Internal sizing improves paper's resistance to liquid absorption by treating fibers within the pulp, enhancing durability without altering the surface texture. Surface sizing applies a thin coating on the paper's exterior, increasing smoothness and printability while providing a protective barrier against water and ink penetration.
Table of Comparison
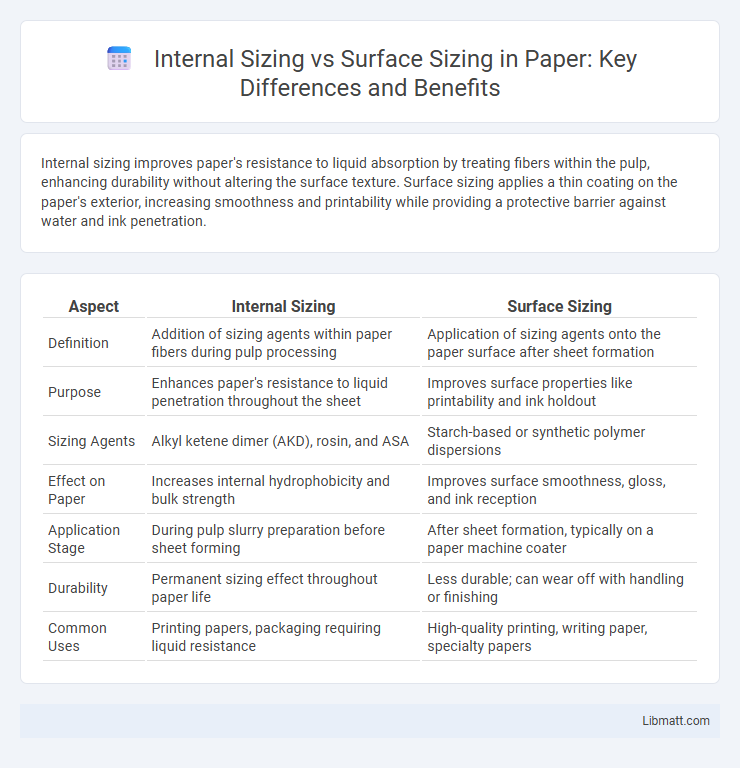
| Aspect | Internal Sizing | Surface Sizing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Addition of sizing agents within paper fibers during pulp processing | Application of sizing agents onto the paper surface after sheet formation |
| Purpose | Enhances paper's resistance to liquid penetration throughout the sheet | Improves surface properties like printability and ink holdout |
| Sizing Agents | Alkyl ketene dimer (AKD), rosin, and ASA | Starch-based or synthetic polymer dispersions |
| Effect on Paper | Increases internal hydrophobicity and bulk strength | Improves surface smoothness, gloss, and ink reception |
| Application Stage | During pulp slurry preparation before sheet forming | After sheet formation, typically on a paper machine coater |
| Durability | Permanent sizing effect throughout paper life | Less durable; can wear off with handling or finishing |
| Common Uses | Printing papers, packaging requiring liquid resistance | High-quality printing, writing paper, specialty papers |
Understanding Sizing in the Paper Industry
Internal sizing enhances paper's resistance to water and ink absorption by treating fibers during the pulp stage, which improves print quality and durability. Surface sizing applies a protective coating on the paper's exterior after formation, increasing surface strength and smoothness for better ink holdout and reduced linting. Both sizing methods are crucial in the paper industry for tailoring paper properties to specific printing and writing needs, optimizing functionality and performance.
Definition of Internal Sizing
Internal sizing is a papermaking process where a sizing agent is added directly to the pulp before sheet formation, enhancing the paper's resistance to water and ink penetration from within. This method improves the paper's bulk, strength, and printing properties by modifying the fibers internally rather than just coating the surface. Your choice between internal and surface sizing depends on the desired durability and ink absorption characteristics for your specific paper application.
Definition of Surface Sizing
Surface sizing refers to the application of a sizing agent onto the exterior of paper to enhance its surface properties, such as strength, smoothness, and printability. Unlike internal sizing, which treats the fibers within the paper matrix, surface sizing creates a thin film that improves ink holdout and reduces absorbency. Understanding the definition of surface sizing helps you select the right treatment to achieve optimal paper performance for your specific printing or writing needs.
Key Differences Between Internal and Surface Sizing
Internal sizing involves adding sizing agents within the paper fibers during the pulp stage, enhancing water resistance and printability by chemically modifying fiber properties. Surface sizing is applied as a thin coating on the paper exterior, improving surface strength, smoothness, and ink holdout without altering the paper's internal structure. The key differences lie in the application method and resultant paper characteristics--internal sizing affects the entire sheet's absorbency and durability, while surface sizing primarily enhances surface properties for better printing and finishing.
Common Materials Used for Internal Sizing
Common materials used for internal sizing include starch, animal glue, and synthetic polymers such as polyvinyl acetate (PVA) and alkyl ketene dimer (AKD). These substances penetrate the paper fibers, enhancing strength, reducing water absorption, and improving ink holdout without significantly altering surface texture. Starch remains widely favored in traditional papermaking, while synthetic polymers offer enhanced durability and moisture resistance for modern applications.
Common Agents Used in Surface Sizing
Surface sizing commonly utilizes agents such as starch, rosin, and synthetic polymers like polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) to enhance the paper's surface strength, water resistance, and printability. These agents form a protective layer that improves ink adhesion and reduces feathering, critical for high-quality printing applications. Your choice of surface sizing agents significantly impacts the final paper performance and suitability for specific uses.
Effects of Internal Sizing on Paper Properties
Internal sizing enhances paper strength and reduces water absorbency by chemically treating the pulp fibers before sheet formation. This process improves ink holdout, print quality, and durability, making the paper more resistant to moisture penetration and ink bleeding. Your choice of internal sizing influences the paper's absorption rate and overall performance in printing applications.
Impact of Surface Sizing on Paper Performance
Surface sizing significantly enhances paper performance by improving surface strength, printability, and resistance to water and ink penetration. This treatment creates a sizing layer on the paper's exterior, ensuring better ink holdout and sharper image quality, which is critical for high-resolution printing. You can expect smoother sheet formation and improved durability in various applications, from packaging to fine art printing.
Applications Best Suited for Internal versus Surface Sizing
Internal sizing is best suited for high-speed printing and writing paper where excellent ink holdout and rapid absorption are essential, commonly used in offset and digital printing papers. Surface sizing is ideal for coated papers, packaging materials, and specialty papers that require enhanced surface smoothness, print gloss, and moisture resistance. Industries such as publishing and commercial printing often prefer internal sizing for printability, while surface sizing is favored in packaging and label production for improved surface strength and finish.
Choosing the Right Sizing Method for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate sizing method hinges on the type of paper and desired performance characteristics; internal sizing enhances water resistance by chemically treating fibers during papermaking, while surface sizing applies a protective layer to improve printability and reduce ink absorption. Internal sizing is ideal for papers requiring durability and strength in moist environments, whereas surface sizing suits applications needing improved surface smoothness and ink holdout. Understanding these distinctions ensures optimal results tailored to specific printing, packaging, or writing requirements.
internal sizing vs surface sizing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com