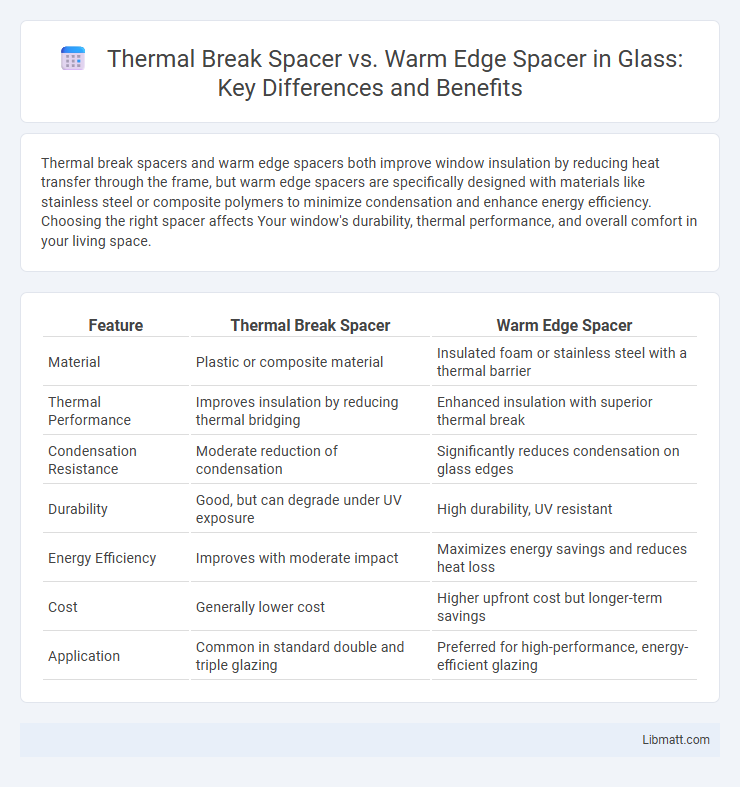
Thermal break spacers and warm edge spacers both improve window insulation by reducing heat transfer through the frame, but warm edge spacers are specifically designed with materials like stainless steel or composite polymers to minimize condensation and enhance energy efficiency. Choosing the right spacer affects Your window's durability, thermal performance, and overall comfort in your living space.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Thermal Break Spacer | Warm Edge Spacer |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Plastic or composite material | Insulated foam or stainless steel with a thermal barrier |
| Thermal Performance | Improves insulation by reducing thermal bridging | Enhanced insulation with superior thermal break |
| Condensation Resistance | Moderate reduction of condensation | Significantly reduces condensation on glass edges |
| Durability | Good, but can degrade under UV exposure | High durability, UV resistant |
| Energy Efficiency | Improves with moderate impact | Maximizes energy savings and reduces heat loss |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher upfront cost but longer-term savings |
| Application | Common in standard double and triple glazing | Preferred for high-performance, energy-efficient glazing |
Introduction to Window Spacer Technologies
Thermal break spacers and warm edge spacers are advanced window spacer technologies designed to reduce heat transfer and improve energy efficiency in insulated glazing units. Thermal break spacers incorporate insulating materials such as foam or polymer to create a barrier between the glass edges, minimizing thermal bridging and condensation risk. Warm edge spacers, typically made from materials like stainless steel or composite polymers, enhance insulation by maintaining lower temperatures at the glass edge, contributing to better thermal performance and enhanced window durability.
What Is a Thermal Break Spacer?
A thermal break spacer is a component used in insulating glass units to reduce heat transfer between the window panes, enhancing energy efficiency by minimizing thermal bridging. It typically consists of materials with low thermal conductivity, such as plastic or rubber, separating the glass panes to prevent heat loss and condensation. Compared to warm edge spacers, thermal break spacers specifically focus on creating a physical barrier that interrupts heat flow, contributing to improved insulation and overall window performance.
Understanding Warm Edge Spacers
Warm edge spacers, often confused with thermal break spacers, are specifically designed to reduce heat transfer around the edges of double or triple glazed windows by using materials with low thermal conductivity such as silicone foam or stainless steel. Thermal break spacers create a physical barrier between the inner and outer parts of the window frame, but warm edge spacers focus on minimizing condensation and improving energy efficiency by maintaining a consistent edge temperature. Understanding these distinctions helps in selecting the right spacer for maximizing insulation performance and reducing energy costs in window installations.
Thermal Insulation Performance Comparison
Thermal break spacers significantly reduce heat transfer between window panes by incorporating insulating materials with low thermal conductivity, improving overall thermal insulation performance. Warm edge spacers utilize advanced composite materials or thermoplastics that minimize thermal bridging more effectively than traditional aluminum spacers, contributing to enhanced energy efficiency in glazing systems. Studies indicate that warm edge spacers typically achieve lower U-values and reduce condensation risks better than standard thermal break spacers, making them superior in thermal insulation performance.
Energy Efficiency and Cost-Savings
Thermal break spacers and warm edge spacers both enhance window energy efficiency by reducing heat transfer and minimizing condensation, but warm edge spacers typically offer superior thermal performance due to advanced materials like silicone or stainless steel. Incorporating warm edge spacers in your windows can lead to greater cost savings on energy bills over time by maintaining consistent indoor temperatures and reducing HVAC load. Choosing the right spacer depends on balancing upfront installation costs with long-term energy savings, with warm edge spacers often providing the best return on investment for improved thermal insulation.
Condensation Resistance Analysis
Thermal break spacers significantly reduce thermal conductivity at the window edge, minimizing condensation risk by maintaining higher surface temperatures. Warm edge spacers, made from materials like silicone foam or stainless steel with low thermal conductivity, enhance condensation resistance by creating a thermal barrier that inhibits cold bridging. Analysis indicates warm edge spacers outperform conventional aluminum spacers, offering up to 50% better condensation resistance, improving overall window energy efficiency and durability.
Durability and Longevity of Spacers
Thermal break spacers and warm edge spacers both enhance window insulation, but warm edge spacers offer superior durability and longevity due to their corrosion-resistant materials such as stainless steel, silicone foam, or thermoplastics. Warm edge spacers maintain structural integrity and thermal performance over time, reducing condensation and preventing seal failure better than traditional aluminum thermal break spacers, which can degrade faster under temperature fluctuations. This resilience significantly extends the lifespan of insulating glass units, making warm edge spacers a preferred choice for energy-efficient, long-lasting window systems.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Thermal break spacers significantly reduce heat transfer in window assemblies, lowering energy consumption and carbon emissions, making them a sustainable choice for eco-friendly building designs. Warm edge spacers, often made from recycled and low-conductivity materials like silicone foam or stainless steel, enhance thermal insulation while minimizing environmental impact through durability and recyclability. Both technologies contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions by improving overall window energy efficiency, supporting sustainable construction practices.
Installation and Compatibility Considerations
Thermal break spacers are typically easier to install due to their rigid structure and compatibility with standard glazing systems, reducing the risk of seal failure and improving energy efficiency in double or triple-pane windows. Warm edge spacers, often made from flexible materials like silicone or foam, provide superior thermal insulation and condensation resistance but may require specialized tools or adhesives for secure installation. Compatibility with window frame materials and glass types is crucial for both spacer types to ensure long-term durability and optimal thermal performance.
Choosing the Right Spacer for Your Needs
Thermal break spacers and warm edge spacers both enhance window insulation by reducing heat transfer, but they differ in materials and performance. Thermal break spacers feature a non-metallic material that interrupts thermal conductivity, ideal for extreme climates requiring maximum energy efficiency. Your choice depends on the balance between budget, climate conditions, and desired energy savings, with warm edge spacers often offering improved flexibility and condensation resistance.
Thermal break spacer vs warm edge spacer Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com