Bagasse pulp, derived from sugarcane residue, offers an eco-friendly alternative with high yield and good fiber strength, making it suitable for paper and packaging applications. Bamboo pulp, on the other hand, provides longer fibers that enhance paper durability and smoothness, ideal for fine printing and textiles; choosing between them depends on your specific product requirements and sustainability goals.
Table of Comparison
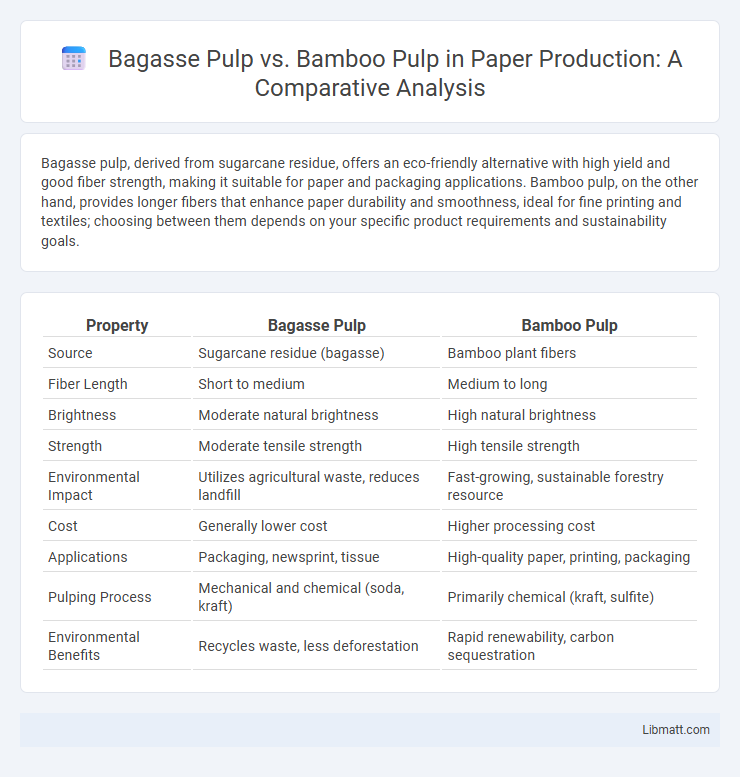
| Property | Bagasse Pulp | Bamboo Pulp |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Sugarcane residue (bagasse) | Bamboo plant fibers |
| Fiber Length | Short to medium | Medium to long |
| Brightness | Moderate natural brightness | High natural brightness |
| Strength | Moderate tensile strength | High tensile strength |
| Environmental Impact | Utilizes agricultural waste, reduces landfill | Fast-growing, sustainable forestry resource |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher processing cost |
| Applications | Packaging, newsprint, tissue | High-quality paper, printing, packaging |
| Pulping Process | Mechanical and chemical (soda, kraft) | Primarily chemical (kraft, sulfite) |
| Environmental Benefits | Recycles waste, less deforestation | Rapid renewability, carbon sequestration |
Introduction to Bagasse Pulp and Bamboo Pulp
Bagasse pulp, derived from the fibrous residue left after extracting sugarcane juice, offers an eco-friendly alternative to traditional wood pulp with high cellulose content ideal for paper production. Bamboo pulp originates from fast-growing bamboo species, prized for its strength, sustainability, and minimal environmental impact during harvesting and processing. Understanding the unique properties of both bagasse pulp and bamboo pulp helps optimize your choice for sustainable paper and packaging applications.
Source Materials: Bagasse vs Bamboo
Bagasse pulp is derived from the fibrous residue left after extracting juice from sugarcane stalks, making it an agricultural byproduct abundant in tropical regions. Bamboo pulp originates from bamboo plants, a fast-growing grass species with high cellulose content, commonly found in Asia and increasingly cultivated globally for sustainable fiber production. The choice between bagasse and bamboo as source materials impacts fiber length, pulp yield, and environmental sustainability in paper manufacturing.
Pulping Process: Methods and Differences
Bagasse pulp is produced primarily through chemical pulping methods like the soda and kraft processes, which remove lignin and hemicellulose to yield a fibrous material from sugarcane residue. Bamboo pulp undergoes similar chemical pulping but often employs mechanical and semi-chemical methods due to bamboo's dense and fibrous structure, requiring more intensive processing to break down lignin content. Your choice between bagasse and bamboo pulp depends on desired fiber properties and production costs linked to these distinct pulping techniques.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bagasse pulp, derived from sugarcane residue, offers a sustainable alternative by utilizing agricultural waste and reducing deforestation, while bamboo pulp is highly renewable due to bamboo's rapid growth and minimal water requirements. Both materials contribute to lower carbon footprints compared to traditional wood pulp, but bagasse pulp often benefits regions with abundant sugarcane production, promoting waste valorization and local economies. Your choice between these pulps can significantly influence environmental outcomes, especially in terms of land use efficiency and resource regeneration cycles.
Physical and Chemical Properties Comparison
Bagasse pulp typically exhibits lower brightness and higher lignin content compared to bamboo pulp, which results in a slightly coarser texture and reduced fiber strength. Bamboo pulp generally has longer fibers and higher cellulose content, contributing to better tensile strength and tear resistance in the final paper products. Understanding these physical and chemical differences helps you select the right pulp for manufacturing applications requiring specific durability and smoothness characteristics.
Paper Quality: Strength, Brightness, and Texture
Bagasse pulp produces paper with moderate strength and a smooth texture, often featuring lower brightness due to higher lignin content compared to bamboo pulp. Bamboo pulp yields paper with superior strength, enhanced brightness, and a naturally fibrous texture attributed to its longer cellulose fibers. The choice between bagasse and bamboo pulp significantly impacts the paper's durability, whiteness, and surface feel, influencing applications in printing, packaging, and specialty paper products.
Cost Efficiency and Production Scalability
Bagasse pulp offers higher cost efficiency due to its utilization of sugarcane waste, reducing raw material expenses and supporting sustainable production. Bamboo pulp provides greater scalability, as bamboo grows rapidly and can be harvested multiple times a year, ensuring a steady and abundant fiber supply for large-scale manufacturing. Both fibers optimize production based on regional resource availability, influencing the economic viability of paper and textile industries.
Applications in the Paper Industry
Bagasse pulp, derived from sugarcane residue, is extensively used in producing packaging materials, tissue paper, and printing paper due to its high cellulose content and brightness. Bamboo pulp, known for its rapid growth and sustainability, is favored in manufacturing high-quality paper products such as writing paper, tissue, and specialty papers with superior strength and smoothness. Both pulps contribute to eco-friendly paper production, with bagasse pulp offering cost-effective solutions and bamboo pulp enhancing durability and fiber quality in the paper industry.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Pulp
Bagasse pulp presents challenges such as lower fiber strength and higher silica content, which can cause equipment wear and affect paper quality. Bamboo pulp's limitations include its high lignin content that requires more intensive chemical treatment, increasing production costs and environmental impact. You must consider these factors when choosing between bagasse and bamboo pulp for sustainable paper manufacturing.
Future Trends and Market Potential
Bagasse pulp, derived from sugarcane residue, offers sustainable advantages and is gaining traction in eco-friendly packaging and paper products, while bamboo pulp is valued for its rapid growth and high fiber strength, making it a preferred choice in textile and paper industries. Emerging market trends indicate increasing demand for biodegradable and renewable materials, driving innovation in both pulp types for specialty and high-performance applications. Your investment in bagasse or bamboo pulp aligns with the growing global emphasis on circular economy and resource-efficient manufacturing.
Bagasse pulp vs bamboo pulp Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com