Dusting involves the physical removal of dust particles from surfaces, improving cleanliness and air quality, while linting refers to the process of cleaning or removing small fibers and debris from fabrics to maintain garment appearance. Understanding the difference helps you choose the appropriate method for maintaining both your physical environment and clothing.
Table of Comparison
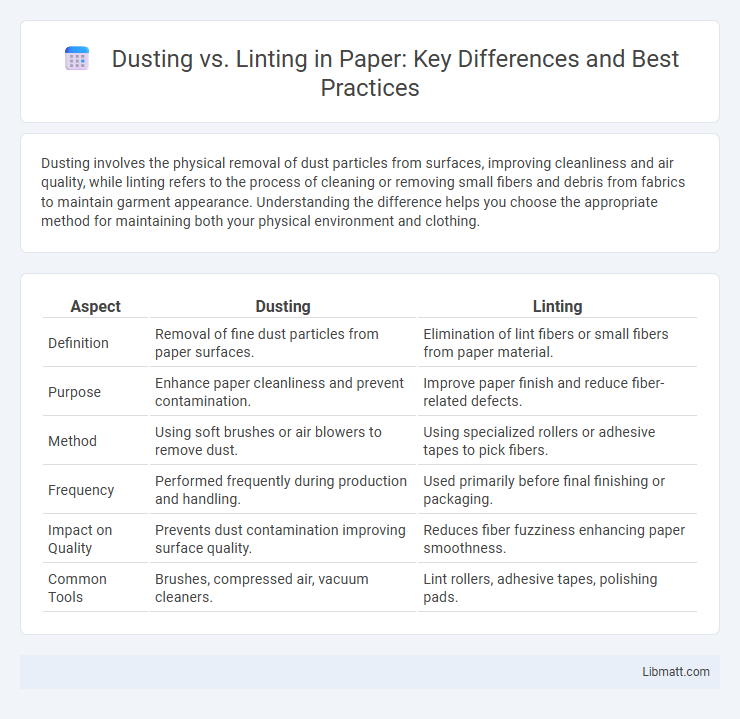
| Aspect | Dusting | Linting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Removal of fine dust particles from paper surfaces. | Elimination of lint fibers or small fibers from paper material. |
| Purpose | Enhance paper cleanliness and prevent contamination. | Improve paper finish and reduce fiber-related defects. |
| Method | Using soft brushes or air blowers to remove dust. | Using specialized rollers or adhesive tapes to pick fibers. |
| Frequency | Performed frequently during production and handling. | Used primarily before final finishing or packaging. |
| Impact on Quality | Prevents dust contamination improving surface quality. | Reduces fiber fuzziness enhancing paper smoothness. |
| Common Tools | Brushes, compressed air, vacuum cleaners. | Lint rollers, adhesive tapes, polishing pads. |
Introduction to Dusting and Linting
Dusting and linting are essential code quality practices that help maintain clean, efficient, and error-free software projects. Dusting refers to the process of removing unnecessary or redundant code and files, improving overall project clarity, while linting involves analyzing source code to detect syntax errors, bugs, or stylistic issues using automated tools. You can enhance your development workflow by integrating both dusting and linting techniques to ensure optimal code performance and maintainability.
What Is Dusting?
Dusting is the process of removing loose dust, dirt, and allergens from surfaces using tools like microfiber cloths, dusters, or vacuum attachments. It targets visible particles and helps maintain cleanliness in homes or offices by preventing dust buildup on furniture, electronics, and other items. Effective dusting improves indoor air quality and reduces the risk of allergies and respiratory issues.
Understanding Linting
Linting is a static code analysis process that helps identify and fix potential errors, code smells, and stylistic inconsistencies before runtime. It improves code quality by enforcing coding standards and preventing bugs, making your development workflow more efficient. Unlike dusting, which involves cleaning surfaces, linting targets source code to ensure it meets predefined guidelines and best practices.
Key Differences Between Dusting and Linting
Dusting involves manually removing visible dust particles from surfaces, whereas linting refers to the automated process of analyzing source code to identify and flag programming errors, bugs, stylistic issues, and suspicious constructs. Dusting is primarily a physical cleaning task targeting environmental cleanliness, while linting is a software development practice aimed at improving code quality and consistency. The key difference lies in their application domains: dusting addresses physical maintenance, while linting enhances code reliability and maintainability through static code analysis tools.
Tools and Materials Needed
Dusting requires microfiber cloths, feather dusters, or electrostatic dusters designed to trap and remove fine particles from surfaces. Linting involves the use of lint rollers, adhesive tapes, or fabric brushes specifically made to lift and collect lint, pet hair, and fibers from clothing and upholstery. Both tasks benefit from tools that enhance particle capture while minimizing surface damage.
Step-by-Step Dusting Techniques
Step-by-step dusting techniques involve starting from the highest surfaces such as shelves or ceiling fans, working downward to prevent re-soiling cleaned areas. Use microfiber cloths or electrostatic dusters to effectively capture dust particles rather than dispersing them into the air. Regular dusting of vents, baseboards, and hidden corners ensures a thorough clean and improves indoor air quality.
Effective Linting Methods
Effective linting methods involve configuring tools like ESLint or Pylint with precise rule sets tailored to your project's coding standards, ensuring consistent code quality and error detection. Integrating linting into your continuous integration pipeline automates code analysis, catching syntax errors and potential bugs early in the development process. You can enhance code maintainability and reduce technical debt by combining linting with automated formatting tools such as Prettier.
Pros and Cons of Dusting vs Linting
Dusting removes surface dust particles, quickly improving air quality and appearance but may not eliminate allergens or finer debris, requiring frequent repetition. Linting, often involving a lint roller or brush, efficiently captures hair, fibers, and smaller particles, making it ideal for fabrics and upholstery, though it may be less effective on large surfaces or heavy dust accumulation. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize speed and surface cleanliness (dusting) or thorough fabric care and allergen removal (linting).
Choosing the Right Method for Your Needs
Choosing between dusting and linting depends on the surface type and the nature of the debris. Dusting is ideal for removing loose particles from delicate surfaces without causing damage, while linting efficiently captures fibers and pet hair from fabrics and upholstery. Evaluating your cleaning priority ensures your method maintains cleanliness and prolongs the life of your belongings.
Maintenance Tips for a Dust- and Lint-Free Environment
Regular dusting with microfiber cloths captures fine particles effectively, reducing allergens and preventing buildup, while lint removal from fabrics and surfaces keeps your environment clean and polished. Maintaining air purifiers and vacuuming with HEPA filters further minimizes airborne dust and lint accumulation. You can enhance overall cleanliness by scheduling frequent cleaning routines focused on these targeted dust and lint control methods.
Dusting vs linting Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com