Overwrapping involves enclosing products in a continuous film, providing a sealed and protective layer often used for multipacks or bundling, while flow wrapping uses a horizontal or vertical flow wrapper to tightly seal individual items in plastic, ensuring freshness and tamper evidence. Your choice depends on product type, packaging speed requirements, and the desired presentation or protection level.
Table of Comparison
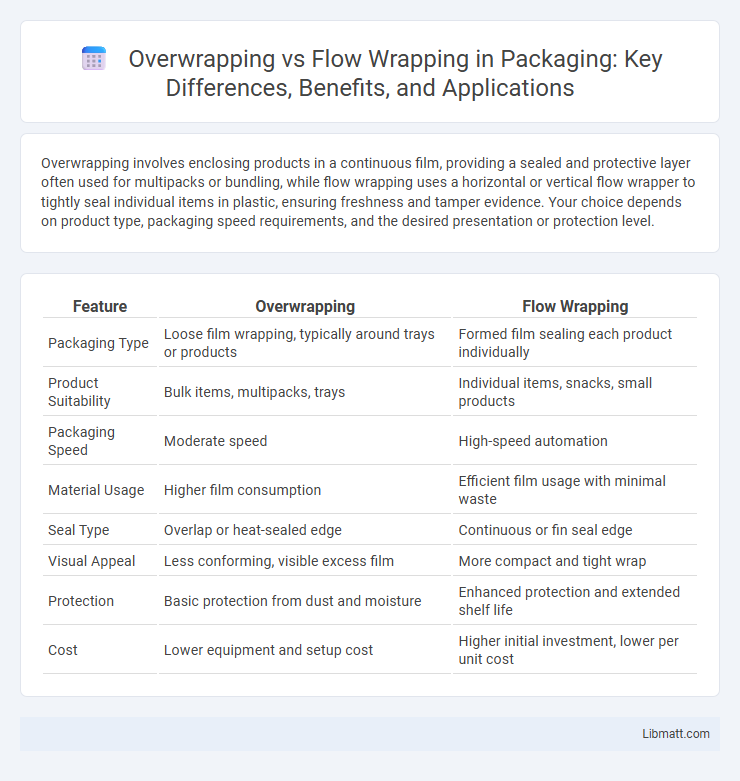
| Feature | Overwrapping | Flow Wrapping |
|---|---|---|
| Packaging Type | Loose film wrapping, typically around trays or products | Formed film sealing each product individually |
| Product Suitability | Bulk items, multipacks, trays | Individual items, snacks, small products |
| Packaging Speed | Moderate speed | High-speed automation |
| Material Usage | Higher film consumption | Efficient film usage with minimal waste |
| Seal Type | Overlap or heat-sealed edge | Continuous or fin seal edge |
| Visual Appeal | Less conforming, visible excess film | More compact and tight wrap |
| Protection | Basic protection from dust and moisture | Enhanced protection and extended shelf life |
| Cost | Lower equipment and setup cost | Higher initial investment, lower per unit cost |
Introduction to Overwrapping and Flow Wrapping
Overwrapping and flow wrapping are two prominent packaging methods used for securing products efficiently. Overwrapping involves enclosing items with a film that is folded and sealed around the product's exterior, commonly used for bundling multiple units. Flow wrapping, however, wraps products in a continuous film using a horizontal wrapper that seals both ends, ideal for individual items and maintaining freshness.
Definition and Process of Overwrapping
Overwrapping is a packaging method where a film is wrapped around a product, usually with the edges sealed on the bottom or side, creating a protective and tamper-evident covering. The process involves feeding the product into a web of film, which wraps around it before being sealed and cut to form individual packages. This technique is commonly used for products like biscuits, books, and other items requiring clear visibility and protection.
Definition and Process of Flow Wrapping
Flow wrapping is a packaging process where a product is wrapped continuously in a flexible film that is heat-sealed along the edges, creating a hermetic enclosure. This method involves feeding the product into the film web, forming a tube around it, and sealing both longitudinal and transverse ends with a flow wrapper machine. Your choice of flow wrapping optimizes packaging speed and product protection, especially for items like confectionery, bakery goods, and medical devices.
Key Differences Between Overwrapping and Flow Wrapping
Overwrapping involves placing a product between two separate films, typically heat-sealed at the edges, ideal for flat or box-shaped items, whereas flow wrapping encloses products in a continuous roll of film, sealed longitudinally and transversely, suitable for irregular shapes. Overwrapping provides a rigid, tamper-evident package with visible product presentation, while flow wrapping offers flexible, cost-effective packaging with enhanced barrier properties. The choice depends on product shape, packaging speed, and desired shelf appeal, with overwrapping often used for multi-packs and flow wrapping preferred for single, high-volume items.
Packaging Materials Used in Overwrapping
Packaging materials used in overwrapping primarily include polyethylene (PE), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and polypropylene (PP) films, chosen for their clarity, flexibility, and protective properties. These films are typically heat-sealed around products, providing a tamper-evident barrier that preserves freshness and prevents contamination. Overwrapping materials are often coated or laminated for enhanced moisture resistance and can range from thin shrink films to thicker wrap films depending on the product requirements.
Packaging Materials Used in Flow Wrapping
Flow wrapping predominantly utilizes flexible packaging materials such as polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), and laminated films that offer excellent sealing properties and product visibility. These materials provide moisture resistance and durability, making them suitable for various food items, pharmaceuticals, and consumer goods. The choice of material in flow wrapping directly influences the packaging's barrier performance, shelf life, and overall product protection.
Applications and Industry Use Cases
Overwrapping is widely used in food packaging, especially for products like baked goods, confectionery, and frozen foods, where airtight protection and extended shelf life are essential. Flow wrapping finds extensive application in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) due to its high-speed operation and ability to form custom-sized packages around irregularly shaped items. Both techniques are integral in manufacturing and distribution sectors, optimizing packaging efficiency and product presentation across diverse industries.
Advantages of Overwrapping
Overwrapping offers superior product protection by creating a tight, tamper-evident seal that enhances shelf life and maintains freshness. Its versatility accommodates a range of product shapes and sizes, making it ideal for businesses aiming to optimize packaging efficiency and reduce material waste. You benefit from improved aesthetics and branding opportunities through clear, smooth film presentation that enhances consumer appeal.
Advantages of Flow Wrapping
Flow wrapping offers superior product protection by creating a hermetic seal that extends shelf life and prevents contamination. Its high-speed operation enhances packaging efficiency, making it ideal for large-scale production runs. You benefit from its versatility in accommodating various shapes and sizes, ensuring consistent quality and visual appeal.
Choosing the Right Wrapping Method for Your Needs
Overwrapping provides excellent product visibility and protection, making it ideal for retail items that require clear branding and tamper evidence. Flow wrapping offers a more flexible, efficient solution suitable for high-speed packaging of irregularly shaped products, ensuring tight, airtight seals. Selecting the right method depends on factors like product shape, packaging speed, shelf appeal, and material cost efficiency.
Overwrapping vs flow wrapping Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com