Polarized glass reduces glare by filtering horizontal light waves, enhancing clarity and reducing eye strain, making it ideal for activities like driving or fishing. Tinted glass primarily darkens your view by absorbing light, offering UV protection and privacy but without the glare-reducing benefits of polarization.
Table of Comparison
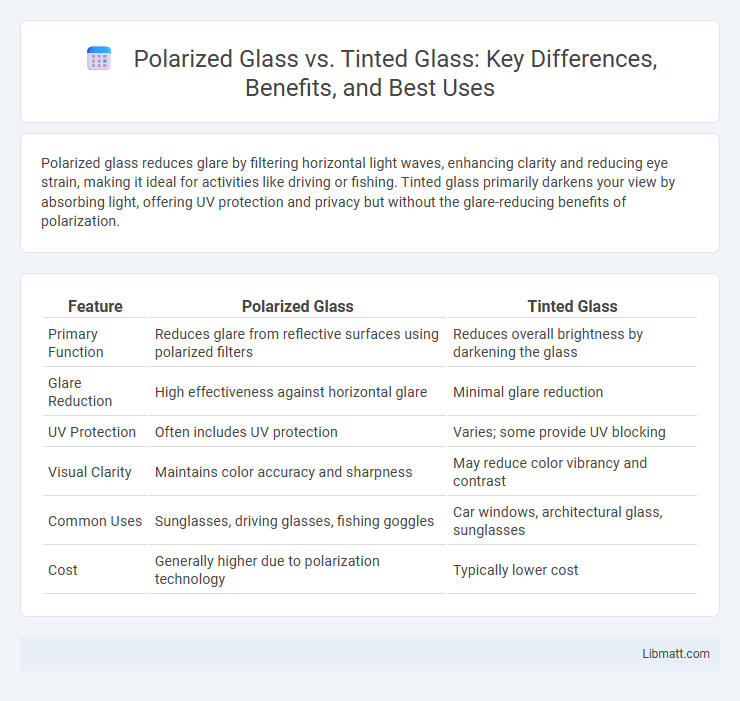
| Feature | Polarized Glass | Tinted Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Reduces glare from reflective surfaces using polarized filters | Reduces overall brightness by darkening the glass |
| Glare Reduction | High effectiveness against horizontal glare | Minimal glare reduction |
| UV Protection | Often includes UV protection | Varies; some provide UV blocking |
| Visual Clarity | Maintains color accuracy and sharpness | May reduce color vibrancy and contrast |
| Common Uses | Sunglasses, driving glasses, fishing goggles | Car windows, architectural glass, sunglasses |
| Cost | Generally higher due to polarization technology | Typically lower cost |
Introduction to Polarized and Tinted Glass
Polarized glass reduces glare by filtering horizontal light waves, improving visual clarity and reducing eye strain, especially in bright outdoor environments. Tinted glass, on the other hand, darkens the vision by absorbing a portion of light across all wavelengths, providing general shading without eliminating glare. Your choice between polarized and tinted glass depends on whether you prioritize glare reduction or overall light dimming for comfort and visibility.
How Polarized Glass Works
Polarized glass works by filtering light waves, blocking horizontal glare while allowing vertical light to pass through, which reduces reflections and enhances visual clarity. This technology uses a special chemical film that aligns molecules to absorb intense reflected light, improving contrast and reducing eye strain. Your vision benefits significantly in bright environments, especially when driving, fishing, or participating in outdoor activities where glare is a common problem.
Understanding Tinted Glass Technology
Tinted glass is manufactured by adding metal oxides or dyes during the glass production process, which reduces visible light transmission and enhances heat absorption. This technology helps in minimizing glare and controlling solar heat gain by filtering specific wavelengths of sunlight. Unlike polarized glass that utilizes a special filter to block horizontally polarized light, tinted glass primarily relies on its coloration to improve comfort and energy efficiency in various applications.
Key Differences Between Polarized and Tinted Glass
Polarized glass contains a special filter that blocks intense reflected light, reducing glare and improving visual clarity, particularly for activities like driving and fishing. Tinted glass, on the other hand, reduces overall brightness by darkening the lens without specifically targeting glare, offering general protection from sunlight but less glare control. The key difference lies in polarization's ability to selectively filter horizontal light waves, while tinted glass uniformly absorbs light across all wavelengths.
Visual Clarity: Polarized vs Tinted Glass
Polarized glass enhances visual clarity by reducing glare from reflective surfaces such as water, roads, and glass, enabling sharper and more vivid vision compared to tinted glass. Tinted glass primarily lowers overall brightness but does not selectively filter light waves, often resulting in less contrast and detail visibility. For activities requiring precise vision, polarized lenses provide superior glare suppression and improved color perception.
UV Protection Comparison
Polarized glass offers superior UV protection by using a special chemical coating that blocks 100% of harmful UVA and UVB rays, reducing eye strain and preventing long-term damage. Tinted glass primarily reduces visible light and glare but typically provides less comprehensive UV protection unless combined with a UV-blocking treatment. For optimal eye safety, polarized lenses are more effective at shielding against ultraviolet radiation compared to standard tinted lenses.
Applications and Use Cases
Polarized glass is essential for reducing glare in environments like driving, fishing, and skiing, where clear vision and eye comfort are critical, effectively blocking reflected light from surfaces such as water and roads. Tinted glass, often used in automotive windows, building facades, and sunglasses, provides general light reduction and UV protection but does not eliminate glare as efficiently as polarized lenses. Your choice between polarized and tinted glass should depend on whether glare reduction or simple light dimming is more important for your specific application.
Pros and Cons of Polarized Glass
Polarized glass reduces glare from reflective surfaces, improving visibility and eye comfort, especially in bright outdoor conditions. Its primary downside is the difficulty in viewing LCD screens, such as those on smartphones or car dashboards, which may appear distorted or darkened. If you spend extended time driving or engaging in water sports, polarized glass can significantly enhance your visual experience by reducing eye strain and enhancing contrast.
Advantages and Limitations of Tinted Glass
Tinted glass reduces glare and improves privacy by absorbing a portion of visible light, making it effective for heat reduction and UV protection in vehicles and buildings. However, tinted glass can impair visibility in low-light conditions and may cause difficulties during night driving or in dim environments. Due to its light absorption properties, it does not eliminate reflected glare like polarized glass, limiting its effectiveness in certain outdoor activities.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Needs
Polarized glass reduces glare by filtering horizontal light waves, making it ideal for activities like driving or fishing where clarity and eye comfort are crucial. Tinted glass primarily decreases overall brightness and UV exposure, suitable for general sun protection and enhancing visual comfort in bright conditions. When choosing the right glass for your needs, consider the specific environment and activities you engage in to maximize vision quality and eye health.
polarized glass vs tinted glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com