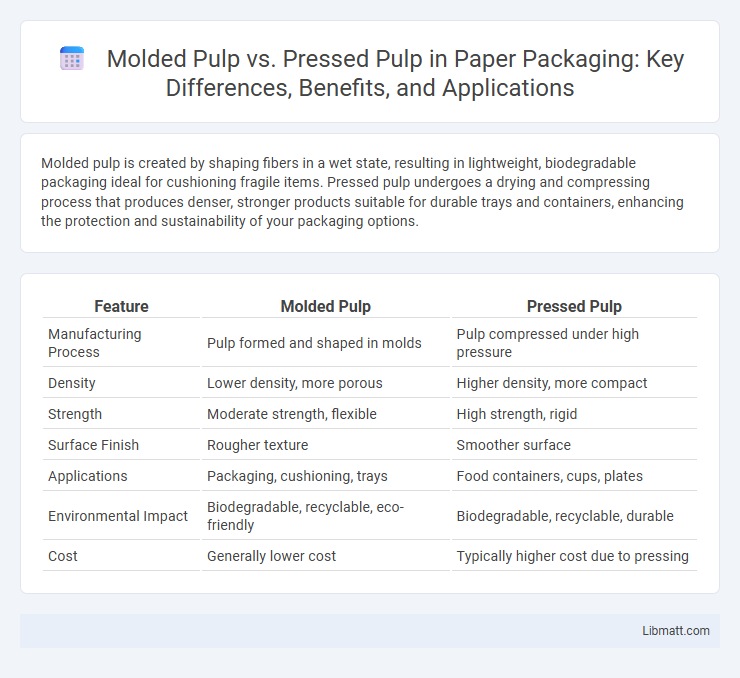
Molded pulp is created by shaping fibers in a wet state, resulting in lightweight, biodegradable packaging ideal for cushioning fragile items. Pressed pulp undergoes a drying and compressing process that produces denser, stronger products suitable for durable trays and containers, enhancing the protection and sustainability of your packaging options.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Molded Pulp | Pressed Pulp |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Pulp formed and shaped in molds | Pulp compressed under high pressure |
| Density | Lower density, more porous | Higher density, more compact |
| Strength | Moderate strength, flexible | High strength, rigid |
| Surface Finish | Rougher texture | Smoother surface |
| Applications | Packaging, cushioning, trays | Food containers, cups, plates |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, recyclable, eco-friendly | Biodegradable, recyclable, durable |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Typically higher cost due to pressing |
Introduction to Molded Pulp and Pressed Pulp
Molded pulp and pressed pulp are sustainable packaging materials derived from recycled paper fibers, offering eco-friendly alternatives to plastic packaging. Molded pulp is formed by suspending fibers in water and shaping them in a mold, creating lightweight, flexible packaging with excellent cushioning properties. Pressed pulp involves compressing fibrous pulp under high pressure, producing denser, stronger packaging suited for protecting heavier or more fragile items.
Defining Molded Pulp Packaging
Molded pulp packaging is a sustainable packaging solution created by shaping recycled paper fibers into rigid forms that protect products during shipping and storage. Unlike pressed pulp, which is formed by compressing fibers under high pressure, molded pulp involves a wet molding process that allows for more complex shapes and cushioning properties. Your choice of molded pulp packaging supports eco-friendly practices by utilizing biodegradable materials and reducing plastic waste.
Understanding Pressed Pulp Packaging
Pressed pulp packaging is created by compressing fibers into dense, uniform shapes, offering enhanced durability and rigidity compared to molded pulp. It is commonly used for protective packaging in electronics, food trays, and automotive parts due to its superior strength and eco-friendly properties. Understanding pressed pulp packaging helps you choose sustainable materials that reduce environmental impact while ensuring product protection.
Production Processes Compared
Molded pulp production involves shaping wet fibers in a mold using a liquid slurry, followed by drying to create lightweight, biodegradable packaging with intricate designs. Pressed pulp production compresses dry pulp fibers under high pressure and heat in a mold, resulting in denser, more rigid products suitable for protective packaging. Your choice between molded pulp and pressed pulp depends on the desired strength, texture, and application requirements for sustainable packaging solutions.
Material Composition Differences
Molded pulp is primarily made from recycled paper fibers, such as old newspapers and cardboard, providing a coarse and fibrous texture that enhances biodegradability and cushioning properties. Pressed pulp, on the other hand, uses a similar recycled fiber base but undergoes a higher pressure molding process that compresses the material into a denser, smoother form ideal for precise packaging needs. Understanding these material composition differences helps you select the right type of pulp for sustainable and protective packaging solutions.
Applications and Use Cases
Molded pulp is widely used for protective packaging of electronics, appliances, and fragile items due to its custom-fit designs and cushioning properties. Pressed pulp is commonly applied in food service products like trays, plates, and containers because of its density and moisture resistance. Your choice between molded and pressed pulp depends on whether you prioritize structural support or surface durability for specific packaging or product needs.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Molded pulp products typically exhibit lower environmental impacts due to their production process, which uses recycled paper fibers and consumes less energy compared to pressed pulp. Pressed pulp often involves denser material formation, potentially increasing resource use and carbon emissions during manufacturing. Life cycle assessments reveal molded pulp's advantages in biodegradability and reduced landfill waste, making it a more sustainable option for eco-friendly packaging solutions.
Cost Analysis: Molded vs Pressed Pulp
Molded pulp generally costs more due to the complex machinery and longer production cycles involved, while pressed pulp offers a more economical solution with simpler equipment and faster turnaround times. Your choice impacts expenses significantly; molded pulp suits high-quality, protective packaging needs, often justifying its higher price, whereas pressed pulp is preferred for budget-sensitive, lightweight applications. Analyzing volume requirements and product protection levels ensures you select the most cost-effective pulp type for your packaging.
Performance and Durability Factors
Molded pulp products offer enhanced cushioning and shock absorption due to their thicker, more fibrous structure, making them ideal for protecting fragile items during transport. Pressed pulp, while thinner and denser, provides superior compression resistance and durability under sustained pressure, suitable for packaging that demands a rigid form. Your choice should consider the specific performance requirements, balancing impact protection with structural strength for optimal packaging effectiveness.
Choosing the Right Pulp Packaging Solution
Choosing the right pulp packaging solution depends on your product's protection needs and environmental goals. Molded pulp offers superior cushioning and is ideal for fragile items, while pressed pulp provides a smoother finish suitable for retail packaging and branding. Understanding the specific benefits of molded pulp versus pressed pulp ensures your packaging balances durability, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness.
Molded pulp vs pressed pulp Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com