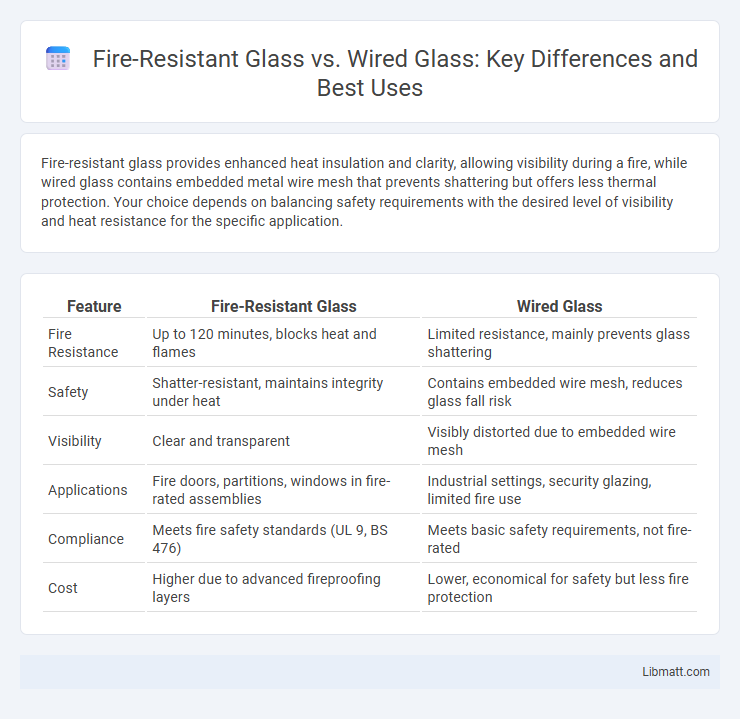
Fire-resistant glass provides enhanced heat insulation and clarity, allowing visibility during a fire, while wired glass contains embedded metal wire mesh that prevents shattering but offers less thermal protection. Your choice depends on balancing safety requirements with the desired level of visibility and heat resistance for the specific application.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fire-Resistant Glass | Wired Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Fire Resistance | Up to 120 minutes, blocks heat and flames | Limited resistance, mainly prevents glass shattering |
| Safety | Shatter-resistant, maintains integrity under heat | Contains embedded wire mesh, reduces glass fall risk |
| Visibility | Clear and transparent | Visibly distorted due to embedded wire mesh |
| Applications | Fire doors, partitions, windows in fire-rated assemblies | Industrial settings, security glazing, limited fire use |
| Compliance | Meets fire safety standards (UL 9, BS 476) | Meets basic safety requirements, not fire-rated |
| Cost | Higher due to advanced fireproofing layers | Lower, economical for safety but less fire protection |
Introduction to Fire-Resistant Glass and Wired Glass
Fire-resistant glass is engineered to withstand high temperatures and prevent the spread of fire and smoke, offering critical safety in buildings. Wired glass incorporates a metal mesh embedded within the glass to hold fragments in place during breakage and adds a degree of fire resistance, though typically less than dedicated fire-resistant glass. Both types serve essential roles in fire safety, with fire-resistant glass excelling in thermal protection and wired glass providing structural integrity under fire exposure.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Fire-resistant glass consists of multiple layers of specially formulated glass and intumescent interlayers designed to expand under heat, providing thermal insulation and preventing fire spread. Wired glass incorporates a steel wire mesh embedded within the glass during manufacturing, enhancing its structural integrity but offering less protection against heat transfer. Your choice affects fire safety performance, as fire-resistant glass excels in heat insulation, while wired glass primarily offers impact resistance.
Key Differences in Fire Performance
Fire-resistant glass provides superior fire protection with the ability to withstand high temperatures for extended periods, typically up to 120 minutes, while maintaining visibility and integrity. Wired glass, embedded with a metal mesh, offers basic fire resistance but often fails faster under extreme heat due to the wire's potential to conduct heat and spall. You should choose fire-resistant glass for critical fire-rated applications requiring longer exposure endurance and minimal compromise on clarity.
Impact Resistance and Safety Considerations
Fire-resistant glass offers superior impact resistance compared to wired glass, as it is engineered to withstand high forces without shattering, maintaining visibility and structural integrity during emergencies. Wired glass, while providing basic fire resistance through embedded metal mesh, is more prone to cracking or breaking upon impact, posing safety risks due to potential falling glass shards. Safety standards prioritize fire-resistant glass for critical applications to enhance both fire protection and occupant safety through improved durability and reduced injury hazards.
Visual Clarity and Design Flexibility
Fire-resistant glass offers superior visual clarity compared to wired glass, which can appear obscured due to embedded wire mesh. Your design flexibility increases with fire-resistant glass as it allows for larger, uninterrupted panes without compromising safety standards. This clarity and versatility make fire-resistant glass an ideal choice for modern architectural applications seeking both protection and aesthetic appeal.
Applications in Modern Architecture
Fire-resistant glass and wired glass serve distinct roles in modern architecture, with fire-resistant glass offering superior thermal protection and visibility in critical safety zones such as stairwells, corridors, and high-rise building facades. Wired glass, embedded with metal mesh, is primarily used for basic fire safety and vandal resistance but often compromises clarity and strength under high heat, limiting its application in contemporary design. Your choice depends on balancing transparency, fire-rating requirements, and the architectural aesthetic desired.
Compliance with Fire Safety Standards
Fire-resistant glass meets stringent fire safety standards such as ASTM E119 and UL 793, providing superior protection against heat and flame compared to wired glass, which typically complies with older standards like NFPA 80 but offers limited fire resistance. Wired glass can crack under heat stress, compromising its integrity, while fire-resistant glass maintains its structural stability during a fire, enhancing safety compliance. Ensuring Your building uses fire-resistant glass helps meet modern fire codes and improves overall fire protection effectiveness.
Cost Comparison and Long-Term Value
Fire-resistant glass typically costs more upfront than wired glass due to advanced technology and enhanced safety features. Over time, fire-resistant glass offers greater long-term value by providing superior heat resistance, improved visibility, and compliance with modern fire safety codes, reducing the need for replacements or upgrades. Your investment in fire-resistant glass ensures enhanced protection and potential insurance savings compared to the traditional yet less effective wired glass.
Pros and Cons of Fire-Resistant Glass vs Wired Glass
Fire-resistant glass offers superior clarity and maintains visibility during a fire while providing up to 120 minutes of fire protection, but its higher cost and fragility can be drawbacks. Wired glass is more affordable and provides decent fire resistance with embedded wire mesh for structural integrity, yet it distorts visibility and may release hot wire fragments under high heat. Both materials meet fire safety standards, but the choice depends on balancing visual clarity, fire rating requirements, budget, and application specifics.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Project
Fire-resistant glass offers superior heat insulation and visibility during fires, making it ideal for safety-critical applications that require compliance with strict building codes. Wired glass, embedded with a metal mesh, provides enhanced impact resistance but may compromise clarity and thermal performance, limiting its use in modern fire-rated installations. Your choice should balance safety requirements, aesthetic preferences, and regulatory standards to ensure optimal protection and functionality.
Fire-resistant glass vs wired glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com