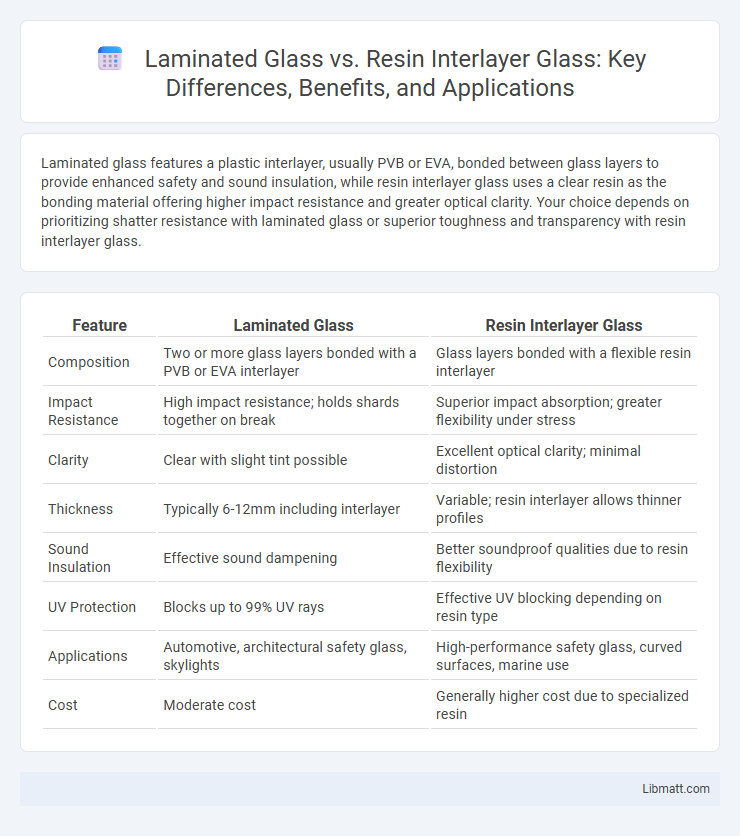
Laminated glass features a plastic interlayer, usually PVB or EVA, bonded between glass layers to provide enhanced safety and sound insulation, while resin interlayer glass uses a clear resin as the bonding material offering higher impact resistance and greater optical clarity. Your choice depends on prioritizing shatter resistance with laminated glass or superior toughness and transparency with resin interlayer glass.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Laminated Glass | Resin Interlayer Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Two or more glass layers bonded with a PVB or EVA interlayer | Glass layers bonded with a flexible resin interlayer |
| Impact Resistance | High impact resistance; holds shards together on break | Superior impact absorption; greater flexibility under stress |
| Clarity | Clear with slight tint possible | Excellent optical clarity; minimal distortion |
| Thickness | Typically 6-12mm including interlayer | Variable; resin interlayer allows thinner profiles |
| Sound Insulation | Effective sound dampening | Better soundproof qualities due to resin flexibility |
| UV Protection | Blocks up to 99% UV rays | Effective UV blocking depending on resin type |
| Applications | Automotive, architectural safety glass, skylights | High-performance safety glass, curved surfaces, marine use |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Generally higher cost due to specialized resin |
Introduction to Laminated Glass vs Resin Interlayer Glass
Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded with a plastic interlayer, typically polyvinyl butyral (PVB), offering enhanced safety and sound insulation. Resin interlayer glass uses a clear resin, such as ionoplast or polyurethane, instead of traditional PVB to improve structural integrity, clarity, and impact resistance. Both types provide superior strength and durability, but resin interlayer glass is favored for applications requiring higher performance in security and design flexibility.
Composition and Structure Differences
Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded by a durable polyvinyl butyral (PVB) resin interlayer, providing enhanced safety and sound insulation. Resin interlayer glass uses advanced resin materials such as ionoplast or SentryGlas, which deliver greater strength, clarity, and impact resistance compared to traditional PVB. The structural difference lies in the resin's molecular composition, where ionoplast resins create a stiffer bond, improving post-breakage performance and durability under stress.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Laminated glass manufacturing involves bonding two or more glass layers with a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) interlayer under heat and pressure, ensuring enhanced safety and sound insulation. Resin interlayer glass uses a liquid resin, typically polyurethane or ionomer-based, injected between glass layers and cured to form a transparent, impact-resistant bond with superior post-breakage performance. Both processes require precise temperature control and lamination pressure to optimize clarity, durability, and mechanical properties tailored to architectural and automotive applications.
Strength and Impact Resistance
Laminated glass consists of multiple glass layers bonded with a resin interlayer, offering superior strength and impact resistance by preventing shattering upon impact. The resin interlayer absorbs and disperses energy, maintaining glass integrity and enhancing safety compared to traditional single-pane glass. Your choice of laminated glass ensures increased durability and protection in environments prone to high impact or stress.
Safety and Security Features
Laminated glass with PVB or SGP interlayers provides enhanced safety by holding shattered pieces together upon impact, reducing injury risk and deterring forced entry. Resin interlayer glass offers superior structural integrity and improved resistance to penetration, making it ideal for high-security applications such as bullet-resistant and blast-resistant windows. Both materials significantly increase occupant protection, but resin interlayers excel in scenarios demanding maximum security and impact resistance.
Acoustic and Thermal Insulation Performance
Laminated glass with resin interlayers offers superior acoustic insulation by effectively dampening sound vibrations and reducing noise transmission, making it ideal for noisy environments. Its thermal insulation properties enhance energy efficiency by minimizing heat transfer, helping to maintain consistent indoor temperatures. Choosing resin interlayer glass can significantly improve your space's comfort by combining soundproofing and energy-saving benefits.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Laminated glass features a robust interlayer, typically polyvinyl butyral (PVB), offering exceptional durability and resistance against impacts and weathering, making it ideal for external applications exposed to harsh elements. Resin interlayer glass, using advanced cast or thermoplastic resins, delivers superior resistance to UV radiation, moisture penetration, and temperature fluctuations, enhancing longevity in marine or high-humidity environments. Selecting laminated glass with the appropriate interlayer ensures your installation maintains clarity and structural integrity despite environmental stresses.
Aesthetic and Design Options
Laminated glass offers a wide range of aesthetic and design options, including clear, tinted, frosted, and patterned interlayers that can enhance architectural appeal and provide custom branding or artistic elements. Resin interlayer glass allows for even greater versatility, enabling incorporation of complex, multi-colored, and gradient designs with a thinner profile, maintaining clarity and light transmission. Both materials improve safety but resin interlayer glass supports innovative design solutions ideal for modern, high-end applications requiring distinctive visual effects.
Cost and Installation Considerations
Laminated glass typically costs more upfront due to its multiple layers of glass and interlayer, but it offers improved durability and safety, potentially lowering long-term expenses. Resin interlayer glass often incurs higher installation costs because it requires precise handling and specialized techniques to ensure proper bonding and clarity. Your choice should balance initial budget constraints with installation complexity and the desired performance benefits of each glass type.
Ideal Applications for Laminated Glass and Resin Interlayer Glass
Laminated glass is ideal for automotive windshields, safety windows, and architectural glazing due to its superior impact resistance and ability to hold fragments together upon breakage. Resin interlayer glass excels in applications requiring enhanced acoustic insulation and optical clarity, such as museum displays, smart glass installations, and high-end storefronts where aesthetic transparency and soundproofing are critical. Both materials provide advanced safety features but are selected based on specific performance needs like sound reduction or structural strength.
laminated glass vs resin interlayer glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com