Sizing improves paper's resistance to water and ink absorption, enhancing print quality and durability, while unsizing leaves the paper more absorbent for applications requiring ink penetration or specific finishes. Your choice depends on the desired balance between ink holdout and surface absorbency for optimal performance.
Table of Comparison
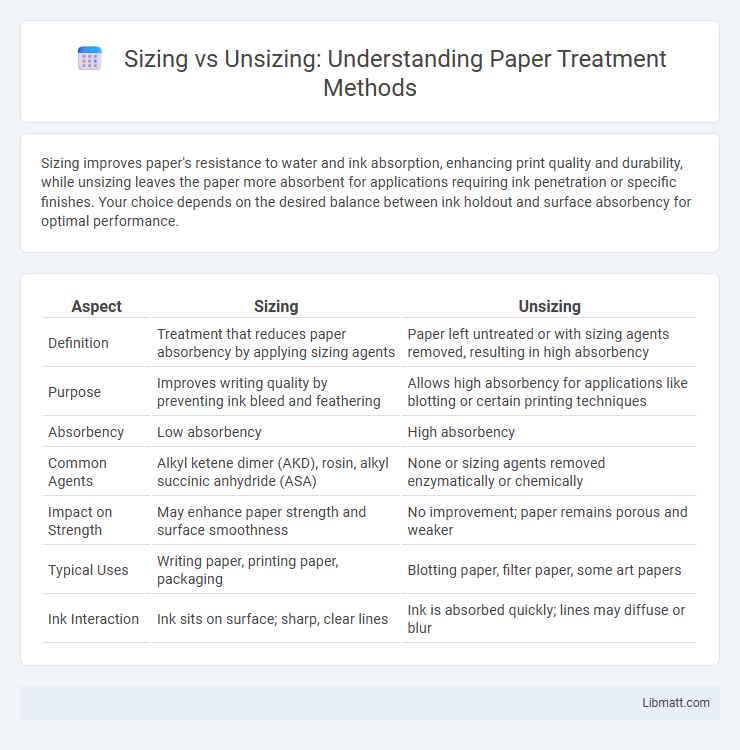
| Aspect | Sizing | Unsizing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Treatment that reduces paper absorbency by applying sizing agents | Paper left untreated or with sizing agents removed, resulting in high absorbency |
| Purpose | Improves writing quality by preventing ink bleed and feathering | Allows high absorbency for applications like blotting or certain printing techniques |
| Absorbency | Low absorbency | High absorbency |
| Common Agents | Alkyl ketene dimer (AKD), rosin, alkyl succinic anhydride (ASA) | None or sizing agents removed enzymatically or chemically |
| Impact on Strength | May enhance paper strength and surface smoothness | No improvement; paper remains porous and weaker |
| Typical Uses | Writing paper, printing paper, packaging | Blotting paper, filter paper, some art papers |
| Ink Interaction | Ink sits on surface; sharp, clear lines | Ink is absorbed quickly; lines may diffuse or blur |
Introduction to Paper Sizing and Unsizing
Paper sizing modifies the surface properties by applying chemicals to reduce absorbency and improve printability, commonly using agents like rosin or starch. Unsizing removes or reverses this treatment, restoring the paper's natural absorbent characteristics for applications like watercolor painting. Understanding sizing vs. unsizing helps you choose the right paper finish tailored to specific printing or artistic needs.
What is Paper Sizing?
Paper sizing is a treatment process that enhances the surface strength and water resistance of paper by applying a hydrophobic substance, such as rosin or synthetic polymers. It controls the absorbency of the paper, preventing ink from spreading and improving print quality for various applications. Your choice between sized and unsized paper impacts durability, ink adhesion, and suitability for different printing techniques.
The Process: How Paper is Sized
Paper sizing involves applying a substance, such as rosin or starch, to the paper fibers during or after the papermaking process, enhancing surface strength and reducing absorbency. Internal sizing is added directly to the pulp slurry before sheet formation, improving resistance to ink penetration, while surface sizing is applied as a coating on the finished sheet to enhance surface smoothness and printability. Your choice between sizing methods depends on the desired paper characteristics and printing requirements.
Benefits and Purposes of Sizing Paper
Sizing paper enhances its surface strength and resistance to moisture, making it ideal for writing, printing, and painting applications. By controlling absorbency, sizing prevents ink or paint from spreading, ensuring sharp, clear lines and vibrant colors. Your documents or artwork benefit from improved durability and longevity due to this essential paper treatment.
What is Unsizing in Paper Treatment?
Unsizing in paper treatment refers to the removal or reduction of sizing agents that were previously applied to paper to control its absorbency and improve surface properties. This process restores the paper's ability to absorb inks, coatings, or adhesives more effectively, which is essential for certain printing or finishing applications. You can optimize paper performance by choosing appropriate unsizing techniques, such as enzymatic or chemical treatments, to achieve desired absorbency levels.
Methods of Unsizing Paper
Methods of unsizing paper primarily involve enzymatic treatments using amylase or cellulase enzymes to break down the sizing agents such as starch or rosin applied during paper manufacturing. Chemical methods include alkaline hydrolysis or treatment with solvents like sodium hypochlorite to remove surface sizing without damaging the paper fibers. Physical techniques such as washing or calendaring can also assist in reducing surface sizing, enhancing absorbency and printability.
Impact of Sizing vs Unsizing on Paper Properties
Sizing enhances paper's resistance to water and ink penetration, improving print quality and durability by reducing absorbency. Unsized paper, lacking these treatments, tends to absorb more moisture and ink, causing fuzzier images and weaker structural integrity. Your choice between sizing and unsizing directly affects paper strength, surface smoothness, and suitability for various printing applications.
Applications: When to Choose Sized or Unsized Paper
Sized paper offers enhanced resistance to ink bleeding and moisture, making it ideal for high-quality printing, calligraphy, and archival documents requiring durability. Unsized paper is preferred for watercolor painting and certain types of printing where absorbency is crucial for achieving specific artistic effects. Your choice depends on the intended medium and desired finish, with sized paper suited for precision work and unsized paper favored for absorbent, textured applications.
Sizing and Archival Quality: Longevity Considerations
Sizing enhances paper's archival quality by improving its resistance to water, ink absorption, and environmental pollutants, which directly impacts its longevity and preservation. Proper sizing prevents the paper fibers from deteriorating prematurely, making the document more durable and less prone to damage over time. Unsized paper absorbs moisture and ink more readily, accelerating degradation and reducing its suitability for long-term archival storage.
Environmental and Artistic Implications of Sizing Choices
Sizing treatments enhance paper durability and ink absorption by applying substances like gelatin or starch, impacting environmental sustainability due to chemical use and water consumption. Unsized papers, often favored in art for their natural texture and absorbency, support eco-friendly practices by minimizing chemical additives but may limit longevity and performance. Your choice between sizing and unsizing balances environmental impact with artistic needs, influencing both the visual outcome and the ecological footprint of paper production.
Sizing vs unsizing (paper treatment) Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com