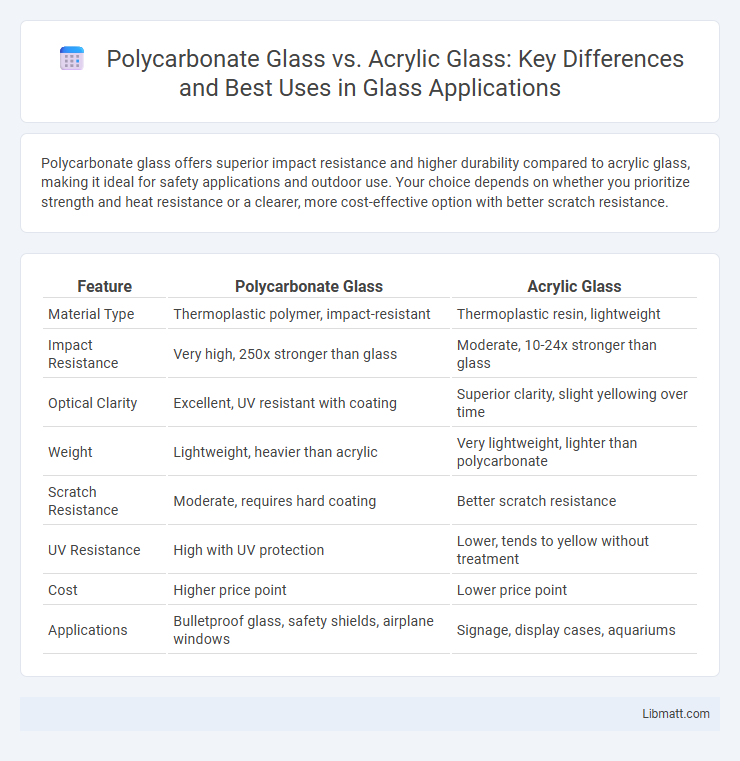
Polycarbonate glass offers superior impact resistance and higher durability compared to acrylic glass, making it ideal for safety applications and outdoor use. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize strength and heat resistance or a clearer, more cost-effective option with better scratch resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polycarbonate Glass | Acrylic Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer, impact-resistant | Thermoplastic resin, lightweight |
| Impact Resistance | Very high, 250x stronger than glass | Moderate, 10-24x stronger than glass |
| Optical Clarity | Excellent, UV resistant with coating | Superior clarity, slight yellowing over time |
| Weight | Lightweight, heavier than acrylic | Very lightweight, lighter than polycarbonate |
| Scratch Resistance | Moderate, requires hard coating | Better scratch resistance |
| UV Resistance | High with UV protection | Lower, tends to yellow without treatment |
| Cost | Higher price point | Lower price point |
| Applications | Bulletproof glass, safety shields, airplane windows | Signage, display cases, aquariums |
Introduction to Polycarbonate and Acrylic Glass
Polycarbonate glass is a highly durable, impact-resistant thermoplastic commonly used in protective eyewear, automotive components, and bullet-resistant windows due to its superior strength and clarity. Acrylic glass, also known as polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), is prized for its optical clarity and weather resistance, often used in signage, aquariums, and skylights. Both materials offer lightweight alternatives to traditional glass, with polycarbonate excelling in toughness and acrylic providing greater scratch resistance and UV stability.
Key Differences Between Polycarbonate and Acrylic
Polycarbonate glass is significantly more impact-resistant, with strength approximately 250 times that of glass, making it ideal for safety applications, while acrylic glass offers superior scratch resistance and clarity, closely resembling real glass. Polycarbonate tends to yellow over time due to UV exposure unless specially treated, whereas acrylic has better UV stability and maintains its transparency longer outdoors. Cost-wise, acrylic is generally more affordable and easier to fabricate, but polycarbonate provides greater durability and flexibility for heavy-duty uses.
Strength and Impact Resistance
Polycarbonate glass offers superior strength and impact resistance compared to acrylic glass, making it ideal for applications requiring high durability and shatterproof properties. Acrylic glass is more prone to cracking under heavy impact but provides good clarity and scratch resistance for less demanding uses. When selecting materials for your project, consider polycarbonate for maximum toughness and safety requirements.
Clarity and Optical Properties
Polycarbonate glass offers excellent impact resistance and UV protection but has slightly lower optical clarity compared to acrylic glass, which provides superior transparency and light transmission rates up to 92%. Acrylic glass maintains better color stability and is less prone to yellowing over time, ensuring clearer visibility for longer periods. While polycarbonate is more scratch-resistant than standard acrylic, acrylic sheets deliver a crisper, clearer view ideal for applications demanding high optical quality.
Weight Comparison
Polycarbonate glass is significantly lighter than acrylic glass, making it an ideal choice for applications where reducing weight is crucial, such as in eyewear and protective gear. Your projects benefit from polycarbonate's weight efficiency without sacrificing strength, as it offers superior impact resistance compared to acrylic. Acrylic glass is heavier but often preferred for its superior scratch resistance and optical clarity in static displays.
Weather and UV Resistance
Polycarbonate glass excels in weather and UV resistance, maintaining clarity and impact strength even under prolonged exposure to sunlight and harsh environmental conditions. Acrylic glass offers good UV resistance but can degrade over time, becoming brittle and prone to yellowing when exposed to continuous sunlight. Your choice depends on the level of durability and long-term exposure resistance required for outdoor or high UV applications.
Ease of Fabrication and Installation
Polycarbonate glass offers superior ease of fabrication due to its higher impact resistance and flexibility, allowing for more intricate shapes without cracking. Acrylic glass, while easier to cut and polish, is more brittle and requires careful handling during installation to prevent damage. Your choice will depend on whether you prioritize durability and shaping ease or straightforward cutting and finishing.
Cost Analysis: Polycarbonate vs Acrylic
Polycarbonate glass typically costs more than acrylic glass due to its superior impact resistance and durability, making it a cost-effective choice for high-risk applications. Acrylic glass is more affordable, offering good clarity and weather resistance, suitable for budget-conscious projects with lower impact demands. You should weigh initial costs against long-term performance and maintenance when deciding between polycarbonate and acrylic materials.
Common Applications and Uses
Polycarbonate glass is widely used in safety equipment, automotive windshields, and protective barriers due to its high impact resistance and durability. Acrylic glass is preferred for display cases, signage, and decorative lighting because of its optical clarity and ease of fabrication. Your choice between these materials depends on whether you need enhanced strength or superior transparency for specific applications.
Which is Better: Polycarbonate or Acrylic?
Polycarbonate glass is better for impact resistance and durability, making it ideal for safety applications and environments with high risk of breakage. Acrylic glass offers superior optical clarity and scratch resistance, making it suitable for decorative and display purposes. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize toughness or visual quality.
polycarbonate glass vs acrylic glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com