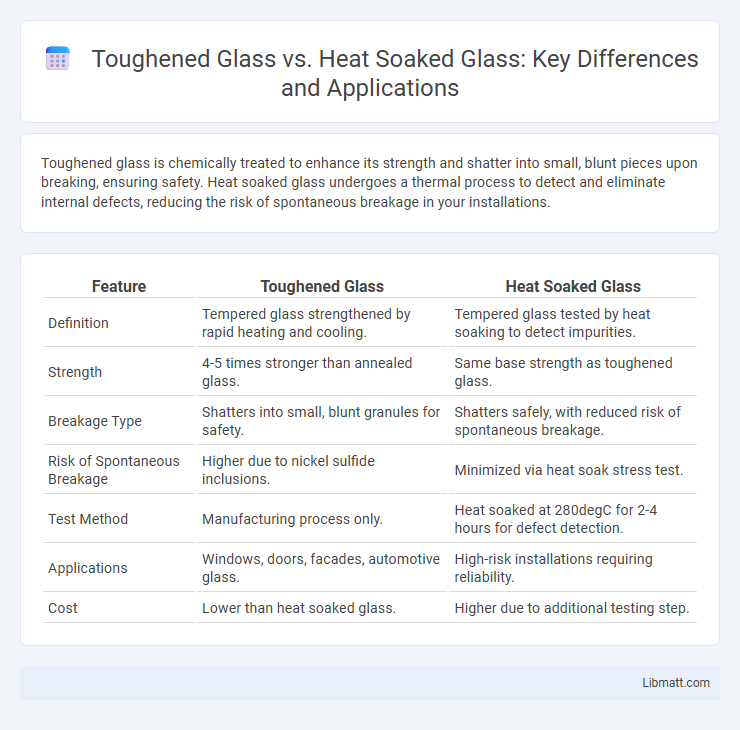
Toughened glass is chemically treated to enhance its strength and shatter into small, blunt pieces upon breaking, ensuring safety. Heat soaked glass undergoes a thermal process to detect and eliminate internal defects, reducing the risk of spontaneous breakage in your installations.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Toughened Glass | Heat Soaked Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Tempered glass strengthened by rapid heating and cooling. | Tempered glass tested by heat soaking to detect impurities. |
| Strength | 4-5 times stronger than annealed glass. | Same base strength as toughened glass. |
| Breakage Type | Shatters into small, blunt granules for safety. | Shatters safely, with reduced risk of spontaneous breakage. |
| Risk of Spontaneous Breakage | Higher due to nickel sulfide inclusions. | Minimized via heat soak stress test. |
| Test Method | Manufacturing process only. | Heat soaked at 280degC for 2-4 hours for defect detection. |
| Applications | Windows, doors, facades, automotive glass. | High-risk installations requiring reliability. |
| Cost | Lower than heat soaked glass. | Higher due to additional testing step. |
Introduction to Toughened and Heat Soaked Glass
Toughened glass is tempered through rapid cooling after heating, resulting in enhanced strength and resistance to impact compared to standard annealed glass. Heat soaked glass undergoes an additional process where it is subjected to prolonged high temperatures to detect and eliminate nickel sulfide inclusions, reducing the risk of spontaneous breakage. Both processes improve safety and durability, but toughened glass focuses on strength, while heat soaked glass emphasizes flaw detection.
What is Toughened Glass?
Toughened glass, also known as tempered glass, is a type of safety glass processed by controlled heating and rapid cooling to increase its strength compared to ordinary glass. It is designed to shatter into small, blunt pieces rather than sharp shards, minimizing injury risk upon breakage. Commonly used in automotive windows, building facades, and shower doors, toughened glass offers enhanced durability and heat resistance.
What is Heat Soaked Glass?
Heat soaked glass is a type of toughened glass that undergoes an additional heat treatment to identify and eliminate nickel sulfide inclusions, which can cause spontaneous breakage. This process involves heating the glass to around 280-310degC in a controlled environment, inducing stress that causes defective panes to break before installation. Your choice of heat soaked glass enhances safety and reliability by reducing the risk of unexpected glass failure in architectural and automotive applications.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Toughened glass undergoes a rapid quenching process after heating to approximately 620degC, creating surface compression and internal tension that enhance its strength and resistance to impact. Heat soaked glass is a type of toughened glass subjected to a controlled heat soak test at around 290degC for several hours to identify and reduce the risk of spontaneous breakage caused by nickel sulfide inclusions. These manufacturing differences ensure that heat soaked glass has undergone additional quality assurance to minimize failure in critical architectural applications.
Strength and Safety Differences
Toughened glass undergoes rapid cooling to increase its strength, making it approximately four to five times stronger than regular glass and resistant to impact and thermal stress. Heat soaked glass, however, is a type of toughened glass that undergoes an additional heat soak test to detect and eliminate chemically tempered glass prone to spontaneous breakage due to nickel sulfide inclusions. While both offer enhanced safety, heat soaked glass provides superior reliability by minimizing the risk of unexpected shattering in architectural and structural applications.
Spontaneous Breakage: Causes and Risks
Toughened glass undergoes rapid cooling during manufacturing to enhance strength but remains susceptible to spontaneous breakage caused by nickel sulfide inclusions expanding under temperature changes. Heat soaked glass undergoes an additional testing phase where panes are exposed to elevated temperatures to induce failures caused by such inclusions before installation, significantly reducing the risk of in-service spontaneous breakage. Understanding these processes is crucial for applications requiring high safety standards, such as building facades and balustrades, where spontaneous breakage can pose serious hazards.
Applications: Where Each Glass Type Excels
Toughened glass excels in applications requiring high impact resistance and safety, such as automobile windows, shower doors, and commercial building facades. Heat soaked glass is specifically designed to reduce the risk of spontaneous breakage caused by nickel sulfide inclusions, making it ideal for structural glazing and overhead glazing where reliability is critical. Your choice between these glass types depends on whether impact resistance or fracture prevention is the primary concern in your application.
Cost Considerations
Toughened glass generally costs less than heat soaked glass due to its simpler manufacturing process. Heat soaked glass involves an additional heat treatment step to detect and eliminate nickel sulfide inclusions, increasing production time and expenses. The higher price of heat soaked glass reflects its enhanced safety and reduced risk of spontaneous breakage, which can be critical in building applications requiring stringent safety standards.
Industry Standards and Certifications
Toughened glass adheres to industry standards such as ASTM C1048 and EN 12150, ensuring its strength and safety through thermal tempering processes. Heat soaked glass undergoes additional testing following standards like BS EN 14179-1 to detect nickel sulphide inclusions, minimizing spontaneous breakage risks. Certifications for both types often include CE marking in Europe and compliance with ANSI Z97.1 in the United States, confirming their suitability for structural and safety applications.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Project
Toughened glass offers high strength and safety through rapid cooling during manufacturing, making it ideal for general applications requiring impact resistance. Heat soaked glass undergoes an additional treatment to reduce the risk of spontaneous breakage due to nickel sulfide inclusions, ensuring greater reliability in structural and safety-critical projects. Understanding your project's specific safety requirements helps you choose between the robust performance of toughened glass and the enhanced fracture prevention of heat soaked glass.
toughened glass vs heat soaked glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com