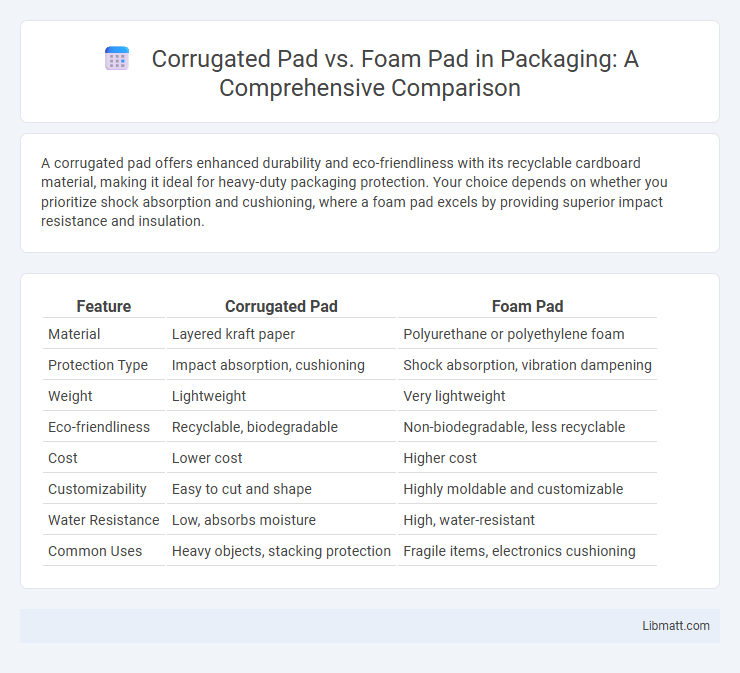
A corrugated pad offers enhanced durability and eco-friendliness with its recyclable cardboard material, making it ideal for heavy-duty packaging protection. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize shock absorption and cushioning, where a foam pad excels by providing superior impact resistance and insulation.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Corrugated Pad | Foam Pad |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Layered kraft paper | Polyurethane or polyethylene foam |
| Protection Type | Impact absorption, cushioning | Shock absorption, vibration dampening |
| Weight | Lightweight | Very lightweight |
| Eco-friendliness | Recyclable, biodegradable | Non-biodegradable, less recyclable |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Customizability | Easy to cut and shape | Highly moldable and customizable |
| Water Resistance | Low, absorbs moisture | High, water-resistant |
| Common Uses | Heavy objects, stacking protection | Fragile items, electronics cushioning |
Introduction to Packaging Pads
Corrugated pads and foam pads serve vital roles in protective packaging by cushioning and stabilizing products during transit. Corrugated pads offer rigidity and impact resistance through multiple layers of fluted cardboard, ideal for heavy or sharp-edged items. Foam pads provide superior shock absorption and flexibility, making them suitable for delicate or irregularly shaped goods.
What is a Corrugated Pad?
A corrugated pad is a protective packaging material made from layers of corrugated fiberboard, designed to provide cushioning and support for fragile items during shipping and storage. Its multi-layered, fluted structure ensures excellent shock absorption and impact resistance, making it ideal for safeguarding heavy or irregularly shaped products. Compared to foam pads, corrugated pads offer better rigidity and recyclability while maintaining effective protection.
What is a Foam Pad?
A foam pad is a cushioning material made from various foam types such as polyurethane or polyethylene, designed to absorb shock and provide comfort or protection in packaging and seating applications. Compared to corrugated pads, foam pads offer superior resilience and flexibility, adapting to irregular shapes and reducing impact more effectively. You can choose a foam pad when enhanced cushioning and vibration dampening are critical for safeguarding fragile or sensitive items.
Key Material Differences
Corrugated pads are made from layered paperboard with fluted inner structures that provide strength and rigidity, making them ideal for cushioning and protecting items during shipping. Foam pads consist of polyurethane or polyethylene foam, offering superior shock absorption and flexibility for delicate or lightweight products. Your choice depends on the level of protection needed and the nature of the items being packed.
Durability and Protection Levels
Corrugated pads offer excellent durability with their rigid structure, providing superior protection against heavy impacts and compression during shipping. Foam pads deliver enhanced cushioning by absorbing shocks and vibrations, making them ideal for delicate or fragile items. Combining both materials can optimize protection by balancing structural support with effective impact absorption.
Cost Comparison: Corrugated vs Foam
Corrugated pads generally offer a more cost-effective solution compared to foam pads due to lower raw material and production expenses, making them ideal for budget-conscious packaging. Foam pads provide superior cushioning and shock absorption but come at a higher price point, often justified for fragile or high-value items. Your choice should balance cost efficiency with protection needs to achieve optimal packaging performance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Corrugated pads are typically more environmentally friendly than foam pads due to their biodegradability and recyclability, significantly reducing landfill waste. Foam pads, often made from non-biodegradable petrochemicals, contribute to long-term environmental pollution and are less sustainable. Choosing corrugated pads supports your commitment to sustainability by minimizing ecological footprints and promoting renewable resource use.
Applications and Industry Usage
Corrugated pads are prevalent in the packaging and shipping industries due to their lightweight, recyclable, and cost-effective nature, providing cushioning and edge protection for heavy or irregularly shaped items. Foam pads find extensive use in electronics, medical, and automotive industries where delicate components require superior shock absorption and insulation properties. Both materials serve critical roles in protecting goods, with corrugated pads favored for sustainability and foam pads preferred for high-impact resistance and versatility.
Pros and Cons of Corrugated Pads
Corrugated pads offer excellent durability and environmental benefits due to their recyclable and biodegradable materials, making them ideal for sustainable packaging solutions. They provide strong cushioning and impact resistance but may lack the softness and shock absorption qualities of foam pads, which can be crucial for delicate items. Corrugated pads are cost-effective and lightweight but can absorb moisture, potentially weakening their protective properties in humid conditions.
Pros and Cons of Foam Pads
Foam pads offer excellent cushioning and shock absorption, making them ideal for delicate or fragile items during shipping. However, their higher cost and limited environmental sustainability compared to corrugated pads can be drawbacks for eco-conscious businesses. Foam pads also tend to retain moisture, potentially affecting the integrity of stored products, unlike the more breathable corrugated alternatives.
Corrugated pad vs foam pad Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com