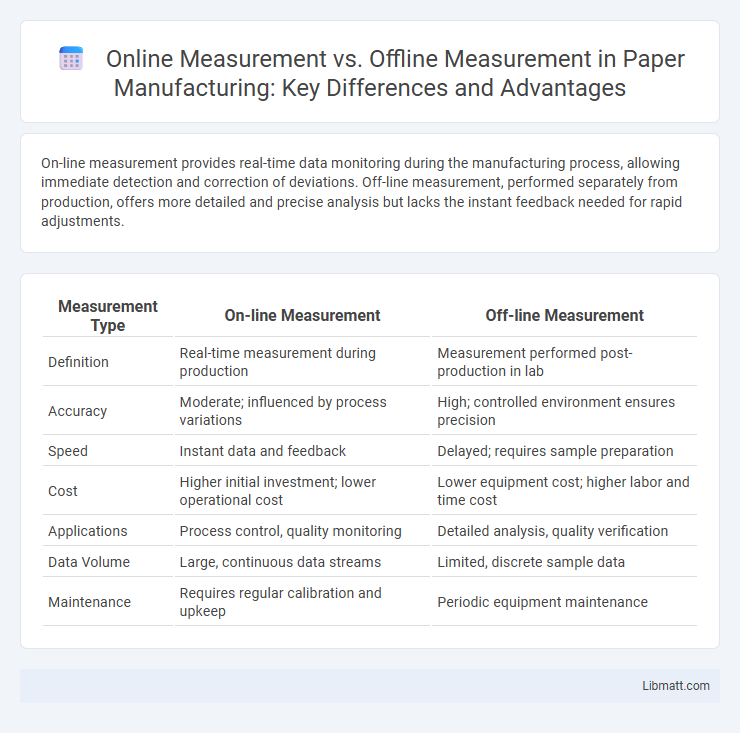
On-line measurement provides real-time data monitoring during the manufacturing process, allowing immediate detection and correction of deviations. Off-line measurement, performed separately from production, offers more detailed and precise analysis but lacks the instant feedback needed for rapid adjustments.
Table of Comparison
| Measurement Type | On-line Measurement | Off-line Measurement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Real-time measurement during production | Measurement performed post-production in lab |
| Accuracy | Moderate; influenced by process variations | High; controlled environment ensures precision |
| Speed | Instant data and feedback | Delayed; requires sample preparation |
| Cost | Higher initial investment; lower operational cost | Lower equipment cost; higher labor and time cost |
| Applications | Process control, quality monitoring | Detailed analysis, quality verification |
| Data Volume | Large, continuous data streams | Limited, discrete sample data |
| Maintenance | Requires regular calibration and upkeep | Periodic equipment maintenance |
Introduction to On-line and Off-line Measurement
On-line measurement involves real-time data collection and analysis directly during the production process, enabling immediate quality control and process adjustments. Off-line measurement requires removing samples from the production line for detailed testing and evaluation in a separate laboratory or environment, often leading to delayed feedback. Both methods are essential in manufacturing and quality assurance, with on-line measurement providing continuous monitoring and off-line ensuring in-depth validation.
Key Differences Between On-line and Off-line Measurements
On-line measurement involves real-time data acquisition directly from operational processes, enabling continuous monitoring and immediate feedback for process control. Off-line measurement requires sample collection and analysis in a separate setting, often leading to delayed results and potential changes in sample conditions. The primary difference lies in speed and integration, with on-line measurement providing instantaneous, automated data while off-line methods offer detailed, often more precise but time-consuming analysis.
Advantages of On-line Measurement Systems
On-line measurement systems provide real-time data acquisition, enabling immediate process adjustments that enhance manufacturing efficiency and product quality. These systems minimize the need for manual sampling, reducing labor costs and human error while ensuring continuous monitoring of critical parameters. Integration with automated control systems allows for proactive detection of anomalies, resulting in decreased downtime and improved overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
Benefits of Off-line Measurement Methods
Off-line measurement methods offer increased accuracy and reliability by allowing thorough analysis in controlled environments, reducing the risk of measurement errors caused by real-time operational fluctuations. These techniques enable detailed inspection and calibration without interrupting production processes, minimizing downtime and costly disruptions. Off-line measurements are essential for validating sensor performance and ensuring long-term quality assurance in manufacturing and research applications.
Use Cases for On-line Measurement
On-line measurement is essential for real-time process monitoring and immediate quality control in manufacturing environments, enabling rapid detection of deviations and minimizing downtime. It is widely used in industries such as pharmaceuticals, food processing, and chemical production, where continuous data acquisition ensures product consistency and compliance with regulatory standards. Your operations benefit from on-line measurement by improving efficiency, reducing waste, and facilitating timely decision-making through instant data availability.
Applications of Off-line Measurement
Off-line measurement is essential for quality control in manufacturing environments where precise, detailed inspection is required without disrupting production lines. Common applications include dimensional analysis, surface finish evaluation, and material property testing, often performed in laboratories or dedicated inspection stations. This method allows for thorough verification of components and assemblies, ensuring compliance with design specifications and industry standards before final assembly or shipment.
Accuracy and Reliability: On-line vs Off-line
On-line measurement systems provide real-time data acquisition, enhancing process control accuracy and enabling immediate adjustments to maintain optimal performance. Off-line measurements, while often more precise due to controlled laboratory conditions, lack the immediacy and continuity, potentially delaying identification of deviations. Your choice between on-line and off-line measurement depends on the balance you need between continuous monitoring reliability and the detailed accuracy of periodic testing.
Cost Implications and Return on Investment
On-line measurement systems often require higher initial investment due to advanced sensors and integration with existing processes, but they deliver real-time data that enhances process control and reduces costly downtime. Off-line measurement generally involves lower upfront costs but can lead to increased labor expenses and delays, impacting overall productivity and increasing the risk of defects. Over time, on-line measurement typically generates a higher return on investment by improving operational efficiency, minimizing waste, and enabling faster decision-making.
Integration and Automation Considerations
On-line measurement systems offer seamless integration with automated processes, enabling real-time data collection and immediate feedback for quality control. Off-line measurement requires manual intervention, leading to potential delays and reduced efficiency in production workflows. Optimizing your manufacturing process benefits significantly from on-line measurement's capability to integrate directly with automation platforms, enhancing accuracy and operational speed.
Choosing the Right Measurement Approach
On-line measurement offers real-time monitoring and immediate data analysis, making it ideal for processes requiring continuous quality control and rapid adjustments. Off-line measurement provides higher accuracy and detailed analysis, suitable for validation, calibration, and situations where precise data is critical but time constraints are less stringent. Choosing the right measurement approach depends on your specific needs for speed, accuracy, and the nature of the process being monitored.
On-line measurement vs off-line measurement Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com