Coated paper offers a smooth, glossy surface ideal for vibrant images and sharp text, enhancing the visual impact of your printed materials. Uncoated paper provides a natural, tactile feel with better ink absorption, making it perfect for designs that require a matte finish and a more organic appearance.
Table of Comparison
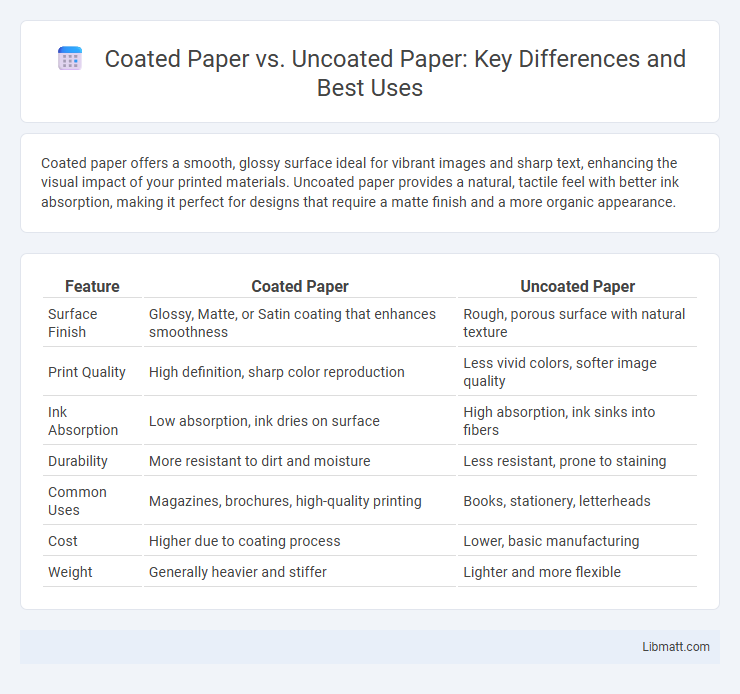
| Feature | Coated Paper | Uncoated Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Finish | Glossy, Matte, or Satin coating that enhances smoothness | Rough, porous surface with natural texture |
| Print Quality | High definition, sharp color reproduction | Less vivid colors, softer image quality |
| Ink Absorption | Low absorption, ink dries on surface | High absorption, ink sinks into fibers |
| Durability | More resistant to dirt and moisture | Less resistant, prone to staining |
| Common Uses | Magazines, brochures, high-quality printing | Books, stationery, letterheads |
| Cost | Higher due to coating process | Lower, basic manufacturing |
| Weight | Generally heavier and stiffer | Lighter and more flexible |
Introduction to Coated vs Uncoated Paper
Coated paper features a smooth surface sealed with a layer of compound, enhancing brightness, color vibrancy, and sharpness, making it ideal for high-quality printing such as brochures and magazines. Uncoated paper lacks this coating, offering a more porous texture that absorbs ink differently, which is preferred for stationery, books, and materials needing a natural feel. Understanding the differences in finish, ink absorption, and intended use between coated and uncoated paper is essential for selecting the right paper type for specific printing projects.
What is Coated Paper?
Coated paper is a type of paper that has been treated with a surface coating, usually made from clay, latex, or polymers, to create a smoother, glossier finish that enhances color vibrancy and sharpness in printing. This coating reduces ink absorption, resulting in sharper images and more vibrant colors, making it ideal for high-quality prints such as magazines, brochures, and photo books. Your choice of coated paper can significantly impact the visual appeal and durability of printed materials.
What is Uncoated Paper?
Uncoated paper is a type of paper that lacks a surface coating, resulting in a natural, porous texture that absorbs ink more readily. It is commonly used for stationery, books, and packaging due to its matte finish and ease of writing. Unlike coated paper, uncoated paper provides a more tactile feel and is often preferred for projects requiring a more organic, less glossy appearance.
Key Differences Between Coated and Uncoated Paper
Coated paper features a smooth, glossy or matte finish achieved by applying a surface coating of clay or other substances, enhancing print quality and color vibrancy. Uncoated paper lacks this surface coating, resulting in a more porous texture that absorbs ink differently, often giving prints a softer, more natural look. The choice between coated and uncoated paper significantly impacts print sharpness, drying time, and tactile experience, with coated paper preferred for high-resolution images and uncoated paper favored for writing or environmentally friendly applications.
Pros and Cons of Coated Paper
Coated paper offers a smooth surface that enhances color vibrancy and sharpness, making it ideal for high-quality prints like brochures and magazines. Its resistance to dirt and moisture improves durability, but coated paper can be more expensive and less environmentally friendly than uncoated options. You should consider coated paper when precise image reproduction and a polished finish are priorities for your project.
Pros and Cons of Uncoated Paper
Uncoated paper offers superior absorbency, which enhances the natural texture and tactile feel, making it ideal for writing and printing applications requiring a matte finish. It is generally more environmentally friendly due to less chemical processing and easier recyclability compared to coated paper. However, uncoated paper tends to have lower durability, reduced resistance to smudging and moisture, and less vibrant color reproduction in printed materials.
Common Uses for Coated Paper
Coated paper is commonly used for high-quality printing needs such as magazines, brochures, and product packaging due to its smooth finish and ability to enhance color vibrancy. Its non-porous surface makes it ideal for detailed graphics and photography, ensuring sharp and vivid images. You'll find coated paper preferred in marketing materials where presentation and visual impact are critical.
Common Uses for Uncoated Paper
Uncoated paper is widely used for everyday printing tasks such as letterheads, envelopes, and stationery due to its smooth, porous surface that absorbs ink well. It is preferred for printing books, notepads, and flyers where a natural, matte finish enhances readability and reduces glare. The paper's cost-effectiveness and versatility make it ideal for office documents and various marketing materials that do not require glossy, high-shine effects.
How to Choose the Right Paper for Your Project
Choosing between coated paper and uncoated paper depends on the desired finish and project requirements. Coated paper offers a smooth surface with vibrant color reproduction, ideal for high-quality images and detailed graphics, while uncoated paper provides a natural, matte texture suitable for writing and projects needing a more tactile feel. Your decision should balance visual impact, print durability, and usability to ensure the best outcome for your project.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
Coated paper typically uses more chemicals and energy in its production, resulting in a higher environmental footprint compared to uncoated paper, which requires fewer resources and is more easily recyclable. Uncoated paper often supports sustainability goals better due to its lower chemical usage and greater biodegradability, making it a preferred choice for eco-conscious printing and packaging. Certified uncoated papers, such as those with FSC or PEFC labels, further enhance environmental responsibility by ensuring sustainable forestry practices.
Coated paper vs uncoated paper Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com