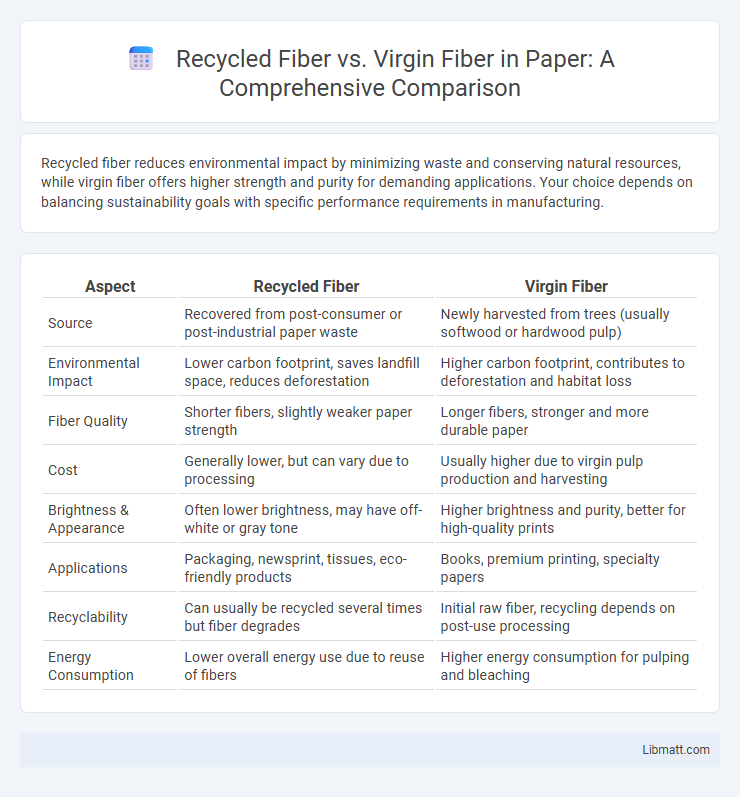
Recycled fiber reduces environmental impact by minimizing waste and conserving natural resources, while virgin fiber offers higher strength and purity for demanding applications. Your choice depends on balancing sustainability goals with specific performance requirements in manufacturing.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Recycled Fiber | Virgin Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Recovered from post-consumer or post-industrial paper waste | Newly harvested from trees (usually softwood or hardwood pulp) |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint, saves landfill space, reduces deforestation | Higher carbon footprint, contributes to deforestation and habitat loss |
| Fiber Quality | Shorter fibers, slightly weaker paper strength | Longer fibers, stronger and more durable paper |
| Cost | Generally lower, but can vary due to processing | Usually higher due to virgin pulp production and harvesting |
| Brightness & Appearance | Often lower brightness, may have off-white or gray tone | Higher brightness and purity, better for high-quality prints |
| Applications | Packaging, newsprint, tissues, eco-friendly products | Books, premium printing, specialty papers |
| Recyclability | Can usually be recycled several times but fiber degrades | Initial raw fiber, recycling depends on post-use processing |
| Energy Consumption | Lower overall energy use due to reuse of fibers | Higher energy consumption for pulping and bleaching |
Introduction to Fiber Types: Recycled vs Virgin
Recycled fiber originates from reclaimed materials such as post-consumer waste or production scraps, reducing environmental impact by conserving resources and lowering carbon emissions. Virgin fiber is produced directly from raw materials like trees or cotton plants, offering superior strength and quality essential for specific high-performance applications. Understanding the distinct properties of recycled and virgin fibers helps optimize your product's sustainability and durability.
Defining Recycled Fiber and Virgin Fiber
Recycled fiber is produced from reclaimed materials such as post-consumer or post-industrial waste, reducing the demand for new raw resources and lowering environmental impact. Virgin fiber refers to fiber directly sourced from natural raw materials like wood pulp, offering high strength and purity essential for premium quality paper and textiles. Understanding the distinction helps you make sustainable choices in manufacturing and product design.
Manufacturing Processes: Recycled vs Virgin Fiber
Recycled fiber manufacturing involves collecting, sorting, and processing post-consumer or post-industrial materials to create new fibers, reducing waste and energy consumption compared to virgin fiber production. Virgin fiber production starts with the extraction of raw materials like wood pulp or cotton, followed by chemical or mechanical treatments to produce fresh fiber, often requiring more water and energy inputs. Your choice of recycled versus virgin fiber directly impacts environmental footprint and resource efficiency in the textile or packaging industry.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Recycled fiber significantly reduces environmental impact by lowering energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions compared to virgin fiber production. Virgin fiber requires more water, land, and chemicals, contributing to deforestation and habitat loss, whereas recycled fiber helps conserve natural resources and reduces waste sent to landfills. Choosing recycled fiber supports sustainability and minimizes Your carbon footprint in textile manufacturing.
Performance and Quality Differences
Recycled fiber often exhibits lower tensile strength and durability compared to virgin fiber due to fiber shortening during processing, which can affect overall fabric performance. Virgin fiber maintains higher quality standards with consistent fiber length and strength, resulting in better resilience, color retention, and texture. Selecting recycled fiber may impact Your product's longevity and appearance, but advancements in technology are narrowing the quality gap between recycled and virgin fibers.
Cost Analysis: Recycled vs Virgin Fiber
Recycled fiber generally offers a lower raw material cost compared to virgin fiber due to reduced energy consumption and resource extraction in its production process. Virgin fiber, derived from fresh wood pulp or synthetic sources, incurs higher expenses related to harvesting, processing, and environmental compliance. However, recycled fiber may involve additional sorting and cleaning costs, which can affect the overall cost advantage depending on the scale and efficiency of recycling operations.
Applications in Various Industries
Recycled fiber is extensively utilized in the textile industry for producing eco-friendly apparel, home furnishings, and insulation materials, reducing environmental impact compared to virgin fiber. Virgin fiber, derived from fresh raw materials, remains preferred in high-performance applications such as medical textiles, automotive components, and premium packaging, where durability and consistency are critical. Both fibers serve vital roles across industries like paper manufacturing, construction, and fashion, with recycled fiber promoting sustainability and virgin fiber ensuring uncompromised quality.
Consumer Perception and Market Trends
Consumer perception of recycled fiber increasingly values its environmental benefits, driving demand for sustainable products in fashion and packaging industries. Market trends show a significant rise in brands adopting recycled fibers to meet growing eco-conscious consumer preferences, with recycled fiber often marketed as a premium, eco-friendly alternative to virgin fiber. Your choice of products made with recycled fiber supports sustainability initiatives and aligns with the expanding green market movement.
Challenges in Adopting Recycled Fiber
Challenges in adopting recycled fiber include inconsistent quality and limited availability, which can impact production efficiency and product performance. The presence of contaminants and fiber degradation also reduces the strength and durability compared to virgin fiber, complicating its use in high-quality textile and packaging applications. Your supply chain may face higher costs and complexities due to the need for specialized processing technology and stringent sorting protocols.
Future Outlook for Sustainable Fiber Choices
Recycled fiber offers a promising future for sustainable fiber choices by reducing environmental impact through lower water usage, energy consumption, and waste generation compared to virgin fiber production. Innovations in recycling technologies are enhancing the quality and durability of recycled fibers, making them increasingly competitive with virgin fibers in textile and packaging industries. Your commitment to using recycled fiber supports circular economies and helps meet growing consumer demand for eco-friendly products.
Recycled fiber vs virgin fiber Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com