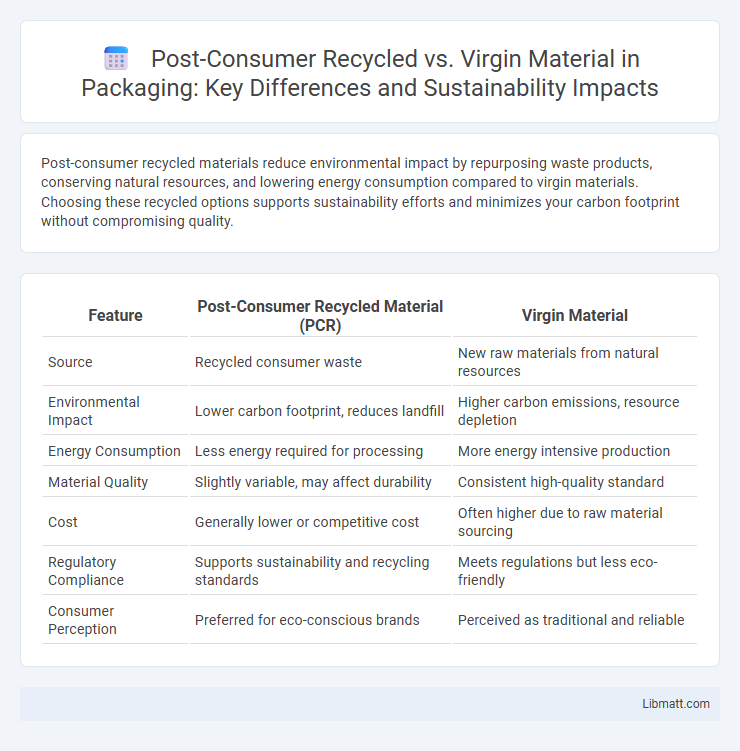
Post-consumer recycled materials reduce environmental impact by repurposing waste products, conserving natural resources, and lowering energy consumption compared to virgin materials. Choosing these recycled options supports sustainability efforts and minimizes your carbon footprint without compromising quality.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Post-Consumer Recycled Material (PCR) | Virgin Material |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Recycled consumer waste | New raw materials from natural resources |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint, reduces landfill | Higher carbon emissions, resource depletion |
| Energy Consumption | Less energy required for processing | More energy intensive production |
| Material Quality | Slightly variable, may affect durability | Consistent high-quality standard |
| Cost | Generally lower or competitive cost | Often higher due to raw material sourcing |
| Regulatory Compliance | Supports sustainability and recycling standards | Meets regulations but less eco-friendly |
| Consumer Perception | Preferred for eco-conscious brands | Perceived as traditional and reliable |
Introduction to Post-Consumer Recycled and Virgin Materials
Post-consumer recycled (PCR) materials are derived from products that have completed their initial lifecycle and been processed for reuse, reducing waste and conserving natural resources. Virgin materials refer to raw, naturally-sourced inputs that have never been used or processed before, often resulting in higher environmental impact due to extraction and manufacturing. Understanding the distinctions between PCR and virgin materials helps you make sustainable choices by balancing quality, cost, and environmental responsibility.
Defining Post-Consumer Recycled Materials
Post-consumer recycled materials consist of products that have been used by consumers and then collected for recycling, reducing waste and conserving natural resources. These materials differ from virgin materials, which are newly extracted and processed from raw resources such as petroleum, minerals, or forests. Utilizing post-consumer recycled content in manufacturing decreases environmental impact by lowering energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions compared to sourcing virgin materials.
Understanding Virgin Materials
Virgin materials are raw resources extracted directly from natural reserves without prior industrial use, ensuring maximum purity and performance consistency for manufacturing. These materials often provide superior strength and structural integrity, making them essential for applications requiring high durability and quality standards. In contrast to post-consumer recycled materials, virgin materials typically have fewer impurities and lower contamination risks, resulting in more predictable processing and end-product outcomes.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Post-consumer recycled materials significantly reduce environmental impact by lowering greenhouse gas emissions, conserving natural resources, and reducing landfill waste compared to virgin materials. Virgin material production requires extensive mining, deforestation, and higher energy consumption, leading to increased carbon footprint and ecosystem disruption. Utilizing post-consumer recycled content supports circular economy principles and enhances resource efficiency in manufacturing processes.
Production Process Differences
Post-consumer recycled materials undergo a different production process compared to virgin materials, involving collection, sorting, cleaning, and reprocessing of used products to create usable raw materials. Virgin material production requires extraction from natural resources followed by refining and manufacturing, which can consume more energy and generate higher emissions. Your choice between these materials impacts environmental sustainability by influencing resource depletion and manufacturing footprints.
Cost Analysis: Recycled vs Virgin Materials
Post-consumer recycled materials typically offer cost savings compared to virgin materials due to reduced raw material extraction and lower energy consumption during production. However, fluctuations in supply availability and sorting expenses can affect the overall price competitiveness of recycled content. Your choice between recycled and virgin materials should consider long-term economic benefits alongside environmental impact and market demand trends.
Performance and Quality Considerations
Post-consumer recycled materials often exhibit slightly lower mechanical strength and durability compared to virgin materials due to potential contamination and polymer degradation during recycling. Virgin materials provide consistent performance with superior purity, making them ideal for applications requiring high structural integrity and aesthetic quality. Advances in recycling technology continue to narrow the quality gap, enabling recycled materials to meet stricter performance standards in various industries.
Market Trends and Consumer Preferences
Post-consumer recycled materials are gaining significant traction in the market due to increasing consumer demand for sustainable and eco-friendly products. Brands investing in recycled content often see enhanced customer loyalty and positive brand perception, reflecting a broader trend toward environmental responsibility. Understanding these market dynamics can help you align product strategies with evolving consumer preferences for greener alternatives.
Regulatory Framework and Certifications
Post-consumer recycled materials are increasingly favored under global regulatory frameworks such as the EU Circular Economy Action Plan and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency guidelines, which promote waste reduction and sustainable resource use. Certifications like the Global Recycled Standard (GRS) and Recycled Content Certification (RCC) verify the percentage and ethical sourcing of recycled content, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations. Virgin materials, while traditionally unrestricted, face rising scrutiny under tightening policies aimed at reducing carbon footprints and encouraging material reuse.
Future Outlook for Sustainable Material Choices
Post-consumer recycled materials reduce environmental impact by lowering carbon emissions and conserving natural resources compared to virgin materials, making them vital for sustainable manufacturing. Advances in recycling technology and increasing regulatory pressures will drive wider adoption of recycled content across industries such as packaging, textiles, and construction. The future outlook emphasizes circular economy models and innovation in material recovery to enhance quality and performance, accelerating the shift from virgin to recycled feedstocks.
Post-consumer recycled vs virgin material Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com