Glass cladding offers a sleek, modern aesthetic with excellent natural light transmission and thermal insulation benefits, while aluminum cladding provides superior durability, corrosion resistance, and lightweight structural support. Your choice depends on balancing visual appeal with maintenance needs and environmental performance for your building project.
Table of Comparison
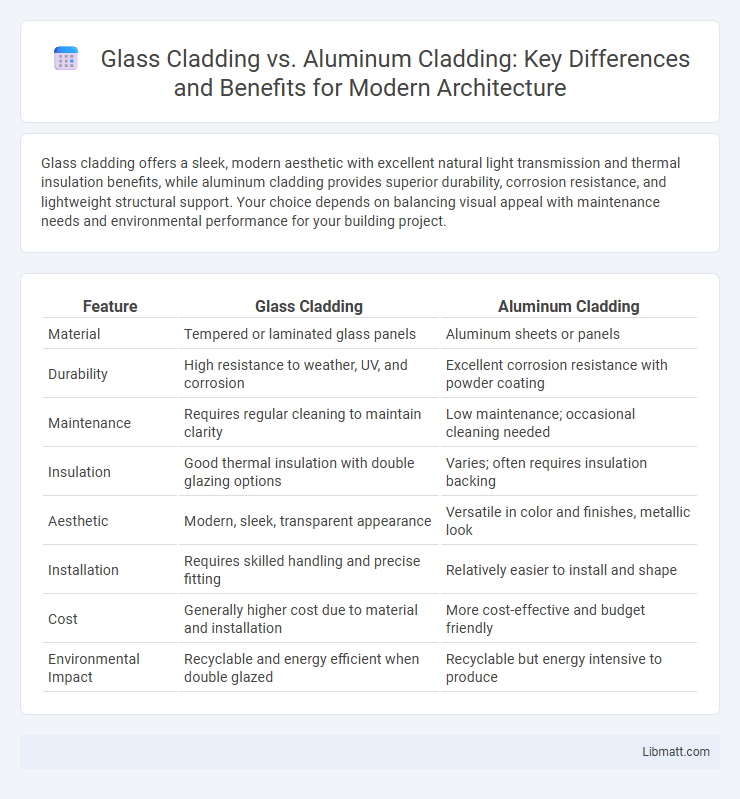
| Feature | Glass Cladding | Aluminum Cladding |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Tempered or laminated glass panels | Aluminum sheets or panels |
| Durability | High resistance to weather, UV, and corrosion | Excellent corrosion resistance with powder coating |
| Maintenance | Requires regular cleaning to maintain clarity | Low maintenance; occasional cleaning needed |
| Insulation | Good thermal insulation with double glazing options | Varies; often requires insulation backing |
| Aesthetic | Modern, sleek, transparent appearance | Versatile in color and finishes, metallic look |
| Installation | Requires skilled handling and precise fitting | Relatively easier to install and shape |
| Cost | Generally higher cost due to material and installation | More cost-effective and budget friendly |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable and energy efficient when double glazed | Recyclable but energy intensive to produce |
Introduction to Cladding: Glass vs Aluminum
Glass cladding offers a sleek, modern aesthetic with high transparency and natural light benefits, ideal for contemporary architecture, while aluminum cladding provides superior durability, lightweight properties, and excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for diverse climates and structural needs. Both materials enhance building insulation and weather protection, but your choice depends on the desired visual impact, maintenance requirements, and environmental conditions. Understanding the thermal performance and design flexibility of glass versus aluminum cladding helps optimize your building's energy efficiency and facade appeal.
Material Composition and Properties
Glass cladding consists primarily of tempered or laminated glass panels that provide excellent transparency, natural light transmission, and weather resistance, while aluminum cladding is made from lightweight, corrosion-resistant aluminum alloy sheets offering high durability and ease of fabrication. Glass panels provide superior thermal insulation and aesthetic appeal, whereas aluminum cladding offers enhanced impact resistance and requires less maintenance. Your choice between glass and aluminum cladding depends on the balance of visual design preferences, performance requirements, and structural support constraints.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Flexibility
Glass cladding offers a sleek, modern aesthetic with reflective and transparent qualities that enhance natural light and create visually dynamic facades, while aluminum cladding provides a versatile range of finishes and colors, allowing for custom designs with a lightweight and durable structure. You can achieve seamless, minimalist looks with glass panels, perfect for contemporary architecture, whereas aluminum's malleability supports intricate patterns and textured surfaces. Choosing between these materials depends on whether your priority is maximizing light interaction or exploring diverse design textures and colors.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Glass cladding offers excellent resistance to weathering and corrosion, maintaining its clarity and structural integrity for decades with minimal maintenance. Aluminum cladding is highly durable, featuring strong resistance to rust and impact, but may require periodic repainting or surface treatment to prevent oxidation over time. Your choice between glass and aluminum cladding should consider the desired balance between low maintenance longevity and resistance to physical damage.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Performance
Glass cladding offers superior thermal insulation with its ability to reduce heat transfer due to double or triple glazing technology, making it ideal for energy-efficient buildings. Aluminum cladding, while durable and lightweight, generally provides lower thermal insulation and requires additional insulation materials to match glass's performance. Your choice depends on prioritizing enhanced acoustic insulation, where glass cladding excels by significantly reducing external noise compared to aluminum's limited soundproofing capabilities.
Installation Process and Complexity
Glass cladding installation requires precise alignment and handling to ensure structural integrity and aesthetic appeal, often involving specialized frameworks and skilled labor for sealing and mounting. Aluminum cladding offers a more straightforward installation process, thanks to its lightweight nature and prefabricated panel systems, reducing labor time and complexity on-site. Your choice between these materials will influence project timelines and the need for expert installation teams.
Maintenance Requirements and Lifespan
Glass cladding requires regular cleaning to maintain its transparency and prevent stains but resists corrosion and weathering, offering a lifespan of 25 to 30 years with proper care. Aluminum cladding demands minimal maintenance due to its corrosion resistance and durable powder-coated finishes, typically lasting 40 to 50 years without significant degradation. Both materials benefit from periodic inspections, but aluminum's extended lifespan and lower upkeep costs make it a preferred choice for long-term durability.
Cost Analysis: Upfront and Long-Term
Glass cladding typically involves higher upfront costs due to specialized materials and installation techniques, but offers superior aesthetics and natural light benefits that can increase property value. Aluminum cladding is generally more cost-effective initially, with lower material and labor expenses, while providing excellent durability and low maintenance, which reduces long-term costs. Your choice depends on balancing initial investment with potential energy savings and maintenance expenses over the building's lifespan.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Glass cladding offers superior recyclability and energy efficiency by enhancing natural daylight usage and reducing HVAC loads, promoting sustainability in building design. Aluminum cladding, while lightweight and durable, requires high energy consumption in extraction and production but benefits from nearly 100% recyclability, lowering its environmental footprint over its lifecycle. Choosing between glass and aluminum cladding depends on balancing embodied energy, material recyclability, and long-term sustainability goals in construction projects.
Best Applications: Choosing the Right Cladding
Glass cladding excels in modern commercial buildings, offering high transparency and natural light penetration ideal for office facades and retail spaces. Aluminum cladding is preferred for industrial and residential applications due to its durability, lightweight properties, and resistance to corrosion. Selecting the right cladding depends on factors like aesthetic goals, weather resistance, thermal insulation, and structural requirements.
glass cladding vs aluminum cladding Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com