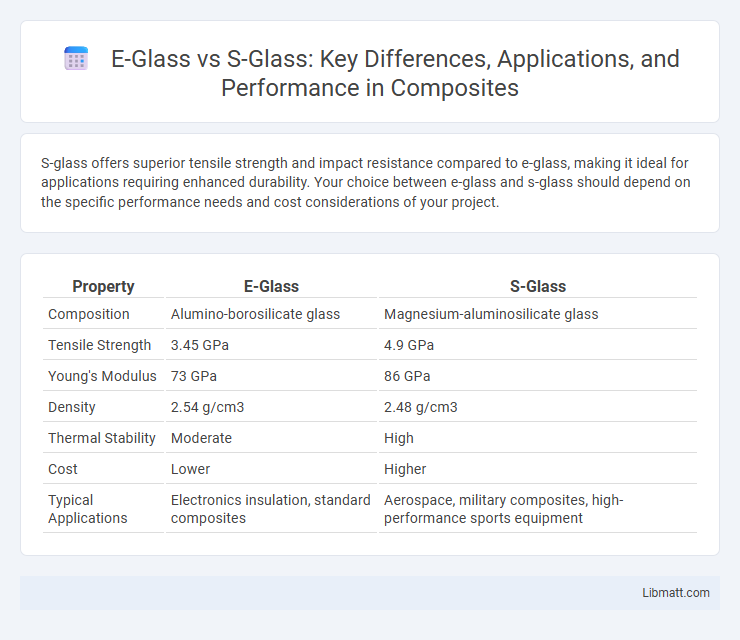
S-glass offers superior tensile strength and impact resistance compared to e-glass, making it ideal for applications requiring enhanced durability. Your choice between e-glass and s-glass should depend on the specific performance needs and cost considerations of your project.
Table of Comparison
| Property | E-Glass | S-Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Alumino-borosilicate glass | Magnesium-aluminosilicate glass |
| Tensile Strength | 3.45 GPa | 4.9 GPa |
| Young's Modulus | 73 GPa | 86 GPa |
| Density | 2.54 g/cm3 | 2.48 g/cm3 |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate | High |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Typical Applications | Electronics insulation, standard composites | Aerospace, military composites, high-performance sports equipment |
Introduction to E-Glass and S-Glass
E-glass, also known as electrical glass, is a type of fiberglass primarily composed of alumino-borosilicate glass, offering excellent electrical insulation and moderate tensile strength, making it ideal for use in electronics and reinforcement applications. S-glass, or structural glass, features a higher silica and alumina content, providing superior tensile strength and impact resistance compared to E-glass, which makes it suitable for aerospace, military, and high-performance composites. Both fibers serve distinct roles based on mechanical requirements and electrical properties, with E-glass favored for cost efficiency and insulation, while S-glass is chosen for enhanced durability and strength.
Chemical Composition of E-Glass vs S-Glass
E-glass primarily consists of approximately 54-56% silicon dioxide (SiO2), 12-16% aluminum oxide (Al2O3), and 16-25% calcium oxide (CaO), providing excellent electrical insulation and moderate strength. In contrast, S-glass contains a higher amount of silica (SiO2) around 63-65%, with increased magnesium oxide (MgO) and alumina (Al2O3) content, which results in enhanced tensile strength and impact resistance. Understanding the distinct chemical compositions of E-glass and S-glass helps you choose the right glass fiber for applications requiring specific mechanical and thermal properties.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
S-glass fibers exhibit superior mechanical properties compared to E-glass, including higher tensile strength ranging from 4.9 to 5.8 GPa versus E-glass's 3.4 to 4.8 GPa. The modulus of elasticity for S-glass is typically around 86 to 93 GPa, significantly greater than E-glass's 72 to 76 GPa, enhancing stiffness and durability in composite materials. These improved mechanical characteristics make S-glass particularly suitable for high-performance applications such as aerospace and military industries.
Thermal Performance Differences
S-glass fibers exhibit superior thermal performance compared to E-glass fibers, with higher melting points around 1740degC versus 1150degC for E-glass. This makes S-glass more suitable for applications requiring elevated temperature resistance and enhanced mechanical stability under thermal stress. E-glass is more cost-effective but less efficient in handling extreme thermal environments.
Electrical Insulation Capabilities
S-glass offers superior electrical insulation capabilities compared to e-glass due to its higher tensile strength and better resistance to electrical breakdown under high-voltage conditions. E-glass is widely used for general electrical insulation but may degrade faster in demanding environments with high thermal or mechanical stress. Your choice should consider the specific electrical insulation requirements and the durability needed for optimal performance in your application.
Applications in Composite Materials
E-glass is widely used in composite materials for applications such as automotive parts, marine structures, and wind turbine blades due to its excellent electrical insulation and cost-effectiveness. S-glass offers higher tensile strength and better impact resistance, making it ideal for aerospace components, ballistic armor, and high-performance sporting goods. Your choice between e-glass and s-glass depends on balancing budget and mechanical performance requirements in composite manufacturing.
Cost Analysis: E-Glass vs S-Glass
E-glass offers a more cost-effective solution for applications requiring good mechanical strength and insulation properties, typically priced lower due to its widespread availability and established manufacturing processes. S-glass, known for superior tensile strength and durability, carries a higher price point reflecting its advanced material performance, making it suitable for high-stress environments where reliability is critical. Your choice between E-glass and S-glass hinges on balancing budget constraints with performance requirements to optimize cost-efficiency in composite materials.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
S-glass offers superior durability and environmental resistance compared to e-glass, providing higher tensile strength and better performance in harsh conditions such as moisture, chemicals, and temperature fluctuations. You benefit from enhanced structural integrity and longer service life when choosing S-glass for demanding applications. E-glass remains cost-effective but is less resistant to mechanical stress and environmental degradation.
Weight and Density Considerations
E-glass fibers have a density of approximately 2.54 g/cm3, making them lighter than S-glass fibers, which typically have a density around 2.48 g/cm3 but offer higher tensile strength. Your choice between E-glass and S-glass impacts the overall weight and structural performance of composites, with S-glass providing enhanced strength-to-weight ratio despite slightly higher density. Considering these weight and density variations is crucial when optimizing materials for aerospace, automotive, or sporting applications.
Choosing the Right Glass Fiber for Your Needs
E-glass and S-glass fibers differ primarily in strength and durability, with E-glass offering excellent electrical insulation and cost-effectiveness for general applications, while S-glass provides superior tensile strength and impact resistance ideal for high-performance composites in aerospace and military industries. Selecting the right glass fiber depends on the specific mechanical properties required, environmental conditions, and budget constraints. Evaluating factors such as tensile modulus, chemical resistance, and application environment ensures optimal performance and longevity of the composite material.
e-glass vs s-glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com