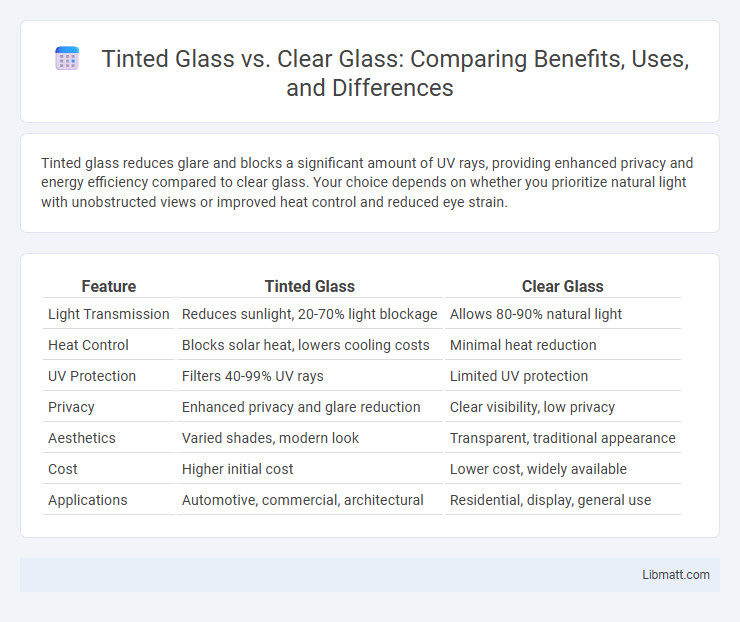
Tinted glass reduces glare and blocks a significant amount of UV rays, providing enhanced privacy and energy efficiency compared to clear glass. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize natural light with unobstructed views or improved heat control and reduced eye strain.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Tinted Glass | Clear Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Light Transmission | Reduces sunlight, 20-70% light blockage | Allows 80-90% natural light |
| Heat Control | Blocks solar heat, lowers cooling costs | Minimal heat reduction |
| UV Protection | Filters 40-99% UV rays | Limited UV protection |
| Privacy | Enhanced privacy and glare reduction | Clear visibility, low privacy |
| Aesthetics | Varied shades, modern look | Transparent, traditional appearance |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower cost, widely available |
| Applications | Automotive, commercial, architectural | Residential, display, general use |
Introduction to Tinted Glass and Clear Glass
Tinted glass reduces glare and improves energy efficiency by filtering sunlight, making it ideal for homes and vehicles seeking comfort and privacy. Clear glass offers maximum transparency and natural light transmission, suitable for unobstructed views and aesthetic clarity. Your choice between the two depends on balancing visibility needs with heat and light control preferences.
Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Tinted glass incorporates metal oxide or chemical additives during the molten stage, altering its color and reducing solar heat transmission compared to clear glass, which is made primarily from silica, soda ash, and limestone with no colorants. Manufacturing tinted glass involves adding precise amounts of colorants or films to achieve desired shading and UV protection levels, whereas clear glass undergoes fewer processing steps and lacks these modifications. The inclusion of these additives in tinted glass affects its thermal performance, light absorption, and structural properties distinctively from clear glass.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Flexibility
Tinted glass enhances aesthetic appeal by offering a sleek, modern look with customizable color options that reduce glare and improve privacy. Clear glass provides versatility in design with its transparent nature, allowing maximum natural light and unobstructed views, ideal for creating open, airy spaces. Combining both types allows architects to balance functionality and style, tailoring visual effects to specific environmental and design requirements.
Light Transmission and Visibility
Tinted glass reduces light transmission significantly, typically allowing only 20-40% of natural light to pass through, which enhances privacy and reduces glare but can slightly impair visibility, especially in low-light conditions. Clear glass offers maximum light transmission, often exceeding 80%, providing optimal visibility and natural illumination without color distortion. The choice between tinted and clear glass depends on the need for light control versus the desire for unobstructed views and brightness.
Energy Efficiency and Thermal Insulation
Tinted glass enhances energy efficiency by reducing solar heat gain, lowering cooling costs, and improving thermal insulation compared to clear glass. Its ability to block ultraviolet and infrared rays helps maintain a stable indoor temperature, reducing reliance on air conditioning. By choosing tinted glass, your space benefits from improved comfort and significant energy savings throughout the year.
Privacy and Security Considerations
Tinted glass enhances privacy by limiting visibility from the outside while allowing natural light to enter, making it ideal for residential and commercial spaces seeking discreet comfort. Clear glass offers minimal privacy, making interiors more exposed and requiring additional window treatments for security purposes. Your choice should balance aesthetic preferences with desired levels of privacy and protection against potential breaches.
UV Protection and Fading Prevention
Tinted glass offers superior UV protection compared to clear glass, effectively blocking up to 99% of harmful ultraviolet rays that cause skin damage and interior fading. Your furnishings, upholstery, and artwork remain vibrant longer with tinted glass, as it reduces the rate of color deterioration caused by prolonged sun exposure. Clear glass allows more UV penetration, increasing the risk of fading and potential damage over time.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Tinted glass requires less frequent cleaning than clear glass because it better conceals dirt, smudges, and water spots, reducing visible streaks and grime buildup. Clear glass needs more regular cleaning to maintain its transparency and aesthetic appeal, especially in high-traffic or dusty environments. Your choice between tinted and clear glass impacts the time and effort spent on maintenance, with tinted glass offering a more forgiving surface for busy lifestyles or commercial settings.
Cost Comparison and Installation Factors
Tinted glass generally incurs higher costs than clear glass due to added manufacturing processes and specialized coatings that enhance heat resistance and UV protection. Installation of tinted glass may require extra care and professional expertise to prevent damage or uneven appearance, potentially increasing labor expenses compared to clearer panes. Your choice should balance budget constraints with desired benefits like glare reduction and energy efficiency, considering both upfront investment and long-term savings.
Best Applications for Tinted vs Clear Glass
Tinted glass is ideal for reducing glare and heat gain in automotive windows, commercial buildings, and residential homes, enhancing energy efficiency and privacy. Clear glass is preferred in applications requiring maximum natural light and unobstructed views, such as storefronts, interior partitions, and skylights. Selecting between tinted and clear glass depends on balancing factors like light transmission, solar control, and aesthetic preferences for each specific use.
tinted glass vs clear glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com