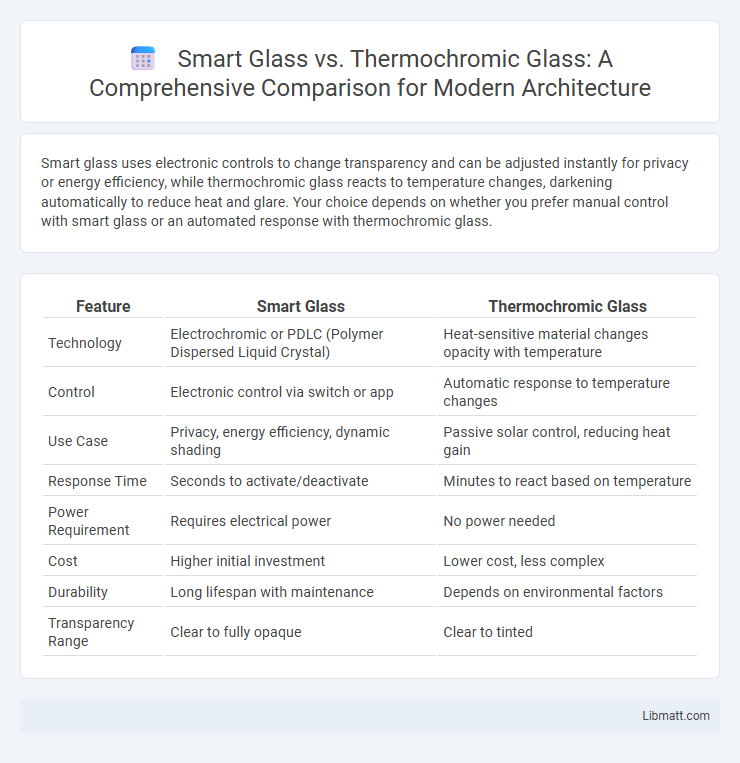
Smart glass uses electronic controls to change transparency and can be adjusted instantly for privacy or energy efficiency, while thermochromic glass reacts to temperature changes, darkening automatically to reduce heat and glare. Your choice depends on whether you prefer manual control with smart glass or an automated response with thermochromic glass.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Smart Glass | Thermochromic Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Electrochromic or PDLC (Polymer Dispersed Liquid Crystal) | Heat-sensitive material changes opacity with temperature |
| Control | Electronic control via switch or app | Automatic response to temperature changes |
| Use Case | Privacy, energy efficiency, dynamic shading | Passive solar control, reducing heat gain |
| Response Time | Seconds to activate/deactivate | Minutes to react based on temperature |
| Power Requirement | Requires electrical power | No power needed |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower cost, less complex |
| Durability | Long lifespan with maintenance | Depends on environmental factors |
| Transparency Range | Clear to fully opaque | Clear to tinted |
Introduction to Smart Glass and Thermochromic Glass
Smart glass utilizes electrochromic technology to control light transmission through electrical voltage, offering dynamic tint adjustment and energy efficiency in buildings and vehicles. Thermochromic glass changes its transparency based on temperature variations by incorporating heat-sensitive materials that react to sunlight intensity, reducing glare and heat gain passively. Both technologies enhance comfort and energy savings but operate through distinct mechanisms: active electrical control in smart glass versus passive temperature response in thermochromic glass.
How Smart Glass Works
Smart glass operates by using embedded liquid crystals, suspended particles, or electrochromic materials that alter light transmission when an electrical voltage is applied, enabling instant control over transparency and glare. Thermochromic glass changes its properties based on temperature fluctuations, using heat-sensitive coatings that darken or lighten in response to solar heat, without electrical input. Your choice between smart glass and thermochromic glass depends on whether you need precise, on-demand control or passive, temperature-driven tinting.
How Thermochromic Glass Functions
Thermochromic glass functions by changing its tint in response to temperature variations, utilizing materials that alter their optical properties when heated. This technology relies on thermochromic coatings or films that become darker as the glass temperature rises, reducing solar heat gain and glare. Unlike smart glass, which typically requires electrical input to adjust transparency, thermochromic glass operates passively, providing energy-efficient climate control without external power.
Key Differences Between Smart Glass and Thermochromic Glass
Smart glass uses electrical voltage to control transparency, enabling instant switching between clear and tinted states, while thermochromic glass relies on temperature changes to alter its tint gradually. Smart glass offers precise control and rapid response times suited for energy-efficient buildings, whereas thermochromic glass provides passive modulation of solar heat without external power. The key distinction lies in smart glass's active, user-controlled functionality versus thermochromic glass's passive, temperature-dependent behavior.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Smart glass utilizes electrochromic technology to dynamically control solar heat gain, reducing cooling costs by up to 20% in commercial buildings. Thermochromic glass reacts passively to temperature changes, offering consistent energy savings during peak sunlight but less control overall. Your choice depends on whether active energy management or passive, maintenance-free efficiency aligns better with your building's needs.
Applications and Use Cases
Smart glass is widely used in commercial buildings, automotive windows, and healthcare facilities for its ability to switch between transparent and opaque states through electronic controls, offering privacy and energy efficiency. Thermochromic glass finds applications in residential and office buildings where temperature-sensitive tinting helps reduce solar heat gain, enhancing comfort and lowering cooling costs without requiring external power. Your choice depends on whether you need instant, user-controlled opacity or passive temperature-responsive shading.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Smart glass installation involves integrating electronic components, such as wiring and control systems, requiring professional expertise to ensure proper functionality and safety. Thermochromic glass, relying on temperature-sensitive coatings, generally demands simpler installation without electrical connections but may require periodic inspection of coating integrity. Maintenance for smart glass includes monitoring electrical systems and occasional calibration, while thermochromic glass maintenance focuses on preserving coating performance and preventing physical damage.
Cost Analysis and ROI
Smart glass typically has higher upfront costs due to advanced electronic components and installation complexity, while thermochromic glass offers a lower initial investment by utilizing passive temperature-sensitive materials. Your return on investment (ROI) for smart glass can be accelerated through energy savings and dynamic light control, which reduces HVAC and lighting expenses more significantly than thermochromic glass. Cost analysis should consider maintenance, lifespan, and energy efficiency, with smart glass generally providing greater long-term financial benefits for commercial buildings despite the higher initial price.
Aesthetic and Design Flexibility
Smart glass offers superior aesthetic and design flexibility through its ability to switch transparencies with the touch of a button, enabling dynamic control over light and privacy without altering the window structure. Thermochromic glass relies on temperature changes to transition, providing a natural and subtle visual effect but limiting control and customization in design. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize active, customizable aesthetics or passive, energy-responsive design elements.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Project
Smart glass offers precise control over transparency through electrical signals, making it ideal for projects requiring instant privacy or dynamic light management. Thermochromic glass changes tint based on temperature, providing passive energy savings by reducing heat gain without additional power. Consider your project's need for active versus passive control, installation costs, and desired energy efficiency to choose the right glass for your specific application.
smart glass vs thermochromic glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com