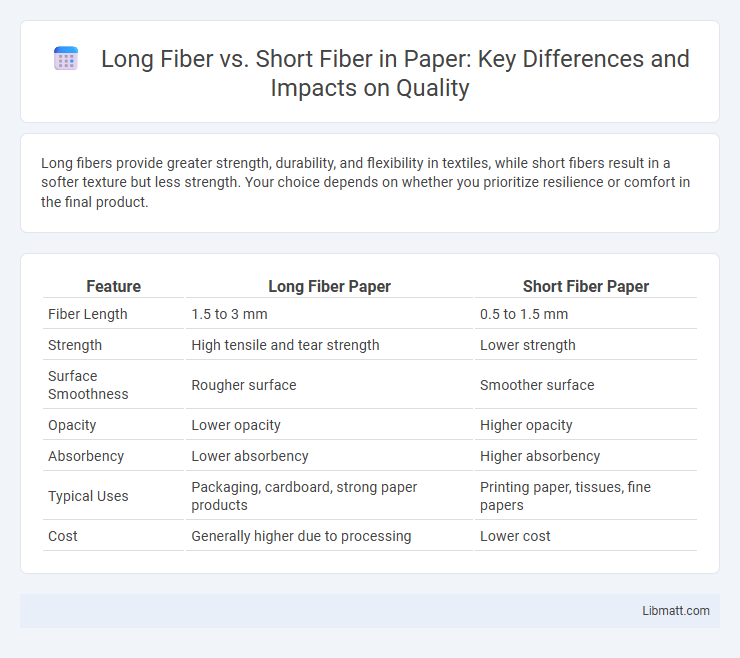
Long fibers provide greater strength, durability, and flexibility in textiles, while short fibers result in a softer texture but less strength. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize resilience or comfort in the final product.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Long Fiber Paper | Short Fiber Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber Length | 1.5 to 3 mm | 0.5 to 1.5 mm |
| Strength | High tensile and tear strength | Lower strength |
| Surface Smoothness | Rougher surface | Smoother surface |
| Opacity | Lower opacity | Higher opacity |
| Absorbency | Lower absorbency | Higher absorbency |
| Typical Uses | Packaging, cardboard, strong paper products | Printing paper, tissues, fine papers |
| Cost | Generally higher due to processing | Lower cost |
Understanding Long Fiber and Short Fiber
Long fibers typically measure over 1.5 inches and provide superior strength, durability, and flexibility, crucial in textile production and paper manufacturing for enhanced quality products. Short fibers, generally less than 1 inch, offer better softness and smoothness but lower tensile strength, making them ideal for applications requiring fine texture like cotton garments. Understanding the differences in fiber length directly impacts choosing appropriate materials for specific industrial uses, affecting the final product's performance and cost-efficiency.
Key Differences Between Long and Short Fibers
Long fibers, typically exceeding 10 mm in length, provide superior strength, durability, and flexibility, making them ideal for high-quality textiles and composite materials. Short fibers, usually under 10 mm, offer easier processing and uniformity but result in weaker, less flexible products due to their shorter length and increased fiber ends. Your choice depends on the desired balance between material performance and manufacturing efficiency.
Material Sources: Natural vs Synthetic Fibers
Long fibers typically come from natural sources such as cotton, flax, and wool, offering superior strength and durability compared to short fibers, which are often derived from synthetic materials like polyester and nylon. Natural long fibers provide enhanced breathability and comfort, making them ideal for high-quality textiles, whereas synthetic short fibers offer advantages in cost efficiency and moisture resistance. Understanding the differences between your material sources helps optimize fabric performance for specific applications in fashion, upholstery, or technical textiles.
Mechanical Properties and Performance
Long fibers enhance the mechanical properties of composites by providing superior tensile strength, impact resistance, and stiffness compared to short fibers. The continuous nature of long fibers allows for more efficient load transfer, resulting in increased durability and fatigue resistance in your engineered materials. Short fibers, while easier to process, typically yield lower mechanical performance and reduce the overall strength and toughness of the final product.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Long fiber materials exhibit higher durability and an extended lifespan compared to short fiber alternatives due to their superior tensile strength and resistance to wear. Short fibers tend to break down faster under stress, leading to quicker degradation and reduced overall lifespan. Investing in long fiber options enhances the longevity of your products, ensuring better performance over time.
Applications in Industry
Long fibers are primarily used in the automotive and aerospace industries for manufacturing composite materials that require high tensile strength and durability, such as structural panels and reinforcements. Short fibers find extensive application in injection molding and extrusion processes, ideal for producing lightweight, cost-effective components with moderate mechanical properties, commonly seen in consumer goods and packaging. The choice between long and short fibers significantly influences the mechanical performance, processing methods, and end-use applications in various industrial sectors.
Cost Implications and Economic Considerations
Long fiber materials typically incur higher production costs due to more complex processing and sourcing requirements, impacting overall project budgets. Short fibers offer cost efficiency with easier manufacturing and lower raw material expenses, making them favorable for large-scale or budget-sensitive applications. Economic considerations must balance durability and performance needs against these varying cost structures to determine optimal material selection.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Long fiber materials generally have a lower environmental impact than short fiber products due to their durability and reduced need for frequent replacement, which conserves resources. Short fiber items often require more energy-intensive processing and generate higher waste volumes during production and disposal. Your choice of long fiber products supports sustainability by reducing resource consumption and promoting longer product lifecycles.
Choosing the Right Fiber for Your Needs
Long fibers offer enhanced strength, durability, and resistance to wear, making them ideal for applications like textiles, ropes, and composites where structural integrity is crucial. Short fibers provide better surface area for bonding, resulting in improved flexibility and ease of processing, suited for products such as paper, nonwovens, and molded plastics. Selecting the right fiber depends on the required mechanical properties, processing methods, and end-use performance criteria to optimize functionality and cost-efficiency.
Future Trends in Fiber Technology
Long fiber technology is advancing with innovations in bio-based and high-performance materials aimed at enhancing strength, durability, and sustainability for industrial applications. Short fiber composites are increasingly optimized for recyclability and cost-efficiency, making them ideal for mass-produced automotive and consumer goods. Emerging trends focus on nanofiber integration and hybrid fiber systems to combine the benefits of both long and short fibers, driving improvements in lightweight construction and environmental impact.
long fiber vs short fiber Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com