Acid sizing uses acidic chemicals to improve paper strength and printability but can lead to equipment corrosion and environmental concerns, whereas neutral sizing relies on neutral or alkaline agents providing better durability, reduced yellowing, and compatibility with modern digital printing processes. Understanding the difference helps you choose the right paper treatment for specific printing needs and long-term preservation.
Table of Comparison
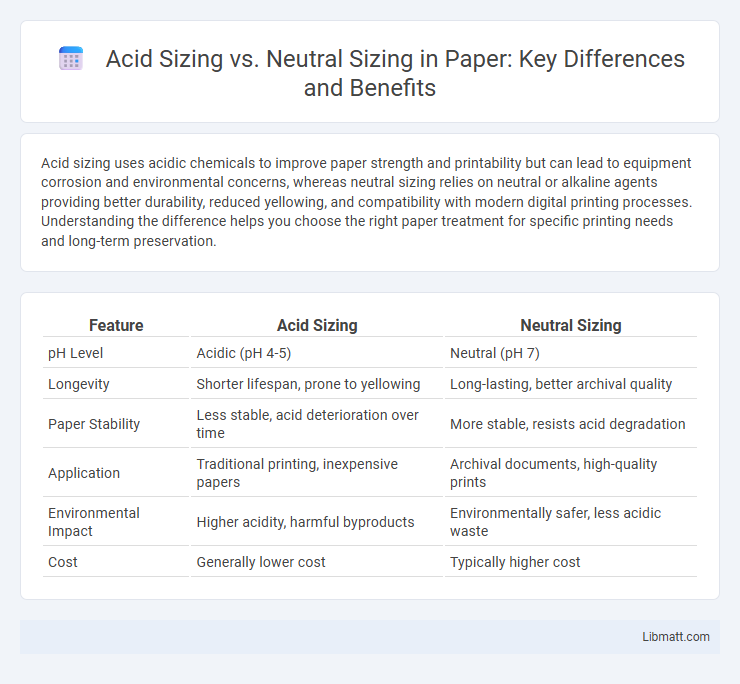
| Feature | Acid Sizing | Neutral Sizing |
|---|---|---|
| pH Level | Acidic (pH 4-5) | Neutral (pH 7) |
| Longevity | Shorter lifespan, prone to yellowing | Long-lasting, better archival quality |
| Paper Stability | Less stable, acid deterioration over time | More stable, resists acid degradation |
| Application | Traditional printing, inexpensive papers | Archival documents, high-quality prints |
| Environmental Impact | Higher acidity, harmful byproducts | Environmentally safer, less acidic waste |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Typically higher cost |
Introduction to Paper Sizing
Acid sizing and neutral sizing are essential processes in paper manufacturing that influence the paper's resistance to water and ink absorption. Acid sizing uses alum and rosin to improve surface strength and printability but can cause paper to become brittle over time due to acidity. Neutral sizing employs synthetic sizing agents like alkyl ketene dimer (AKD) or alkenyl succinic anhydride (ASA), providing better durability and stability, which is crucial for your archival and high-quality printing needs.
What is Acid Sizing?
Acid sizing is a chemical treatment process in papermaking where acidic compounds, typically rosin and alum, are added to the pulp to improve the paper's resistance to water and ink absorption. This method enhances surface strength and printability by creating a hydrophobic layer on the fibers. Your choice between acid sizing and neutral sizing depends on the desired paper qualities and compatibility with modern, environmentally friendly processes.
What is Neutral Sizing?
Neutral sizing is a paper manufacturing process used to improve the surface properties of paper by applying neutral or slightly alkaline chemicals, typically with pH values around 7, to enhance ink receptivity and print quality. Unlike acid sizing, which uses acidic agents like alum and rosin causing paper to become brittle over time, neutral sizing employs synthetic resins such as alkyl ketene dimer (AKD) or alkenyl succinic anhydride (ASA) that provide durable resistance to water and improve paper longevity. This method supports environmentally sustainable manufacturing practices by reducing acid-related degradation and is favored in producing high-quality, archival-grade papers.
Chemical Composition Differences
Acid sizing primarily involves aluminum salts such as aluminum sulfate combined with rosin, forming hydrophobic barriers in paper fibers. Neutral sizing uses synthetic chemicals like alkyl ketene dimer (AKD) or alkenyl succinic anhydride (ASA), which react differently, providing sizing without affecting paper acidity. Your paper's intended use plays a key role in choosing between these chemical compositions for optimal durability and archival quality.
Impact on Paper Durability
Acid sizing reduces paper durability by accelerating cellulose degradation, leading to brittleness and yellowing over time. Neutral sizing, using neutral or alkaline chemicals, significantly enhances paper longevity by preventing acid hydrolysis and maintaining fiber strength. Your choice of sizing directly affects archival quality and the lifespan of paper products.
Environmental Considerations
Acid sizing typically uses aluminum sulfate and rosin, which can generate acidic wastewater requiring careful treatment to prevent environmental harm. Neutral sizing employs synthetic polymers like AKD or ASA, producing less acidic effluent and offering improved biodegradability, reducing ecological impact. Choosing neutral sizing enhances water recycling potential and aligns with stricter environmental regulations on pH and chemical discharge.
Effect on Printing and Writing Quality
Acid sizing enhances ink absorption and drying speed, resulting in sharper and more vibrant printing with reduced smudging on coated papers. Neutral sizing maintains pH stability, preventing paper degradation and ensuring consistent writing quality by minimizing ink feathering and bleed-through on uncoated papers. Optimal printing and writing performance depends on selecting the appropriate sizing type matched to the paper's intended use and ink formulation.
Cost Comparison
Acid sizing typically incurs higher costs due to the need for specialized chemicals and equipment to handle acidic conditions, increasing overall production expenses. Neutral sizing uses less corrosive agents, resulting in lower maintenance and safety costs, making it more economical for many paper manufacturing processes. Your choice depends on balancing material compatibility and budget constraints, with neutral sizing generally offering a more cost-effective solution.
Industry Applications
Acid sizing is primarily used in industries requiring enhanced surface strength and water resistance, such as papermaking, textiles, and packaging, due to its ability to improve fiber bonding and printability. Neutral sizing finds applications in environments where pH stability is critical, including food packaging and archival paper production, because it minimizes acid-related degradation and promotes long-term durability. The choice between acid and neutral sizing significantly impacts product performance, shelf life, and environmental compliance across various industrial sectors.
Choosing the Right Sizing Method
Selecting the appropriate sizing method depends on the desired fabric properties and production requirements; acid sizing offers enhanced fiber adhesion and strength for cotton and synthetic blends, while neutral sizing provides better compatibility with sensitive fibers and reduces equipment corrosion. Consider factors such as fabric type, pH sensitivity, and end-use performance to optimize sizing effectiveness and durability. Evaluating sizing agent composition, application conditions, and environmental impact ensures efficient processing and improved fabric quality.
Acid sizing vs neutral sizing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com