Wet pressing uses water to soften and shape materials, resulting in a smoother surface and reduced dust, ideal for ceramics and paper production. Dry pressing compacts powders without moisture, offering faster processing and better control for dense, uniform products in ceramics and metallurgy.
Table of Comparison
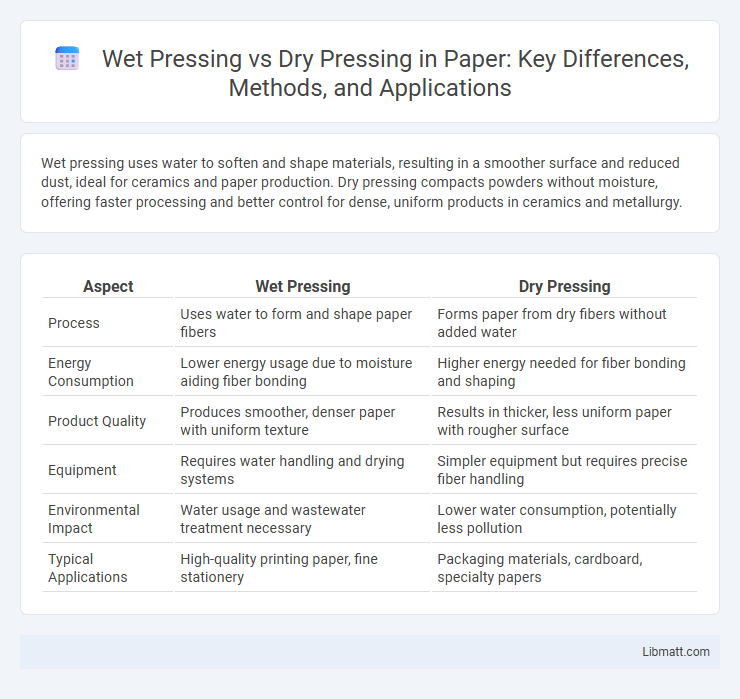
| Aspect | Wet Pressing | Dry Pressing |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Uses water to form and shape paper fibers | Forms paper from dry fibers without added water |
| Energy Consumption | Lower energy usage due to moisture aiding fiber bonding | Higher energy needed for fiber bonding and shaping |
| Product Quality | Produces smoother, denser paper with uniform texture | Results in thicker, less uniform paper with rougher surface |
| Equipment | Requires water handling and drying systems | Simpler equipment but requires precise fiber handling |
| Environmental Impact | Water usage and wastewater treatment necessary | Lower water consumption, potentially less pollution |
| Typical Applications | High-quality printing paper, fine stationery | Packaging materials, cardboard, specialty papers |
Introduction to Wet Pressing and Dry Pressing
Wet pressing and dry pressing are two fundamental techniques used in material compaction and shaping, particularly in ceramics and paper manufacturing. Wet pressing involves applying pressure to a slurry or moist material, enhancing density and strength by removing excess liquid, which results in improved structural integrity and uniformity. Dry pressing compacts dry powders under high pressure without added moisture, providing precise dimensional control and is widely used for producing dense, complex-shaped components in industrial applications.
Overview of Wet Pressing Process
Wet pressing involves applying pressure to a moist material to remove excess water, enhancing density and strength before drying. This process is commonly used in paper manufacturing, ceramic production, and metal powder compaction to improve product uniformity and reduce drying time. The controlled moisture content during pressing allows for better moldability and structural integrity in the final product.
Overview of Dry Pressing Process
Dry pressing involves compacting powdered materials into a desired shape using high pressure without the addition of liquid binders, leading to improved dimensional control and reduced drying times. This process is commonly used in the manufacturing of ceramics, metal powders, and pharmaceuticals, where consistent density and mechanical strength are critical. The absence of moisture eliminates shrinkage and cracking during drying, making dry pressing ideal for producing complex, high-precision components.
Key Differences Between Wet Pressing and Dry Pressing
Wet pressing involves the use of water to reduce moisture content and enhance fiber bonding during paper or textile manufacturing, resulting in higher density and improved strength. Dry pressing, by contrast, applies mechanical pressure without added water, yielding faster processing but often producing materials with lower density and durability. The choice between wet and dry pressing depends on the desired product properties, production speed, and cost efficiency.
Material Suitability for Wet Pressing vs Dry Pressing
Wet pressing is ideal for materials with high moisture content such as pulp fibers, clay, and ceramic slurries, as it effectively removes water and increases density. Dry pressing suits powders and granular materials like metal powders, ceramics, and pharmaceutical ingredients that require compacting without moisture. Selecting between wet and dry pressing depends on the material's moisture level, particle size, and deformation characteristics.
Advantages of Wet Pressing
Wet pressing improves pulp sheet formation by removing more water efficiently, resulting in higher fiber consolidation and stronger paper quality. The process reduces energy consumption during drying due to higher initial moisture removal, enhancing overall production efficiency. Wet pressing also minimizes fiber damage, maintaining better paper strength and uniformity compared to dry pressing.
Advantages of Dry Pressing
Dry pressing offers advantages such as reduced energy consumption since it eliminates the need for water evaporation, leading to faster production cycles and lower operational costs. This method enables precise control over shape and density, producing parts with consistent mechanical properties and minimal shrinkage. It also reduces environmental impact by minimizing water use and wastewater generation compared to wet pressing processes.
Applications of Wet Pressing in Industry
Wet pressing is extensively used in the paper manufacturing industry to enhance fiber bonding and improve sheet density before drying, resulting in stronger and smoother paper products. In ceramic production, wet pressing enables uniform compaction of powder mixtures, facilitating the creation of complex shapes with high mechanical strength and minimal defects. This method also finds applications in metal powder processing, where it helps achieve better particle cohesion and improved structural integrity in sintered components.
Applications of Dry Pressing in Industry
Dry pressing is extensively used in the ceramics and powder metallurgy industries for shaping metal powders and ceramic materials into complex, high-density components with minimal moisture content. This method offers precise control over the material's density and structural integrity, making it ideal for manufacturing automotive parts, electronic substrates, and cutting tools. Dry pressing enables cost-effective mass production of durable components with consistent quality, especially when moisture-sensitive materials are involved.
Choosing the Right Pressing Method for Your Needs
Wet pressing offers superior dewatering efficiency and higher pulp density, making it ideal for applications requiring rapid moisture removal and enhanced sheet formation. Dry pressing provides better control over sheet thickness and surface smoothness, suitable for materials sensitive to moisture or requiring uniform texture. Selecting the right pressing method depends on factors such as material properties, desired product quality, and production speed.
Wet pressing vs dry pressing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com