Cardboard typically refers to a general category of thick paper-based materials, while corrugated board features a layered structure with a fluted corrugated sheet sandwiched between linerboards, providing enhanced strength and durability. Choosing corrugated board for packaging ensures better protection and support for your items during shipping compared to standard cardboard options.
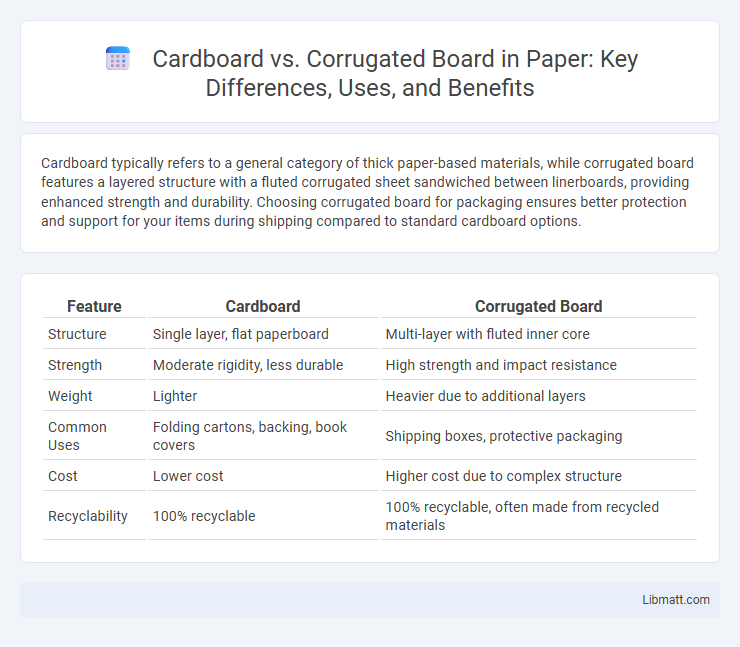
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cardboard | Corrugated Board |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Single layer, flat paperboard | Multi-layer with fluted inner core |
| Strength | Moderate rigidity, less durable | High strength and impact resistance |
| Weight | Lighter | Heavier due to additional layers |
| Common Uses | Folding cartons, backing, book covers | Shipping boxes, protective packaging |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to complex structure |
| Recyclability | 100% recyclable | 100% recyclable, often made from recycled materials |
Introduction to Cardboard and Corrugated Board
Cardboard and corrugated board serve distinct purposes in packaging and shipping industries. Cardboard is typically a single-layer, rigid material used for lightweight packaging, while corrugated board consists of a fluted corrugated sheet sandwiched between two linerboards, offering enhanced strength and cushioning. Understanding the differences in structure helps you choose the appropriate material for protecting and presenting your products effectively.
Defining Cardboard: Composition and Uses
Cardboard refers to a broad category of heavy paper-based materials, typically consisting of multiple layers of paper pulp pressed together to form a solid sheet. It is commonly used for packaging, stationery, and craft projects due to its lightweight and versatile nature. Unlike corrugated board, which features a fluted inner layer for added strength, cardboard's simpler composition makes it ideal for applications requiring moderate durability and rigidity.
What is Corrugated Board? Structure and Properties
Corrugated board consists of a fluted corrugated sheet sandwiched between two flat linerboards, providing enhanced strength and rigidity compared to standard cardboard. Its multi-layered structure offers excellent cushioning and resistance to compression, making it ideal for protective packaging applications. Key properties include lightweight durability, moisture resistance, and the ability to absorb shocks during transportation.
Key Differences Between Cardboard and Corrugated Board
Cardboard is a broad term referring to various heavy-duty paper-based materials, often single-layered and lacking internal structure. Corrugated board specifically features a fluted corrugated sheet sandwiched between two linerboards, providing enhanced strength, cushioning, and durability for packaging. This structural difference results in corrugated board being preferred for shipping and protection, while cardboard is commonly used for lightweight or decorative purposes.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Corrugated board offers superior strength and durability compared to standard cardboard due to its multi-layered construction, which includes a fluted inner layer sandwiched between two flat linerboards. This design provides enhanced resistance to crushing, bending, and impacts, making corrugated board ideal for shipping and heavy-duty packaging applications. In contrast, regular cardboard is typically thinner and less rigid, suitable for lightweight packaging and basic protective uses.
Typical Applications in Packaging
Cardboard is commonly used for lightweight packaging applications such as cereal boxes, shoe boxes, and product displays, offering a smooth surface ideal for printing and branding. Corrugated board is preferred for shipping and protective packaging, providing strength and durability for heavy or fragile items like electronics, appliances, and industrial goods. Your choice depends on the level of protection required and the nature of the product being packaged.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Corrugated board offers superior sustainability compared to regular cardboard due to its structure of multiple layers, which increases durability and recyclability. Made primarily from recycled paper fibers, corrugated board reduces waste and supports circular economy practices. Its lightweight design lowers transportation emissions, making it an environmentally friendly packaging solution in the logistics industry.
Cost Analysis and Budget Considerations
Cardboard typically costs less than corrugated board, making it a budget-friendly option for lightweight or short-term packaging needs. Corrugated board offers enhanced durability and protection, which can reduce damage-related expenses despite its higher price. Balancing your budget involves evaluating the trade-off between initial material costs and potential savings from reduced product damage.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Needs
Cardboard typically refers to a single layer of thick paper-based material, ideal for lightweight packaging and craft projects. Corrugated board consists of a fluted corrugated sheet sandwiched between two linerboards, offering superior strength and durability for shipping and heavy-duty protection. Selecting between cardboard and corrugated board depends on factors such as required strength, weight capacity, and the nature of the items to be packaged or shipped.
Conclusion: Cardboard vs Corrugated Board
Corrugated board offers superior strength and durability compared to regular cardboard, making it ideal for packaging heavy or fragile items. Cardboard, being thinner and less rigid, is more suitable for lightweight packaging or crafting purposes. Your choice depends on the required protection level and the specific application of the material.
Cardboard vs corrugated board Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com