Solar glass offers superior energy efficiency by filtering harmful UV rays and reducing heat transfer compared to standard glass, making it ideal for sustainable building designs. Your space gains enhanced insulation and natural light control, resulting in lower energy costs and increased comfort.
Table of Comparison
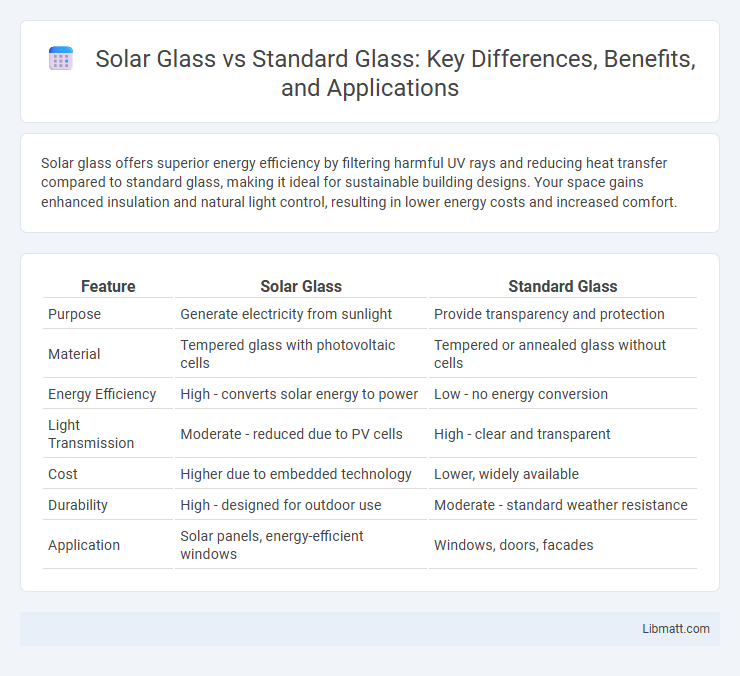
| Feature | Solar Glass | Standard Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Generate electricity from sunlight | Provide transparency and protection |
| Material | Tempered glass with photovoltaic cells | Tempered or annealed glass without cells |
| Energy Efficiency | High - converts solar energy to power | Low - no energy conversion |
| Light Transmission | Moderate - reduced due to PV cells | High - clear and transparent |
| Cost | Higher due to embedded technology | Lower, widely available |
| Durability | High - designed for outdoor use | Moderate - standard weather resistance |
| Application | Solar panels, energy-efficient windows | Windows, doors, facades |
Introduction to Solar Glass and Standard Glass
Solar glass integrates photovoltaic technology to convert sunlight into electricity while maintaining transparency, making it ideal for energy-efficient building facades and windows. Standard glass, typically made from silica-based materials, serves primarily as a passive barrier for insulation and visibility without energy generation capabilities. The key difference lies in solar glass's ability to harness solar energy, supporting sustainability goals in architectural design.
Key Differences Between Solar Glass and Standard Glass
Solar glass differs from standard glass primarily in its ability to harness and convert sunlight into energy through embedded photovoltaic cells, enhancing energy efficiency in building applications. Standard glass provides transparency and basic insulation without energy generation capabilities, making it suitable for conventional windows and facades. The durability and coating properties of solar glass are specially designed to maximize light absorption and minimize reflection, unlike standard glass which focuses mainly on clarity and weather resistance.
How Solar Glass Works
Solar glass works by incorporating photovoltaic cells or coatings that convert sunlight into electricity, enhancing energy efficiency compared to standard glass, which simply transmits light without energy conversion. This specialized glass often features anti-reflective and heat control properties, reducing heat loss and improving insulation in buildings. Your choice of solar glass can significantly reduce energy consumption by harnessing solar power while maintaining transparency and durability.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Solar glass outperforms standard glass in energy efficiency by significantly reducing heat transfer and enhancing insulation, leading to lower cooling and heating costs. Its specialized coatings reflect solar radiation while allowing natural light, maintaining indoor comfort and reducing reliance on HVAC systems. Your energy consumption decreases substantially with solar glass, making it a smart investment for sustainable and cost-effective building solutions.
Light Transmission and Transparency
Solar glass typically transmits around 70-85% of visible light, balancing transparency with energy efficiency by filtering infrared and ultraviolet rays. Standard glass offers higher light transmission, often exceeding 90%, providing clearer visibility but less control over heat and UV exposure. The slight reduction in transparency of solar glass contributes to improved thermal insulation and reduced glare, making it ideal for energy-conscious architectural applications.
Durability and Lifespan
Solar glass, engineered with reinforced coatings and tempered layers, offers superior durability compared to standard glass, resisting impacts, scratches, and harsh weather conditions more effectively. Its lifespan typically extends beyond 25 years, maintaining structural integrity and optical clarity essential for solar panel efficiency. Standard glass, lacking these specialized treatments, generally exhibits a shorter lifespan and higher susceptibility to environmental wear and mechanical damage.
Environmental Impact
Solar glass significantly reduces environmental impact by enhancing energy efficiency through increased solar panel performance, lowering carbon emissions compared to standard glass. It utilizes advanced coatings that maximize light transmission while minimizing heat loss, contributing to sustainable energy consumption. Unlike standard glass, solar glass supports renewable energy technologies, diminishing reliance on fossil fuels and reducing overall ecological footprint.
Cost Analysis: Solar Glass vs Standard Glass
Solar glass typically incurs higher upfront costs than standard glass due to advanced photovoltaic coatings and materials that generate electricity. Over time, the energy savings and potential incentives can offset the initial investment, making solar glass a more cost-effective choice for energy-conscious projects. Your long-term expenses will benefit from reduced electricity bills and increased property value when opting for solar glass.
Applications and Use Cases
Solar glass is engineered for use in photovoltaic panels and building-integrated photovoltaics, offering high transparency and durability to maximize solar energy conversion, making it ideal for renewable energy projects and eco-friendly architecture. Standard glass is mainly used in windows, doors, and facades, focusing on insulation, safety, and aesthetics without energy-harvesting properties. Your choice between solar glass and standard glass depends on whether energy generation or traditional glazing functions are prioritized in construction and design.
Future Trends in Glass Technology
Emerging trends in glass technology highlight solar glass's enhanced role in energy-efficient architecture, featuring advancements such as increased photovoltaic transparency and improved thermal insulation compared to standard glass. Innovations like bifacial solar glass and smart glass integration are set to revolutionize building facades by enabling dynamic solar energy harvesting and adaptive light control. The growing demand for sustainable construction materials is accelerating research into multifunctional solar glass that optimizes power generation while maintaining structural and aesthetic qualities.
solar glass vs standard glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com